|
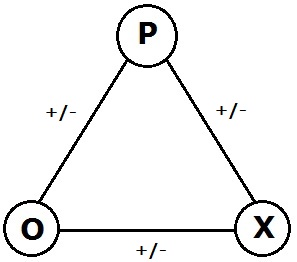
Seidel Adjacency Matrix
In mathematics, in graph theory, the Seidel adjacency matrix of a simple undirected graph ''G'' is a symmetric matrix with a row and column for each vertex, having 0 on the diagonal, −1 for positions whose rows and columns correspond to adjacent vertices, and +1 for positions corresponding to non-adjacent vertices. It is also called the Seidel matrix or—its original name—the (−1,1,0)-adjacency matrix. It can be interpreted as the result of subtracting the adjacency matrix of ''G'' from the adjacency matrix of the complement of ''G''. The multiset of eigenvalues of this matrix is called the Seidel spectrum. The Seidel matrix was introduced by J. H. van Lint and in 1966 and extensively exploited by Seidel and coauthors. The Seidel matrix of ''G'' is also the adjacency matrix of a signed complete graph ''KG'' in which the edges of ''G'' are negative and the edges not in ''G'' are positive. It is also the adjacency matrix of the two-graph associated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Theory
In mathematics, graph theory is the study of '' graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of '' vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') which are connected by ''edges'' (also called ''links'' or ''lines''). A distinction is made between undirected graphs, where edges link two vertices symmetrically, and directed graphs, where edges link two vertices asymmetrically. Graphs are one of the principal objects of study in discrete mathematics. Definitions Definitions in graph theory vary. The following are some of the more basic ways of defining graphs and related mathematical structures. Graph In one restricted but very common sense of the term, a graph is an ordered pair G=(V,E) comprising: * V, a set of vertices (also called nodes or points); * E \subseteq \, a set of edges (also called links or lines), which are unordered pairs of vertices (that is, an edge is associated with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph (discrete Mathematics)
In discrete mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a graph is a structure amounting to a set of objects in which some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects correspond to mathematical abstractions called '' vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an ''edge'' (also called ''link'' or ''line''). Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges. Graphs are one of the objects of study in discrete mathematics. The edges may be directed or undirected. For example, if the vertices represent people at a party, and there is an edge between two people if they shake hands, then this graph is undirected because any person ''A'' can shake hands with a person ''B'' only if ''B'' also shakes hands with ''A''. In contrast, if an edge from a person ''A'' to a person ''B'' means that ''A'' owes money to ''B'', th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetric Matrix
In linear algebra, a symmetric matrix is a square matrix that is equal to its transpose. Formally, Because equal matrices have equal dimensions, only square matrices can be symmetric. The entries of a symmetric matrix are symmetric with respect to the main diagonal. So if a_ denotes the entry in the ith row and jth column then for all indices i and j. Every square diagonal matrix is symmetric, since all off-diagonal elements are zero. Similarly in characteristic different from 2, each diagonal element of a skew-symmetric matrix must be zero, since each is its own negative. In linear algebra, a real symmetric matrix represents a self-adjoint operator represented in an orthonormal basis over a real inner product space. The corresponding object for a complex inner product space is a Hermitian matrix with complex-valued entries, which is equal to its conjugate transpose. Therefore, in linear algebra over the complex numbers, it is often assumed that a symmetric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjacency Matrix
In graph theory and computer science, an adjacency matrix is a square matrix used to represent a finite graph. The elements of the matrix indicate whether pairs of vertices are adjacent or not in the graph. In the special case of a finite simple graph, the adjacency matrix is a (0,1)-matrix with zeros on its diagonal. If the graph is undirected (i.e. all of its edges are bidirectional), the adjacency matrix is symmetric. The relationship between a graph and the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of its adjacency matrix is studied in spectral graph theory. The adjacency matrix of a graph should be distinguished from its incidence matrix, a different matrix representation whose elements indicate whether vertex–edge pairs are incident or not, and its degree matrix, which contains information about the degree of each vertex. Definition For a simple graph with vertex set , the adjacency matrix is a square matrix such that its element is one when there is an edge from vertex to vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the complement or inverse of a graph is a graph on the same vertices such that two distinct vertices of are adjacent if and only if they are not adjacent in . That is, to generate the complement of a graph, one fills in all the missing edges required to form a complete graph, and removes all the edges that were previously there.. The complement is not the set complement of the graph; only the edges are complemented. Definition Let be a simple graph and let consist of all 2-element subsets of . Then is the complement of , where is the relative complement of in . For directed graphs, the complement can be defined in the same way, as a directed graph on the same vertex set, using the set of all 2-element ordered pairs of in place of the set in the formula above. In terms of the adjacency matrix ''A'' of the graph, if ''Q'' is the adjacency matrix of the complete graph of the same number of vertices (i.e. all entries ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiset
In mathematics, a multiset (or bag, or mset) is a modification of the concept of a set that, unlike a set, allows for multiple instances for each of its elements. The number of instances given for each element is called the multiplicity of that element in the multiset. As a consequence, an infinite number of multisets exist which contain only elements and , but vary in the multiplicities of their elements: * The set contains only elements and , each having multiplicity 1 when is seen as a multiset. * In the multiset , the element has multiplicity 2, and has multiplicity 1. * In the multiset , and both have multiplicity 3. These objects are all different when viewed as multisets, although they are the same set, since they all consist of the same elements. As with sets, and in contrast to tuples, order does not matter in discriminating multisets, so and denote the same multiset. To distinguish between sets and multisets, a notation that incorporates square brackets i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eigenvalue
In linear algebra, an eigenvector () or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a nonzero vector that changes at most by a scalar factor when that linear transformation is applied to it. The corresponding eigenvalue, often denoted by \lambda, is the factor by which the eigenvector is scaled. Geometrically, an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction in which it is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed. Loosely speaking, in a multidimensional vector space, the eigenvector is not rotated. Formal definition If is a linear transformation from a vector space over a field into itself and is a nonzero vector in , then is an eigenvector of if is a scalar multiple of . This can be written as T(\mathbf) = \lambda \mathbf, where is a scalar in , known as the eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic roo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signed Graph
In the area of graph theory in mathematics, a signed graph is a graph in which each edge has a positive or negative sign. A signed graph is balanced if the product of edge signs around every cycle is positive. The name "signed graph" and the notion of balance appeared first in a mathematical paper of Frank Harary in 1953. Dénes Kőnig had already studied equivalent notions in 1936 under a different terminology but without recognizing the relevance of the sign group. At the Center for Group Dynamics at the University of Michigan, Dorwin Cartwright and Harary generalized Fritz Heider's psychological theory of balance in triangles of sentiments to a psychological theory of balance in signed graphs. Signed graphs have been rediscovered many times because they come up naturally in many unrelated areas. For instance, they enable one to describe and analyze the geometry of subsets of the classical root systems. They appear in topological graph theory and group theory. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-graph
In mathematics, a two-graph is a set of (unordered) triples chosen from a finite vertex set ''X'', such that every (unordered) quadruple from ''X'' contains an even number of triples of the two-graph. A regular two-graph has the property that every pair of vertices lies in the same number of triples of the two-graph. Two-graphs have been studied because of their connection with equiangular lines and, for regular two-graphs, strongly regular graphs, and also finite groups because many regular two-graphs have interesting automorphism groups. A two-graph is not a graph and should not be confused with other objects called 2-graphs in graph theory, such as 2-regular graphs. Examples On the set of vertices the following collection of unordered triples is a two-graph: :123 124 135 146 156 236 245 256 345 346 This two-graph is a regular two-graph since each pair of distinct vertices a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongly Regular Graph
In graph theory, a strongly regular graph (SRG) is defined as follows. Let be a regular graph with vertices and degree . is said to be strongly regular if there are also integers and such that: * Every two adjacent vertices have common neighbours. * Every two non-adjacent vertices have common neighbours. The complement of an is also strongly regular. It is a . A strongly regular graph is a distance-regular graph with diameter 2 whenever μ is non-zero. It is a locally linear graph whenever . Etymology A strongly regular graph is denoted an srg(''v'', ''k'', λ, μ) in the literature. By convention, graphs which satisfy the definition trivially are excluded from detailed studies and lists of strongly regular graphs. These include the disjoint union of one or more equal-sized complete graphs, and their complements, the complete multipartite graphs with equal-sized independent sets. Andries Brouwer and Hendrik van Maldeghem (see #References) use an alternate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derek Corneil
Derek Gordon Corneil is a Canadian mathematician and computer scientist, a professor ''emeritus'' of computer science at the University of Toronto, and an expert in graph algorithms and graph theory. Life When he was leaving high school, Corneil was told by his English teacher that doing a degree in mathematics and physics was a bad idea, and that the best he could hope for was to go to a technical college. His interest in computer science began when, as an undergraduate student at Queens College, he heard that a computer was purchased by the London Life insurance company in London, Ontario, where his father worked. As a freshman, he took a summer job operating the UNIVAC Mark II at the company. One of his main responsibilities was to operate a printer. An opportunity for a programming job with the company sponsoring his college scholarship appeared soon after. It was a chance that Corneil jumped at after being denied a similar position at London Life. There was an initial mix-up a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |