|
Sekhukhune Campaign
Sekhukhune I (Matsebe; circa 1814 – 13 August 1882) was the paramount King of the Marota, more commonly known as the Bapedi, from 21 September 1861 until his assassination on 13 August 1882 by his rival and half-brother, Mampuru II. As the Pedi paramount leader he was faced with political challenges from boer settlers, the independent South African Republic (Dutch: ''Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek''), the British Empire, and considerable social change caused by Christian missionaries. Sekhukhune was the son of Sekwati I, and succeeded him upon his death in 20 September 1861 after forcibly taking the throne from his half-brother and the heir apparent Mampuru II. His other known siblings were; Legolwana, Johannes Dinkwanyane, and Kgoloko. Sekhukhune married Legoadi IV in 1862, and lived at a mountain, now known as or Leolo Mountains which he fortified. To strengthen his kingdom and to guard against European colonisation, he had his young subjects work in white mines and on farms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedi People
The Pedi or (also known as the Northern Sotho or and the Marota or ) – are a Southern Africa, southern African ethnic group that speak Pedi or ''Sepedi'', a dialect belonging to the Sotho-Tswana peoples, Sotho-Tswana Ethnolinguistic group, enthnolinguistic group. Northern Sotho is a term used to refer to one of South Africa's 11 official languages. Northern Sotho or Sesotho sa Leboa consist of 33 dialects, of which Pedi is one of them. The BaPedi people are almost exclusively found in South Africa's Points of the compass, northeastern Provinces of South Africa, provinces which are Limpopo, and parts of northern Mpumalanga. There is confusion regarding the distinction between BaPedi people, and tribes referred to Northern Sotho (''Basotho ba Lebowa).'' On the one hand, one military explanation is that the BaPedi people became powerful at one point under a powerful king that ruled over a large piece of land. During this period, a powerful army of the BaPedi conquered small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Merensky
Alexander Merensky (8 June 1837 in Panten near Liegnitz – 22 May 1918 in Berlin) was a German missionary, working in South Africa (Transvaal) since 1859. Life Alexander was orphaned early in life and grew up among relatives. In 1855, he entered the mission seminary of the Berlin Missionary Society and was sent out on 23 November 1858. Together with a fellow missionary, Karl-Heinrich Theodor Grützner, he travelled by sailboat from Amsterdam to Cape Town and on to Natal. On 14 August 1860, he co-founded the mission station Gerlachshoop, the first mission station of the Berlin Missionary Society north of the Vaal River, together with Grützner. Merensky was ordained as missionary in Gerlachshoop on 11 January 1861. A further mission station, Kgalatlou/ Schoonoord, was dedicated in August 1861. On 15 October 1863 Merensky was married to Marie Liers from Breslau. Seven children were born to this union, among them as fourth child Hans Merensky. They lived in Kgalatlou until M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boer Commando
The Boer Commandos or "Kommandos" were volunteer military units of guerilla militia organized by the Boer people of South Africa. From this came the term "commando" into the English language during the Second Boer War of 1899-1902 as per Costica Andrew. History In 1658, war erupted between the Dutch settlers at Cape Colony and the Khoi-khoi. In order to protect the settlement, all able bodied men were conscripted. After the conclusion of this war, all men in the colony were liable for military service and were expected to be ready on short notice. By 1700, the size of the colony had increased immensely and it was divided into districts. The small military garrison stationed at the Castle de Goede Hoop could not be counted on to react swiftly in the border districts, therefore the commando system was expanded and formalized. Each district had a Kommandant who was charged with calling up all burghers in times of need. In 1795, with the First British Occupation and again in 1806 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand River Convention
The Sand River Convention ( af, Sandrivierkonvensie) of 17 January 1852 was a convention whereby the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland formally recognised the independence of the Boers north of the Vaal River. Background The convention was signed on 17 January 1852, by Commandant-General Andries Pretorius and others, on behalf of the new country, and Major William Samuel Hogge and Charles Mostyn Owen, clerk to the Civil Commissioner of Winburg, duly authorised to, and on behalf of, the British government. The treaty was signed on the farm called Sand River belonging to P. A. Venter, near Ventersburg. Provisions The treaty contained the following provisions: # The British government guarantees and grants the emigrant farmers across the Vaal river the right to govern themselves, according to their own laws free from any and all British interference and that the British Government wishes to promote peace, free trade and friendly intercourse with the new country # Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inboekstelsel
Inboekstelsel was a system of indentured child labour instituted by Europeans in Southern Africa during the 18th and 19th centuries. The word is derived from the Dutch verb ''inboeken'' (register; literally "in-book"), referring to the requirement of entering the names and details of the ''inboekeling'' (also spelled ''inboekseling''), or apprentices, in the Landdros's register. It is widely seen as a form of slavery by historians of South Africa. The system had its origin in the Cape Northern Frontier during the second half of the 18th century, when settlers would capture native children, and force them to work as indentured labourers until adulthood. When Boer trekkers migrated into the Transvaal during the 1840s, they brought the inboekstelsel system with them. Inboekelinge children were captured during raids, or handed over as apprentices by their conquered parents in return for land or goods. In some cases they were sold by Boer settlers to other burghers, in what became kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Cornet
A field cornet () is a term formerly used in South Africa for either a local government official or a military officer. The office had its origins in the position of ''veldwachtmeester'' in the Dutch Cape colony, and was regarded as being equivalent to a sergeant. The British administration enhanced its importance with the term field cornet, making it equivalent to an officer's rank. The term was used for a civilian official in a local government district ('' drostdy'') of the Cape Colony, acting as and invested with the authority of a military officer and empowered to act as a magistrate. The field cornet was subject to the landdrost of the district and acted as his representative. As such, a field cornet performed important functions in administrative, judicial and police matters. In addition, in peacetime the field cornet was the head of the militia, was responsible for maintaining law and order in his area, and was tasked with supervising the handover of postal items on arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Barkly
