|
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) is a form of virtual private network (VPN) tunnel that provides a mechanism to transport PPP traffic through an SSL/TLS channel. SSL/TLS provides transport-level security with key negotiation, encryption and traffic integrity checking. The use of SSL/TLS over TCP port 443 (by default, port can be changed) allows SSTP to pass through virtually all firewalls and proxy servers except for authenticated web proxies. SSTP servers must be authenticated during the SSL/TLS phase. SSTP clients can optionally be authenticated during the SSL/TLS phase and must be authenticated in the PPP phase. The use of PPP allows support for common authentication methods, such as EAP-TLS and MS-CHAP. SSTP is available for Linux, BSD, and Windows. SSTP is available on Windows Vista SP1 and later, in RouterOS since version 5.0, and in SEIL since its firmware version 3.50. It is fully integrated with the RRAS architecture in these operating systems, allowing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Private Network
A virtual private network (VPN) extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network. The benefits of a VPN include increases in functionality, security, and management of the private network. It provides access to resources that are inaccessible on the public network and is typically used for remote workers. Encryption is common, although not an inherent part of a VPN connection. A VPN is created by establishing a virtual point-to-point connection through the use of dedicated circuits or with tunneling protocols over existing networks. A VPN available from the public Internet can provide some of the benefits of a wide area network (WAN). From a user perspective, the resources available within the private network can be accessed remotely. Types Virtual private networks may be classified into several categories: ;Remote ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IIJ SEIL
(IIJ, ) was founded in 1992 by Koichi Suzuki, as Japan’s first Internet service provider An Internet service provider (ISP) is an organization that provides services for accessing, using, or participating in the Internet. ISPs can be organized in various forms, such as commercial, community-owned, non-profit, or otherwise private ... (ISP). From 1999 IIJ were listed on NASDAQ, USA (listed August 1999; ticker symbol IIJI) and as of 2006 were listed on the First Section of the Tokyo Stock Exchange (listed December 2006; stock ticker number: 3774). References External links Internet in Japan Internet service providers of Japan Companies formerly listed on the Nasdaq Companies listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange Telecommunications companies established in 1992 Domain name registrars Mobile virtual network operators Internet properties established in 1992 Japanese companies established in 1992 {{Japan-company-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Open Specification Promise
The Microsoft Open Specification Promise (or OSP) is a promise by Microsoft, published in September 2006, to not assert its patents, in certain conditions, against implementations of a certain list of specifications. The OSP is not a licence, but rather a covenant not to sue. It promises protection but does not grant any rights. The OSP is limited to implementations to the extent that they conform to those specifications. This allows for conformance to be partial. So if an implementation follows the specification for some aspects, and deviates in other aspects, then the Covenant Not to Sue applies only to the implementation's aspects which follow the specification. Relations with free software / open source projects The protections granted by the OSP are independent to the licence of implementations. There is disagreement as to whether the conditions of the OSP can be fulfilled by free software / open source projects, and whether they thus gain any protection from the OSP. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
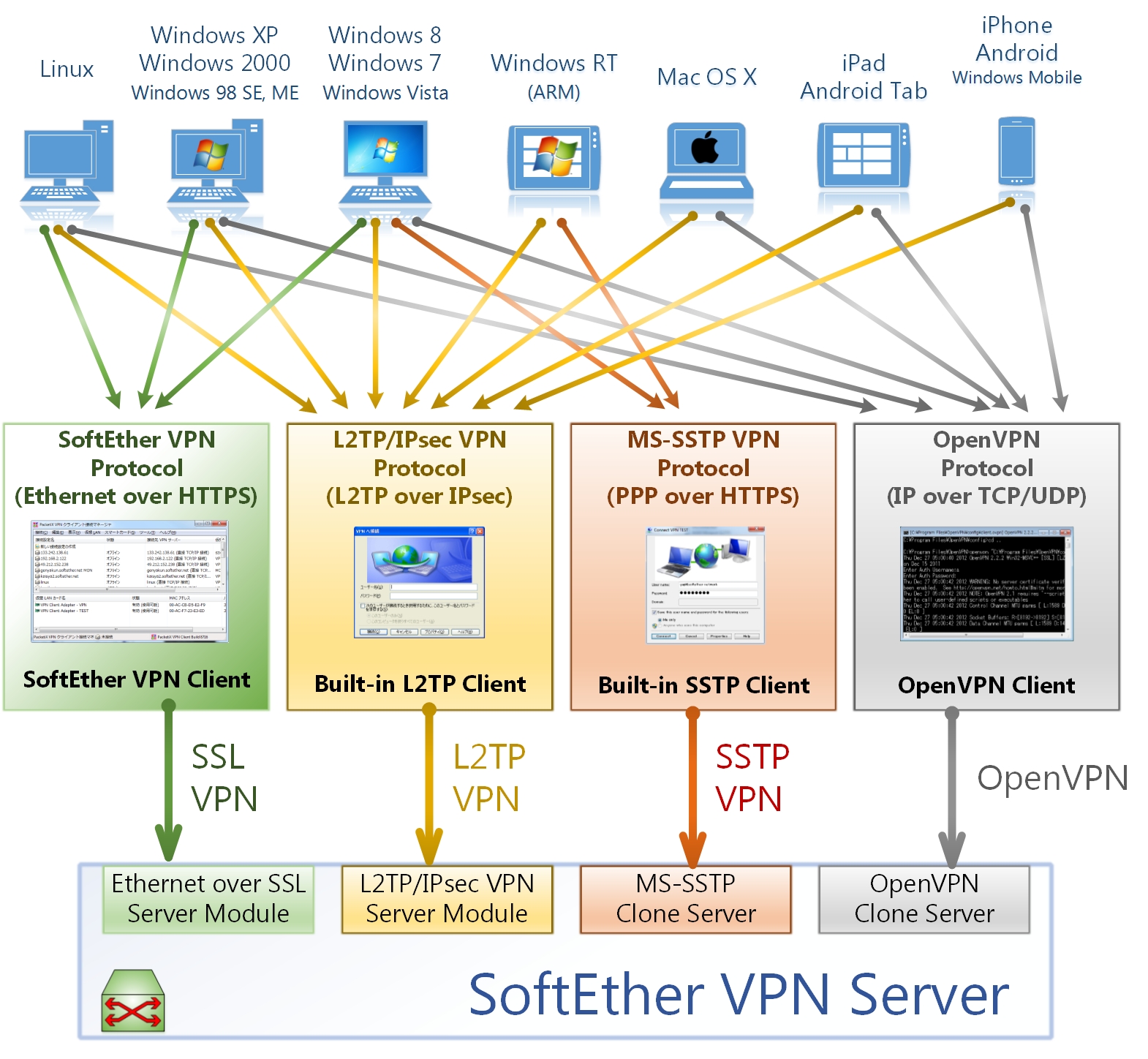
SoftEther VPN
SoftEther VPN is free open-source, cross-platform, multi-protocol VPN client and VPN server software, developed as part of Daiyuu Nobori's master's thesis research at the University of Tsukuba. VPN protocols such as SSL VPN, L2TP/ IPsec, OpenVPN, and Microsoft Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol are provided in a single VPN server. It was released using the GPLv2 license on January 4, 2014. The license was switched to Apache License 2.0 on January 21, 2019. SoftEther VPN supports NAT traversal, making it useful to run VPN servers on computers that are behind residential gateways, facility routers, and firewalls. Firewalls performing deep packet inspection are unable to detect SoftEther's VPN transport packets as a VPN tunnel because HTTPS is used to camouflage the connection. SoftEther VPN optimizes performance by using full Ethernet frame utilization, reducing memory copy operations, parallel transmission, and clustering. Together, these reduce latency normally associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PPTP
The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is an obsolete method for implementing virtual private networks. PPTP has many well known security issues. PPTP uses a TCP control channel and a Generic Routing Encapsulation tunnel to encapsulate PPP packets. Many modern VPNs use various forms of UDP for this same functionality. The PPTP specification does not describe encryption or authentication features and relies on the Point-to-Point Protocol being tunneled to implement any and all security functionalities. The PPTP implementation that ships with the Microsoft Windows product families implements various levels of authentication and encryption natively as standard features of the Windows PPTP stack. The intended use of this protocol is to provide security levels and remote access levels comparable with typical VPN products. History A specification for PPTP was published in July 1999 as RFC 2637 and was developed by a vendor consortium formed by Microsoft, Ascend Commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenConnect
OpenConnect is an open-source software application for connecting to virtual private networks (VPN), which implement secure point-to-point connections. It was originally written as an open-source replacement for Cisco's proprietary AnyConnect SSL VPN client, which is supported by several Cisco routers. The OpenConnect client added support for Juniper Networks' SSL VPN in version 7.05, then for Palo Alto Networks' GlobalProtect VPN in version 8.00, for Pulse/Junos VPN in version 8.04, and for Fortinet FortiGate, F5 BiGIP, and Array Networks in version 8.20. Protocols Cisco AnyConnect Cisco AnyConnect VPNs utilize TLS to authenticate and configure routing, then DTLS to efficiently encrypt and transport the tunneled VPN traffic, and can fall back to TLS-based transport where firewalls block UDP-based traffic. The DTLS protocol used by Cisco AnyConnect servers was based on a non-standard, pre-release draft of DTLS 1.0, until support for the DTLS 1.2 standard was added in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is a virtual private network (VPN) system that implements techniques to create secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections in routed or bridged configurations and remote access facilities. It implements both client-server architecture, client and server applications. OpenVPN allows peer-to-peer, peers to authentication, authenticate each other using pre-shared key, pre-shared secret keys, public key certificate, certificates or user (computing), username/password. When used in a multiclient-server configuration, it allows the server to release an authentication certificate for every client, using digital signature, signatures and certificate authority. It uses the OpenSSL encryption Library (computing), library extensively, as well as the Transport Layer Security, TLS protocol, and contains many security and control features. It uses a custom security protocol that utilizes Transport Layer Security, SSL/TLS for key exchange. It is capable of traversing network addr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTPS
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or, formerly, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The protocol is therefore also referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL. The principal motivations for HTTPS are authentication of the accessed website, and protection of the privacy and integrity of the exchanged data while in transit. It protects against man-in-the-middle attacks, and the bidirectional encryption of communications between a client and server protects the communications against eavesdropping and tampering. The authentication aspect of HTTPS requires a trusted third party to sign server-side digital certificates. This was historically an expensive operation, which meant fully authenticated HTTPS connections were usually found o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L2TP
In computer networking, Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol used to support virtual private networks (VPNs) or as part of the delivery of services by ISPs. It uses encryption ('hiding') only for its own control messages (using an optional pre-shared secret), and does not provide any encryption or confidentiality of content by itself. Rather, it provides a tunnel for Layer 2 (which may be encrypted), and the tunnel itself may be passed over a Layer 3 encryption protocol such as IPsec. History Published in 2000 as proposed standard RFC 2661, L2TP has its origins primarily in two older tunneling protocols for point-to-point communication: Cisco's Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol (L2F) and Microsoft's Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). A new version of this protocol, L2TPv3, appeared as proposed standard RFC 3931 in 2005. L2TPv3 provides additional security features, improved encapsulation, and the ability to carry data links other than simply Point-to-Poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AuthIP
AuthIP is a Microsoft proprietary extension of the IKE cryptographic protocol. AuthIP is supported in Windows Vista and later on the client and Windows Server 2008 and later on the server. AuthIP adds a second authentication to the standard IKE authentication which, according to Microsoft, increases security and deployability of IPsec VPNs. AuthIP adds support for user-based authentication by using Kerberos v5 or SSL certificates. AuthIP is not compatible with IKEv2, an IETF standard with similar characteristics; however Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 also support IKEv2. See also * SSTP External links AuthIP in Windows Vista- The Cable Guy column at the Microsoft website The Authenticated Internet Protocol- The Cable Guy column at the Microsoft website Cryptographic protocols Windows Server ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Azure
Microsoft Azure, often referred to as Azure ( , ), is a cloud computing platform operated by Microsoft for application management via around the world-distributed data centers. Microsoft Azure has multiple capabilities such as software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) and supports many different programming languages, tools, and frameworks, including both Microsoft-specific and third-party software and systems. Azure, announced at Microsoft's Professional Developers Conference (PDC) in October 2008, went by the internal project codename "Project Red Dog", and was formally released in February 2010 as Windows Azure, before being renamed Microsoft Azure on March 25, 2014. Services Microsoft Azure uses large-scale virtualization at Microsoft data centers worldwide and it offers more than 600 services. Compute services * Virtual machines, infrastructure as a service (IaaS) allowing users to launch general-purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |