|
Seku Amadu
Sheikhu Ahmadu (; ; ) (c. 1776 – 20 April 1845) was the Fulbe founder of the Massina Empire (Diina of Hamdullahi) in the Inner Niger Delta, now the Mopti Region of Mali. He ruled as '' Almami'' from 1818 until his death in 1845, also taking the title ''sisse al-Masini''. Early years Aḥmad bin Muḥammad Būbū bin Abī Bakr bin Sa'id al-Fullānī () was born around 1776 and was raised by Hamman Lobbo, his father's younger brother. Amadu was a pupil of the Qadiriyya Sufi teacher Sidi Mukhtar al-Kunti. In the Inner Niger Delta region, alliances of Fulbe traders ruled the towns like Djenné, but non-Moslem Bambara people controlled the river. The Fulbe ''ardo'en'' were tributary to the Bambara of Ségou, and practiced a form of Islam that was far from pure. Seku Amadu may have served in the Sokoto ''jihad'' before returning to the Massina region. He settled in a village under the authority of Djenné. When his teaching brought him a large following he was expelled, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almami
Almami (; Also: Almamy, Almaami) was the regnal name of Tukulor monarchs from the eighteenth century through the first half of the twentieth century. It is derived from the Arabic Al-Imam, meaning "the leader", and it has since been claimed as the title of rulers in other West African theocratic monarchies. Famous holders of the title *Ibrahim Sori, Imamate of Futa Jallon. * Karamokho Alfa, Imamate of Futa Jallon * Bokar Biro, Imamate of Futa Jallon * Almamy Ahmadou of Timbo *Almany Niamody of the Toucouleur vassal state of Kaarta. *Samori Ture of the Wassoulou Empire. * Maba Diakhou Bâ, almamy of Rip in the Saloum region of Senegal. Places * Almami Rural LLG in Papua New Guinea Proper name In recent times the word has become a proper name in some areas of West Africa in honor of the historical figures known by the title. Malian independence leader Almamy Sylla and Guinean football player Almamy Schuman Bah are examples. References *B. A. Ogot(ed). Africa from the Sixte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdullahi Dan Fodio
Abdullahi ɗan Fodio (; ca. 1766–1828), was a prominent Islamic scholar, jurist, poet and theologian, and the first Amir of Gwandu (r. 1812–1828) and first Grand Vizier of Sokoto. His brother, Usman dan Fodio (1754–1817) was the founder of the Sokoto Caliphate. Usman, being more of a scholar than politician, delegated the practical regency of the western part of his empire to Abdullahi and the eastern part to his son Muhammed Bello, who later became the Sultan of Sokoto after his father. Early life Abdullahi was born in 1766 in a small village called Maganimi. Unlike his brother and other members of his family, who were of "sparse physique" and lighter-skinned, he was described as being "tall, fat and black". His father, Muhammad bin Uthman, was given the nickname Foduye (later Fodio), which meant a scholar or knowledgeable person in their native Fulfulde. The nickname comes from the Arabic word Faqīh meaning jurist. He belonged to the Toronkawa ('Torodbe' in Ful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qadi