Sir Henry Barkly (24 February 1815 – 20 October 1898) was a British politician, colonial governor and patron of the sciences. Early life and education Born on 24 February 1815 at Highbury, Middlesex (now London), he was the eldest son of Susannah Louisa (born ffrith) and Æneas Barkly, a Scottish born West India merchant. He was educated at Bruce Castle School in Tottenham, where the school's particular curriculum endowed him with a lifetime interest in science and statistics. Upon completing his schooling and studies in commerce, Barkly worked for his father. The Barkly family had several connections with the West Indies: Barkly's mother, Susannah Louisa, whose maiden name was ffrith, was the daughter of a Jamaica planter; his father's company was concerned with trade in the West Indies; and the family owned an estate in British Guiana. According to the Legacies of British Slave-ownership database Barkly's father was compensated £132,000 from the Imperial Parliament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Herbert, 4th Earl Of Carnarvon
Henry Howard Molyneux Herbert, 4th Earl of Carnarvon, (24 June 1831 – 29 June 1890), known as Lord Porchester from 1833 to 1849, was a British politician and a leading member of the Conservative Party. He was twice Secretary of State for the Colonies and also served as Lord Lieutenant of Ireland. Origins Born at Grosvenor Square, London, Carnarvon was the eldest son and heir of Henry Herbert, 3rd Earl of Carnarvon (d.1849), by his wife Henrietta Anna Howard, a daughter of Lord Henry Howard-Molyneux-Howard, younger brother of Bernard Howard, 12th Duke of Norfolk. The Hon. Auberon Herbert was his younger brother. Youth He was educated at Eton College. In 1849, aged 18, he succeeded his father in the earldom. He attended Christ Church, Oxford, where his nickname was " Twitters", apparently on account of his nervous tics and twitchy behaviour, and where in 1852 he obtained a first in '' literae humaniores''. Early political career, 1854–66 Carnavon made his maiden speech i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
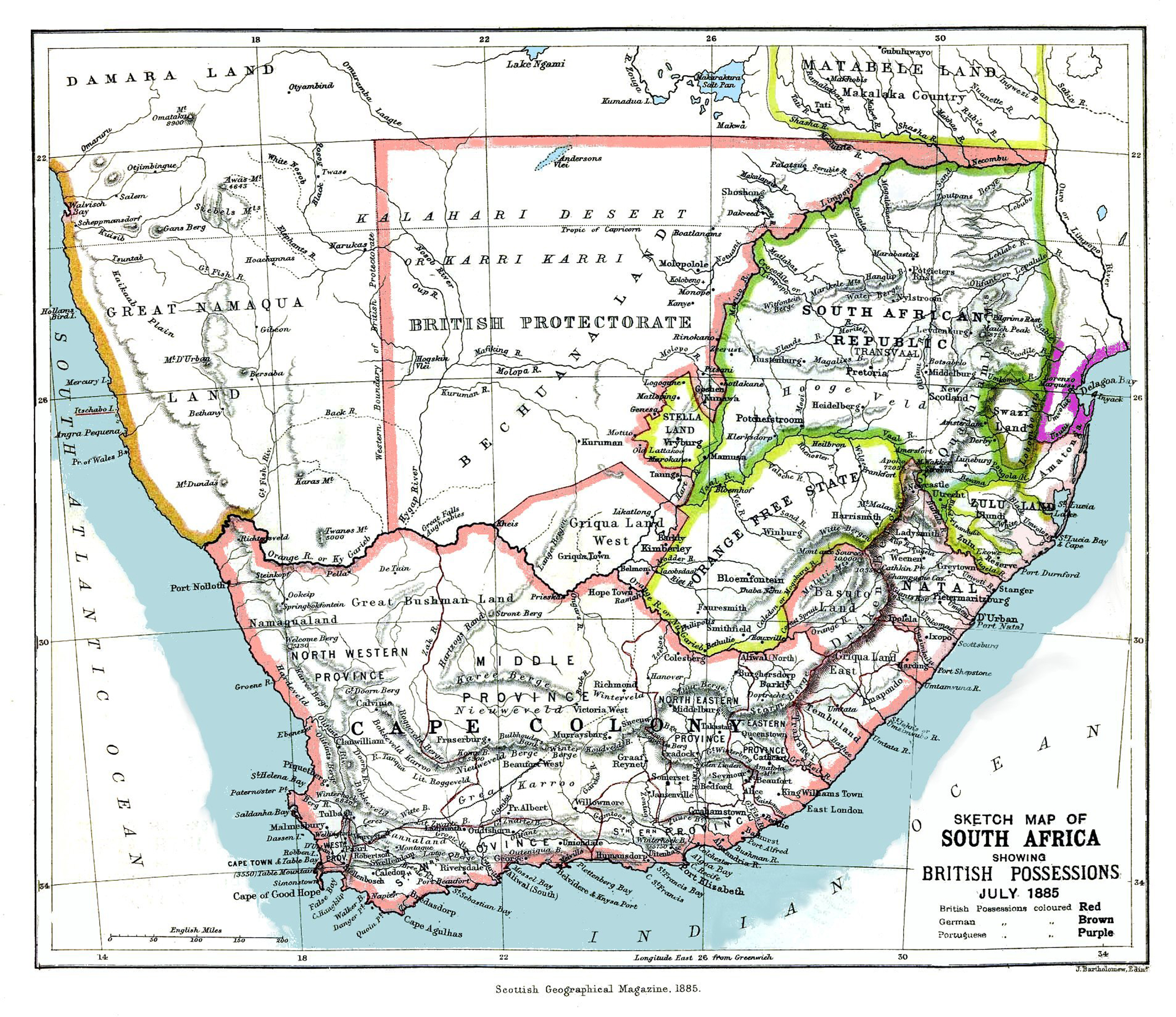
Griqualand West
Griqualand West is an area of central South Africa with an area of 40,000 km2 that now forms part of the Northern Cape Province. It was inhabited by the Griqua people – a semi-nomadic, Afrikaans-speaking nation of mixed-race origin, who established several states outside the expanding frontier of the Cape Colony. It was also inhabited by the pre-existing Tswana and Khoisan peoples. In 1873 it was proclaimed as a British colony, with its capital at Kimberley, and in 1880 it was annexed by the Cape Colony. When the Union of South Africa was formed in 1910, Griqualand West was part of the Cape Province but continued to have its own "provincial" sports teams. Early history The indigenous population of the area were the Khoi-khoi and Bushmen peoples, who were hunter-gatherers or herders. Early on they were joined by the agriculturalist Batswana, who migrated into the area from the north. They comprised the majority of the population throughout the region's history, up unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Von Bismarck
Otto, Prince of Bismarck, Count of Bismarck-Schönhausen, Duke of Lauenburg (, ; 1 April 1815 – 30 July 1898), born Otto Eduard Leopold von Bismarck, was a conservative German statesman and diplomat. From his origins in the upper class of Junker landowners, Bismarck rose rapidly in Prussian politics, and from 1862 to 1890 he was the Minister President of Prussia, minister president and List of foreign ministers of Prussia, foreign minister of Prussia. Before his rise to the Executive (government), executive, he was the Prussian ambassador to Russian Empire, Russia and Second French Empire, France and served in both houses of the Landtag of Prussia, Prussian Parliament. He masterminded the unification of Germany in 1871 and served as the first Chancellor of Germany#Under the Emperor (1871–1918), Chancellor of the German Empire until 1890, in which capacity he dominated European affairs. He had served as the chancellor of the North German Confederation from 1867 to 1871, alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |