|
Seikyo Shimbun
(English: "the newspaper of sacred teachings") is a Japanese newspaper. In 1997, it claimed a 5,5 million circulation, but the number is controversial and impossible to verify..It is owned by the Japanese Buddhist religious movement Soka Gakkai. Background The ''Seikyo Shimbun'' was first published on 20 April 1951. As of 1997, it claimed a circulation of , but that number is controversial and impossible to verify. Unlike the other daily newspapers in Japan, the Seikyo Shinbun is not a member of the Japan Newspaper Publishers and Editors Association nor the . who are officially in charge of the circulation numbers of Japanese newspapers. The publication is owned and operated by the Japanese Buddhist organization Soka Gakkai, and often features news articles about the activities of the president of the Soka Gakkai International (SGI), Daisaku Ikeda, and essays written by him, as well as news and experiences by Soka Gakkai members in Japan and abroad. The newspaper also fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property is often ascribed to objects (a " sacred artifact" that is venerated and blessed), or places (" sacred ground"). French sociologist Émile Durkheim considered the dichotomy between the sacred and the profane to be the central characteristic of religion: "religion is a unified system of beliefs and practices relative to ''sacred things'', that is to say, things set apart and forbidden." Durkheim, Émile. 1915. ''The Elementary Forms of the Religious Life''. London: George Allen & Unwin. . In Durkheim's theory, the sacred represents the interests of the group, especially unity, which are embodied in sacred group symbols, or using team work to help get out of trouble. The profane, on the other hand, involve mundane individual concerns. Etymology The word ''sacred'' des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese New Religions
Japanese new religions are new religious movements established in Japan. In Japanese, they are called or . Japanese scholars classify all religious organizations founded since the middle of the 19th century as "new religions"; thus, the term refers to a great diversity and number of organizations. Most came into being in the mid-to- late twentieth century and are influenced by much older traditional religions including Buddhism and Shinto. Foreign influences include Christianity, the Bible and the writings of Nostradamus. Before World War II In the 1860s Japan began to experience great social turmoil and rapid modernization. As social conflicts emerged in this last decade of the Edo period, known as the Bakumatsu period, some new religious movements appeared. Among them were Tenrikyo, Kurozumikyo and Oomoto, sometimes called ''Nihon Sandai Shinkōshūkyō'' ("Japan's three large new religions"), which were directly influenced by Shinto (the state religion) and shamanism. The soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soka Gakkai
is a Japanese Buddhist religious movement based on the teachings of the 13th-century Japanese priest Nichiren as taught by its first three presidents Tsunesaburō Makiguchi, Jōsei Toda, and Daisaku Ikeda. It is the largest of the Japanese new religions and claims the largest membership among Nichiren Buddhist groups. The organization bases its teachings on Nichiren's interpretation of the ''Lotus Sutra'' and places chanting "Nam Myōhō Renge Kyō at the center of devotional practice. The organization promotes its goals as supporting "''peace, culture, and education''". The movement was founded by educators Makiguchi and Toda on 18 November 1930, and held its inaugural meeting in 1937. It was disbanded during the Second World War when much of the leadership was imprisoned for violations of the 1925 Peace Preservation Law and charges of lèse-majesté. After the war, it expanded to a claimed total of 750,000 households in 1958 through explosive recruitment, held to be unpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Newspaper Publishers And Editors Association
The is an entirely independent and voluntary organization funded and operated by the mass media of Japan. The NSK was established on July 23, 1946. Its express purpose is to elevate ethical standards in reporting and protect and promote the media's common interests. The NSK has been criticized as limiting the foreign press, local Japanese media outlets, over-representing the large national newspapers, and monopolizing representation with government officials, especially in regards to censorship. The functions of the NSK fall into the following six categories: * maintenance and elevation of ethical standards * coordination, protection and promotion of common interests * research * seminars * public relations * international activities The NSK is involved in conducting seminars and lectures, and compiling a newsletter in an effort to increase education of the newspaper business in Japan and around the world. A study by the NSK, "Newspapers Take On The Digital Information Age; Can Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soka Gakkai International
Soka Gakkai International (SGI) is an international Nichiren Buddhist organisation founded in 1975 by Daisaku Ikeda, as an umbrella organization of Soka Gakkai, which declares approximately 12 million adherents in 192 countries and territories as of 2017, more than 1.5 million of whom reside outside of Japan as of 2012. It characterizes itself as a support network for practitioners of Nichiren Buddhism and a global Buddhist movement for "peace, education, and cultural exchange." SGI is also a non-governmental organization (NGO) in consultative status with the United Nations Economic and Social Council since 1983. History The Soka Gakkai International (SGI) was formed at a world peace conference on January 26, 1975, on the island of Guam. Representatives from 51 countries attended the meeting and chose Daisaku Ikeda, who served as third president of the Japanese Buddhist organization Soka Gakkai, to become the SGI's founding president. The SGI was created in part as a new inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daisaku Ikeda
is a Japanese Buddhist philosopher, educator, author, and nuclear disarmament advocate. He served as the third president and then honorary president of the Soka Gakkai, the largest of Japan's new religious movements. Ikeda is the founding president of the Soka Gakkai International (SGI), the world's largest Buddhist lay organization, which claims to have approximately 12 million practitioners in 192 countries and territories, more than 1.5 million of whom reside outside of Japan as of 2012. Ikeda was born in Tokyo, Japan, in 1928, to a family of seaweed farmers. He survived the devastation of World War II as a teenager, which he said left an indelible mark on his life and fueled his quest to solve the fundamental causes of human conflict. At age 19, Ikeda began practicing Nichiren Buddhism and joined a youth group of the Soka Gakkai, which led to his lifelong work developing the global peace movement of SGI and founding dozens of institutions dedicated to fostering peace, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sōka University
, abbreviated typically as or , is a private university in Hachiōji, Tokyo, Japan. In 2014, the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) designated Soka University as one of Japan's Top Global Universities. The university has 8 faculties with a total of around 8,000 students, 400 of whom are international students. History Soka University opened to undergraduate students on April 2, 1971, with its graduate school opening in April 1975. Since the school's founding, more than 50,000 students have graduated from Soka University. Soka University of America is a related school founded in 2001, located in Aliso Viejo, California, which offers both graduate and undergraduate degrees. Educational philosophy Soka University's educational philosophy was established by Tsunesaburō Makiguchi, the first president of the Soka Gakkai (then called the Soka Kyoiku Gakkai, or Value-creating Education Society), who had worked as the principal of an ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soka University Of America
Soka University of America (SUA) is a private liberal arts college in Aliso Viejo, California. Originally founded in 1987, it was established on its current campus in 2001 by Daisaku Ikeda, the founder of the Soka Gakkai International Buddhist movement. Though affiliated with Soka Gakkai, it maintains a secular curriculum which emphasizes pacifism, human rights, and the creative coexistence of nature and humanity. A much larger and older sister school, Sōka University in Japan, is located in Hachiōji, Tokyo. SUA encompasses both a four-year liberal arts college and a graduate school offering a Master's program in Educational Leadership and Societal Change. SUA also hosts the Pacific Basin Research Center and the newly created SUA Center for Race, Ethnicity, and Human Rights. It has an endowment of $1.2 billion , giving it the second-highest endowment per student of any college or university in the United States. History and philosophy SUA is a secular and nonsectarian col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
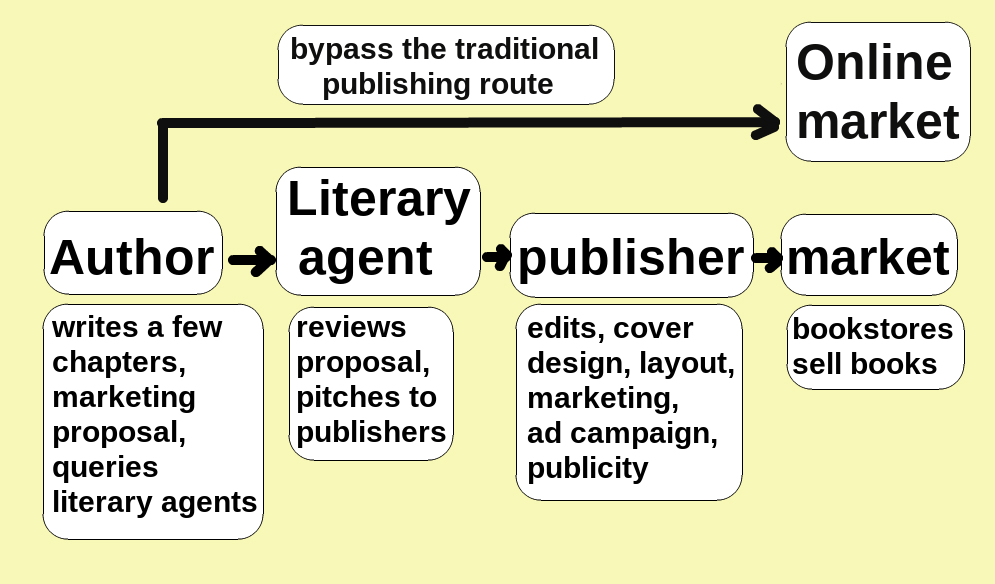
Self-publishing
Self-publishing is the publication of media by its author at their own cost, without the involvement of a publisher. The term usually refers to written media, such as books and magazines, either as an ebook or as a physical copy using POD (print on demand) technology. It may also apply to albums, pamphlets, brochures, games, video content, artwork, and zines. Web fiction is also a major medium for self-publishing. Definitions Although self-publishing is not a new phenomenon, dating back to the 18th century, it has transformed during the internet age with new technologies and services providing increasing alternatives to traditional publishing, becoming a $1 billion market.Jennifer Alsever, Fortune magazine, 30 December 2016The Kindle Effect Retrieved 9 November 2017, "...has become a $1 billion industry..." However, with the increased ease of publishing and the range of services available, confusion has arisen as to what constitutes self-publishing. In 2022, the Society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1951 Establishments In Japan
Events January * January 4 – Korean War: Third Battle of Seoul – Chinese and North Korean forces capture Seoul for the second time (having lost the Second Battle of Seoul in September 1950). * January 9 – The Government of the United Kingdom announces abandonment of the Tanganyika groundnut scheme for the cultivation of peanuts in the Tanganyika Territory, with the writing off of £36.5M debt. * January 15 – In a court in West Germany, Ilse Koch, The "Witch of Buchenwald", wife of the commandant of the Buchenwald concentration camp, is sentenced to life imprisonment. * January 20 – Winter of Terror: Avalanches in the Alps kill 240 and bury 45,000 for a time, in Switzerland, Austria and Italy. * January 21 – Mount Lamington in Papua New Guinea 1951 eruption of Mount Lamington, erupts catastrophically, killing nearly 3,000 people and causing great devastation in Oro Province. * January 25 – Dutch author Anne de Vries releases the first volume of his children's nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publications Established In 1951
To publish is to make content available to the general public.Berne Convention, article 3(3) URL last accessed 2010-05-10.Universal Copyright Convention, Geneva text (1952), article VI . URL last accessed 2010-05-10. While specific use of the term may vary among countries, it is usually applied to text, images, or other content, including paper ( |
.jpg)