A qadi (; ) is the magistrate or judge of a Sharia court, who also exercises extrajudicial functions such as mediation, guardianship over orphans and minors, and supervision and auditing of public works. History The term '' was in use from the time of Muhammad during the early history of Islam, and remained the term used for judges throughout Islamic history and the period of the caliphates. While the and played the role in elucidation of the principles of Islamic jurisprudence () and the Islamic law (), the qadi remained the key person ensuring the establishment of justice on the basis of these very laws and rules. Thus, the qadi was chosen from amongst those who had mastered the sciences of jurisprudence and law. The office of qadi continued to be a very important one in every principality of the caliphates and sultanates of the various Muslim empires over the centuries. The rulers appointed a qadi in every region, town, and village for judicial and administrative cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' refers to immutable, intangible divine law; contrary to ''fiqh'', which refers to its interpretations by Ulama, Islamic scholars. Sharia, or fiqh as traditionally known, has always been used alongside urf, customary law from the very beginning in Islamic history; has been elaborated and developed over the centuries by fatwa, legal opinions issued by mufti, qualified jurists – reflecting the tendencies of Schools of Fiqh, different schools – and integrated and with various economic, penal and administrative laws issued by Muslims, Muslim rulers; and implemented for centuries by Qadi, judges in the courts until recent times, when secularism was widely adopted in Islamic societies. Traditional Principles of Islamic jurisprudence, theory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maliki
The Maliki school or Malikism is one of the four major madhhab, schools of Islamic jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. It was founded by Malik ibn Anas () in the 8th century. In contrast to the Ahl al-Hadith and Ahl al-Ra'y schools of thought, the Maliki school takes a unique position known as ''Ahl al-Amal'', in which they consider the Sunnah to be primarily sourced from the practice of the people of Medina and Urf, living Islamic traditions for their rulings on Sharia, Islamic law. The Maliki school is one of the largest groups of Sunni Muslims, comparable to the Shafi’i madhhab in adherents, but smaller than the Hanafi madhhab. Sharia based on Maliki Fiqh is predominantly found in North Africa (excluding parts of Egypt), West Africa, Chad, Sudan and the Persian Gulf, Arabian Gulf. In the Middle Ages, medieval era, the Maliki school was also found in parts of Islam in Europe, Europe under Islamic rule, particularly Al-Andalus, Islamic Spain and the Emirate of Sicily. A major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amadu III Of Masina
Amadu III of Masina (, ), also known as Amadu Amadu (1830 - 16 May 1862) was the third and last ruler of the theocratic Caliphate of Hamdullahi (Diina of Hamdullahi) in the Inner Niger Delta, now the Mopti Region of Mali. He was elected as successor to his father, Amadu II of Masina, in 1853. Throughout most of his rule he was involved in conflict with the jihadist al-Hajj 'Umar Tall, who defeated and executed him on 16 May 1862. Background Amadu III was the grandson of the founder of the Diina of Hamdullahi, Seku Amadu. Some time between 1810 and 1818 Seku Amadu (Aḥmad bin Muḥammad bin Abi Bakr Lobbo) launched a ''jihad'' against the Fulbe chiefs in Masina, tributaries of the pagan Bambara of Segu, whom he accused of idolatry. The goals of the ''jihad'' soon expanded to that of conquest of the Bambara and others in the region. Aḥmad bin Muḥammad established a large empire based on Hamdallahi, which he had founded as the capital. He received support from Tukolor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Hadj Umar Tall
Hadji Oumarûl Foutiyou Tall (ʿUmar ibn Saʿīd al-Fūtī Ṭaʿl, , – 1864 CE), born in Futa Tooro, present-day Senegal, was a Senegalese Tijani sufi Toucouleur Islamic scholar and military commander who founded the short-lived Toucouleur Empire, which encompassed much of what is now Senegal, Mauritania, Guinea and Mali. Lapidus, Ira M. (2014) ''A History of Islamic Societies''. 3rd ed., New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 472–473. Name Omar Tall’s name is spelt variously: in particular, his first name is commonly transliterated in French as ''Omar'', although some sources prefer ''Umar''; the patronymic, ''ibn Saʿīd'', is often omitted; and the final element of his name, ''Tall'' (), is spelt variously as ''Tall'', ''Taal'' or ''Tal''. The honorific ''El Hadj'' (also ''al-Hajj'' or ''el-Hadj''), reserved for a Muslim who has successfully made the Hajj to Mecca, precedes Omar Tall's name in many texts, especially those in Arabic. Later he also took on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander Of The Faithful
() or Commander of the Faithful is a Muslim title designating the supreme leader of an Islamic community. Name Although etymologically () is equivalent to English "commander", the wide variety of its historical and modern use allows for a range of translations. The historian H.A.R. Gibb, however, counsels against the translation "Prince of the Believers" as "neither philologically nor historically correct". History The title was used for Muslim military commanders during the lifetime of Prophet Muhammad. It was, for example, borne by the Muslim commander at the Battle of al-Qadisiyya. On his accession in 634, the second caliph Umar () adopted the title. This was likely not for its military connotation, but rather deriving from a Quranic injunction to "Obey God and obey the Apostle and those invested with command among you" ( Sura 4, verses 58–62). According to Fred M. Donner, the title's adoption marked a step in the centralization of the nascent Muslim state, as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
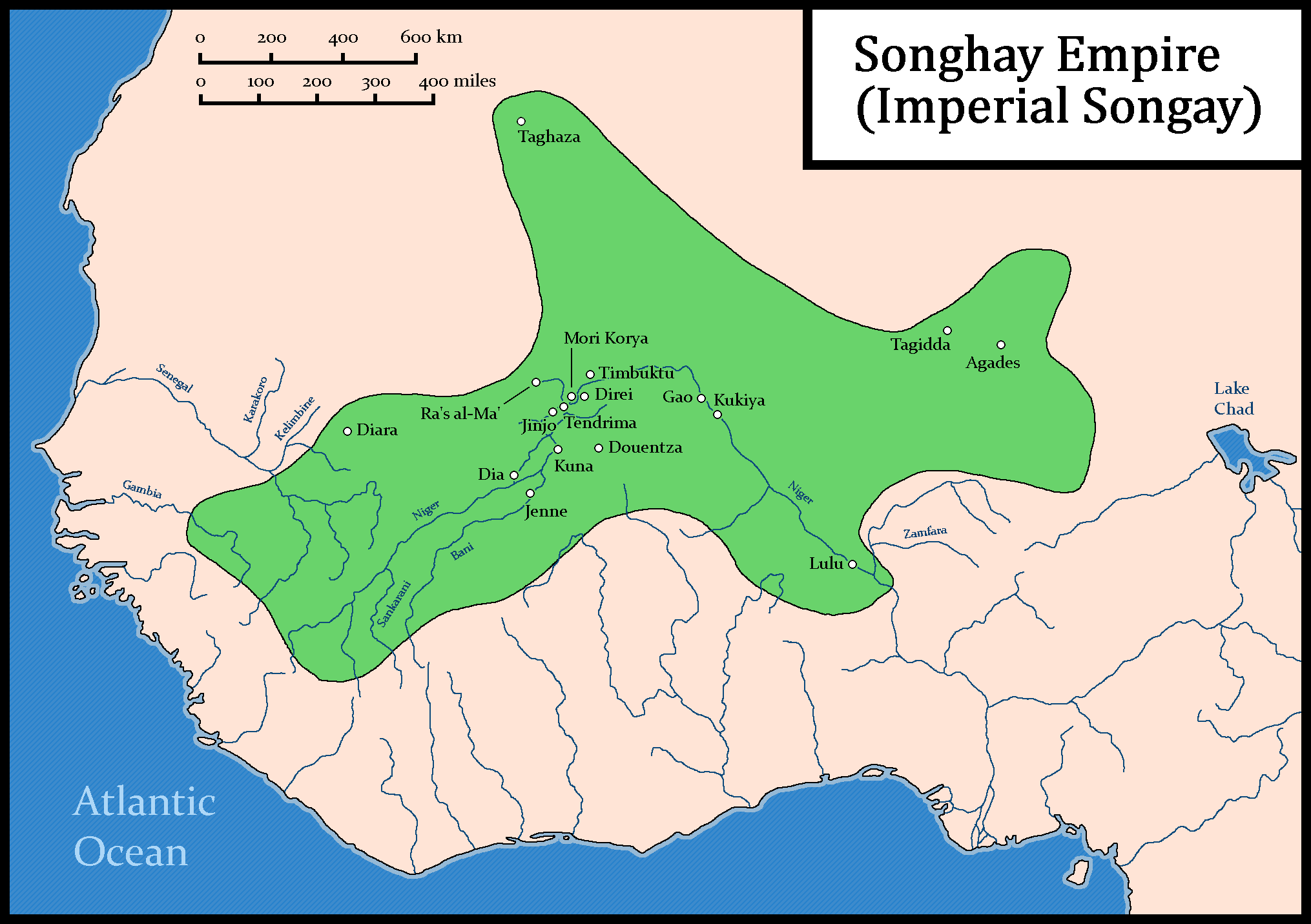
Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire was a state located in the western part of the Sahel during the 15th and 16th centuries. At its peak, it was one of the largest African empires in history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its largest ethnic group and ruling elite, the Songhai people. Sonni Ali established Gao as the empire's capital, although a Songhai state had existed in and around Gao since the 11th century. Other important cities in the kingdom were Timbuktu and Djenné, where urban-centred trade flourished; they were conquered in 1468 and 1475, respectively. Initially, the Songhai Empire was ruled by the Sonni dynasty (–1493), but it was later replaced by the Askia dynasty (1493–1591). During the second half of the 13th century, Gao and the surrounding region had grown into an important trading center and attracted the interest of the expanding Mali Empire. Mali conquered Gao near the end of the 13th century. Gao remained under Malian command until the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askia Mohammad I
Askia Muhammad Ture I (1443–1538), born Muhammad ibn Abi Bakr al-Turi or Muhammad Ture, was the first ruler of the Askia dynasty of the Songhai Empire, reigning from 1493 to 1528. He is also known as Askia the Great, and his name in modern Songhai is Mamar Kassey. Askia Muhammad strengthened his empire and made it the largest empire in West Africa's history. At its peak under his reign, the Songhai Empire encompassed the Hausa states as far as Kano (in present-day Northern Nigeria) and much of the territory that had belonged to the Songhai empire in the east. His policies resulted in a rapid expansion of trade with Europe and Asia, the creation of many schools, and the establishment of Islam as an integral part of the empire. Muhammad was a prominent general under the Songhai ruler Sunni Ali. When Sunni Ali was succeeded by his son, Sunni Baru, in 1492, Muhammad challenged the succession on the grounds that the new ruler was not a faithful Muslim. He defeated Baru and asc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaarta
Kaarta, (Also known as Ka'arta or the Massassi State) was a Bambara kingdom that arose after the fall of the Songhai Empire in what is today the western half of Mali and lasted until its destruction by Umar Tall in the 1850s. History Early history According to legend, Sounsan the first capital of Kaarta was founded near Mourdiah around 1635 by Sunsana, son of Niangolo. His son Massa was famously productive both on the farm and in the bedroom, expanding his power and holdings by marrying his many daughters to men who would come fight for him and raiding his neighbors. In 1710 rule passed to his son Benefali (r. 1710-1745), who fought a long war against the rising power of Bitòn Coulibaly and the Segou Empire. Benefali's son Foulakoro (r. 1745-1754) besieged Mourdiah, whose inhabitants begged for aid from Coulibaly. He came to Kaarta with an army, defeated Foulakoro, and captured him. The ''faama'' of Kaarta soon died in captivity. Re-Founding Kaarta was re-established by Sey B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mopti
Mopti (Fulfulde: Mobti) is a town and an urban commune in the Inner Niger Delta region of Mali. The town is the capital of the Mopti Cercle and the Mopti Region. Situated 630 km northeast of Bamako, the town lies at the confluence of the Niger and the Bani Rivers and is linked by an elevated causeway to the town of Sévaré. The urban commune, which includes both Mopti and Sévaré, had a population of 114,296 in the 2009 census. Geography Mopti lies on the right bank of the Bani River, a few hundred meters upstream of the confluence of the Bani with the Niger River. Between August and December when the rivers flood the Inner Niger Delta, the town becomes a series of islands connected by raised causeways. During this period the only road access to the town is along a 12 km causeway that links Mopti to Sévaré. Mopti lies to the west of the Dogon Plateau and is 66 km northwest of Bandiagara and 76 km north-northeast of Djenné. The town is the capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |