|
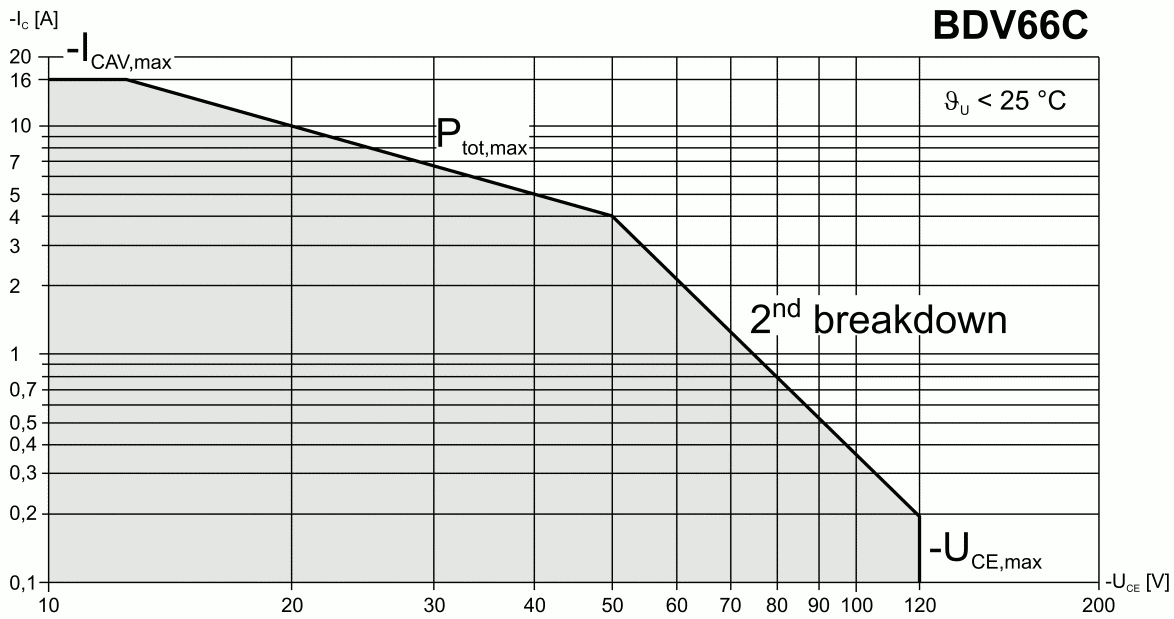
Secondary Breakdown
For power semiconductor devices (such as BJT, MOSFET, thyristor or IGBT), the safe operating area (SOA) is defined as the voltage and current conditions over which the device can be expected to operate without self-damage. SOA is usually presented in transistor datasheets as a graph with VCE (collector-emitter voltage) on the abscissa and ICE (collector-emitter current) on the ordinate; the safe 'area' referring to the area under the curve. The SOA specification combines the various limitations of the device — maximum voltage, current, power, junction temperature, secondary breakdown — into one curve, allowing simplified design of protection circuitry. Often, in addition to the continuous rating, separate SOA curves are also plotted for short duration pulse conditions (1 ms pulse, 10 ms pulse, etc.). The safe operating area curve is a graphical representation of the power handling capability of the device under various conditions. The SOA curve takes into account the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Semiconductor Device
A power semiconductor device is a semiconductor device used as a switch or rectifier in power electronics (for example in a switch-mode power supply). Such a device is also called a power device or, when used in an integrated circuit, a power IC. A power semiconductor device is usually used in "commutation mode" (i.e., it is either on or off), and therefore has a design optimized for such usage; it should usually not be used in linear operation. Linear power circuits are widespread as voltage regulators, audio amplifiers, and radio frequency amplifiers. Power semiconductors are found in systems delivering as little as a few tens of milliwatts for a headphone amplifier, up to around a gigawatt in a high voltage direct current transmission line. History The first electronic device used in power circuits was the electrolytic rectifier - an early version was described by a French experimenter, A. Nodon, in 1904. These were briefly popular with early radio experimenters as they c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithmic Scale
A logarithmic scale (or log scale) is a way of displaying numerical data over a very wide range of values in a compact way—typically the largest numbers in the data are hundreds or even thousands of times larger than the smallest numbers. Such a scale is nonlinear: the numbers 10 and 20, and 60 and 70, are not the same distance apart on a log scale. Rather, the numbers 10 and 100, and 60 and 600 are equally spaced. Thus moving a unit of distance along the scale means the number has been ''multiplied'' by 10 (or some other fixed factor). Often exponential growth curves are displayed on a log scale, otherwise they would increase too quickly to fit within a small graph. Another way to think about it is that the ''number of digits'' of the data grows at a constant rate. For example, the numbers 10, 100, 1000, and 10000 are equally spaced on a log scale, because their numbers of digits is going up by 1 each time: 2, 3, 4, and 5 digits. In this way, adding two digits ''multiplies'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derating
In electronics, derating (or derating) is the operation of a device at less than its rated maximum capability to prolong its life. Typical examples include operations below the maximum power rating, current rating, or voltage rating. In electronics Power semiconductor devices have a maximum power dissipation rating usually quoted at a case temperature of . The datasheet for the device also includes a ''derating curve'' which indicates how much a device will dissipate without getting damaged at any given case temperature, and this must be taken into account while designing a system. As can be seen from the derating curve image for a hypothetical bipolar junction transistor, the device (rated for 100 W at ) cannot be expected to dissipate anything more than about 40 W if the ambient temperature is such that the temperature at which the device's case will stabilize (after heat-sinking) is . This final case temperature is a function of the thermal resistance between the device's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snubber
A snubber is a device used to suppress ("snub") a phenomenon such as voltage transients in electrical systems, pressure transients in fluid systems (caused by for example water hammer) or excess force or rapid movement in mechanical systems. Electrical systems Snubbers are frequently used in electrical systems with an inductive load where the sudden interruption of current flow leads to a large counter-electromotive force: a rise in voltage across the current switching device that opposes the change in current, in accordance with Faraday's law. This transient can be a source of electromagnetic interference (EMI) in other circuits. Additionally, if the voltage generated across the device is beyond what the device is intended to tolerate, it may damage or destroy it. The snubber provides a short-term alternative current path around the current switching device so that the inductive element may be safely discharged. Inductive elements are often unintentional, arising from the curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Horowitz
Paul Horowitz (born 1942) is an American physicist and electrical engineer, known primarily for his work in electronics design, as well as for his role in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (see SETI). Biography At age 8, Horowitz achieved distinction as the world's youngest amateur radio operator. He went on to study physics at Harvard University ( B.A., 1965; M.A., 1967; Ph.D., 1970), where he has also spent all of his subsequent career. His early work was on scanning microscopy (using both protons and X-rays). Horowitz has also conducted astrophysical research on pulsars and investigations in biophysics. His interest in practical electronics has led to a handful of inventions, including an automated voting machine and an acoustic mechanism for landmine detection, and an electronic Morse Code/Baudot code keyboard using a diode matrix and 66 TTL integrated circuits for Amateur Radio use. Since 1974 he has taught a practical course in electronics whose l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalanche Transistor
An avalanche transistor is a bipolar junction transistor designed for operation in the region of its collector-current/collector-to-emitter voltage characteristics beyond the collector-to-emitter breakdown voltage, called ''avalanche breakdown region''. This region is characterized by avalanche breakdown, which is a phenomenon similar to Townsend discharge for gases, and negative differential resistance. Operation in the avalanche breakdown region is called avalanche-mode operation: it gives avalanche transistors the ability to switch very high currents with less than a nanosecond rise and fall times (transition times). Transistors not specifically designed for the purpose can have reasonably consistent avalanche properties; for example 82% of samples of the 15V high-speed switch 2N2369, manufactured over a 12-year period, were capable of generating avalanche breakdown pulses with rise time of 350 ps or less, using a 90V power supply as Jim Williams writes.V_: this is the expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foldback (power Supply Design)
Current limiting is the practice of imposing a limit on the current that may be delivered to a load to protect the circuit generating or transmitting the current from harmful effects due to a short-circuit or overload. The term "current limiting" is also used to define a type of overcurrent protective device. According to the 2020 NEC/NFPA 70, a current limiting overcurrent protective device is defined as, "A device that, when interrupting currents in its current-limiting range, reduces the current flowing in the faulted circuit to a magnitude substantially less than that obtainable in the same circuit if the device were replaced with a solid conductor having compatible impedance." Inrush current limiting An inrush current limiter is a device or group of devices used to limit inrush current. Passive resistive components such as resistors or negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistors are simple options, with power dissipation and cool-down time being their main drawbacks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a result, power supplies are sometimes referred to as electric power converters. Some power supplies are separate standalone pieces of equipment, while others are built into the load appliances that they power. Examples of the latter include power supplies found in desktop computers and consumer electronics devices. Other functions that power supplies may perform include limiting the current drawn by the load to safe levels, shutting off the current in the event of an electrical fault, power conditioning to prevent electronic noise or voltage surges on the input from reaching the load, power-factor correction, and storing energy so it can continue to power the load in the event of a temporary interruption in the source power (uninterruptible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the voltage or current (power, voltage or current amplifier). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a greater amplitude signal at its output. The ratio of output to input voltage, current, or power is termed gain (voltage, current, or power gain). An amplifier, by definition has gain greater than unity (if the gain is less than unity, the device is an attenuator). An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit contained within another device. Amplification is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are widely used in almost all electronic equipment. Amplifiers can be categorize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. A metal-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is a term almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another synonym is IGFET for insulated-gate field-effect transistor. The basic principle of the field-effect transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925.Lilienfeld, Julius Edgar (1926-10-08) "Method and apparatus for controlling electric currents" upright=1.6, Two power MOSFETs in V_in_the_''off''_state,_and_can_conduct_a_continuous_current_of_30 surface-mount_packages._Operating_as_switches,_each_of_these_components_can_su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junction Temperature
Junction temperature, short for transistor junction temperature, is the highest operating temperature of the actual semiconductor in an electronic device. In operation, it is higher than case temperature and the temperature of the part's exterior. The difference is equal to the amount of heat transferred from the junction to case multiplied by the junction-to-case thermal resistance. Microscopic effects Various physical properties of semiconductor materials are temperature dependent. These include the diffusion rate of dopant elements, carrier mobilities and the thermal production of charge carriers. At the low end, sensor diode noise can be reduced by cryogenic cooling. On the high end, the resulting increase in local power dissipation can lead to thermal runaway that may cause transient or permanent device failure. Maximum junction temperature calculation Maximum junction temperature (sometimes abbreviated TJMax) is specified in a part's datasheet and is used when calculating t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |