|
Second-order Monte Carlo Simulation
Second-order may refer to: Mathematics * Second order approximation, an approximation that includes quadratic terms * Second-order arithmetic, an axiomatization allowing quantification of sets of numbers * Second-order differential equation, a differential equation in which the highest derivative is the second * Second-order logic, an extension of predicate logic * Second-order perturbation, in perturbation theory Science and technology * Second-order cybernetics Second-order cybernetics, also known as the cybernetics of cybernetics, is the recursive application of cybernetics to itself and the reflexive practice of cybernetics according to such a critique. It is cybernetics where "the role of the observer ..., the recursive application of cybernetics to itself and the reflexive practice of cybernetics according to this critique. * Second-order fluid, an extension of fluid dynamics * Second order Fresnel lens, a size of lighthouse lens * Second-order reaction, a reaction in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Order Approximation
In science, engineering, and other quantitative disciplines, order of approximation refers to formal or informal expressions for how accurate an approximation is. Usage in science and engineering In formal expressions, the ordinal number used before the word order refers to the highest power in the series expansion used in the approximation. The expressions: a ''zeroth-order approximation'', a ''first-order approximation'', a ''second-order approximation'', and so forth are used as fixed phrases. The expression a ''zero-order approximation'' is also common. Cardinal numerals are occasionally used in expressions like an ''order-zero approximation'', an ''order-one approximation'', etc. The omission of the word ''order'' leads to phrases that have less formal meaning. Phrases like first approximation or to a first approximation may refer to ''a roughly approximate value of a quantity''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-order Arithmetic
In mathematical logic, second-order arithmetic is a collection of axiomatic systems that formalize the natural numbers and their subsets. It is an alternative to axiomatic set theory as a foundation for much, but not all, of mathematics. A precursor to second-order arithmetic that involves third-order parameters was introduced by David Hilbert and Paul Bernays in their book '' Grundlagen der Mathematik''. The standard axiomatization of second-order arithmetic is denoted by Z2. Second-order arithmetic includes, but is significantly stronger than, its first-order counterpart Peano arithmetic. Unlike Peano arithmetic, second-order arithmetic allows quantification over sets of natural numbers as well as numbers themselves. Because real numbers can be represented as ( infinite) sets of natural numbers in well-known ways, and because second-order arithmetic allows quantification over such sets, it is possible to formalize the real numbers in second-order arithmetic. For this reason ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-order Differential Equation
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, and the differential equation defines a relationship between the two. Such relations are common; therefore, differential equations play a prominent role in many disciplines including engineering, physics, economics, and biology. Mainly the study of differential equations consists of the study of their solutions (the set of functions that satisfy each equation), and of the properties of their solutions. Only the simplest differential equations are solvable by explicit formulas; however, many properties of solutions of a given differential equation may be determined without computing them exactly. Often when a closed-form expression for the solutions is not available, solutions may be approximated numerically using computers. The theory of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-order Logic
In logic and mathematics, second-order logic is an extension of first-order logic, which itself is an extension of propositional logic. Second-order logic is in turn extended by higher-order logic and type theory. First-order logic quantifies only variables that range over individuals (elements of the domain of discourse); second-order logic, in addition, also quantifies over relations. For example, the second-order sentence \forall P\,\forall x (Px \lor \neg Px) says that for every formula ''P'', and every individual ''x'', either ''Px'' is true or not(''Px'') is true (this is the law of excluded middle). Second-order logic also includes quantification over sets, functions, and other variables (see section below). Both first-order and second-order logic use the idea of a domain of discourse (often called simply the "domain" or the "universe"). The domain is a set over which individual elements may be quantified. Examples First-order logic can quantify over individua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory
In mathematics and applied mathematics, perturbation theory comprises methods for finding an approximate solution to a problem, by starting from the exact solution of a related, simpler problem. A critical feature of the technique is a middle step that breaks the problem into "solvable" and "perturbative" parts. In perturbation theory, the solution is expressed as a power series in a small parameter The first term is the known solution to the solvable problem. Successive terms in the series at higher powers of \varepsilon usually become smaller. An approximate 'perturbation solution' is obtained by truncating the series, usually by keeping only the first two terms, the solution to the known problem and the 'first order' perturbation correction. Perturbation theory is used in a wide range of fields, and reaches its most sophisticated and advanced forms in quantum field theory. Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics) describes the use of this method in quantum mechanics. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
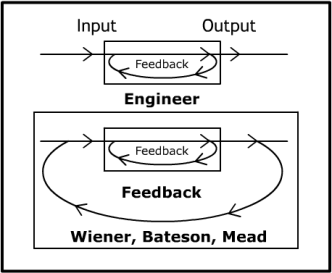
Second-order Cybernetics
Second-order cybernetics, also known as the cybernetics of cybernetics, is the recursive application of cybernetics to itself and the reflexive practice of cybernetics according to such a critique. It is cybernetics where "the role of the observer is appreciated and acknowledged rather than disguised, as had become traditional in western science". Glanville, R. (2002). "Second order cybernetics." In F. Parra-Luna (ed.), Systems science and cybernetics. In ''Encyclopaedia of Life Support Systems'' (EOLSS). OxfordEoLSS Second-order cybernetics was developed between the late 1960s and mid 1970s by Heinz von Foerster and others, with key inspiration coming from Margaret Mead. Foerster referred to it as "the control of control and the communication of communication" and differentiated first order cybernetics as "the cybernetics of observed systems" and second-order cybernetics as "the cybernetics of observing systems". Foerster, Heinz von, ed. ''Cybernetics of Cybernetics: Or, the Contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-order Fluid
A second-order fluid is a fluid where the stress tensor is the sum of all tensors that can be formed from the velocity field with up to two derivatives, much as a Newtonian fluid is formed from derivatives up to first order. This model may be obtained from a retarded motion expansion truncated at the second-order. For an isotropic, incompressible second-order fluid, the total stress tensor is given by : \sigma_ = -p \delta_ + \eta_0 A_ + \alpha_1 A_A_ + \alpha_2 A_, where : -p \delta_ is the indeterminate spherical stress due to the constraint of incompressibility, :A_ is the n-th Rivlin–Ericksen tensor, :\eta_0 is the zero-shear viscosity, :\alpha_1 and \alpha_2 are constants related to the zero shear normal stress coefficient Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to: Film and television * ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson * ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie * ''Norma ...s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
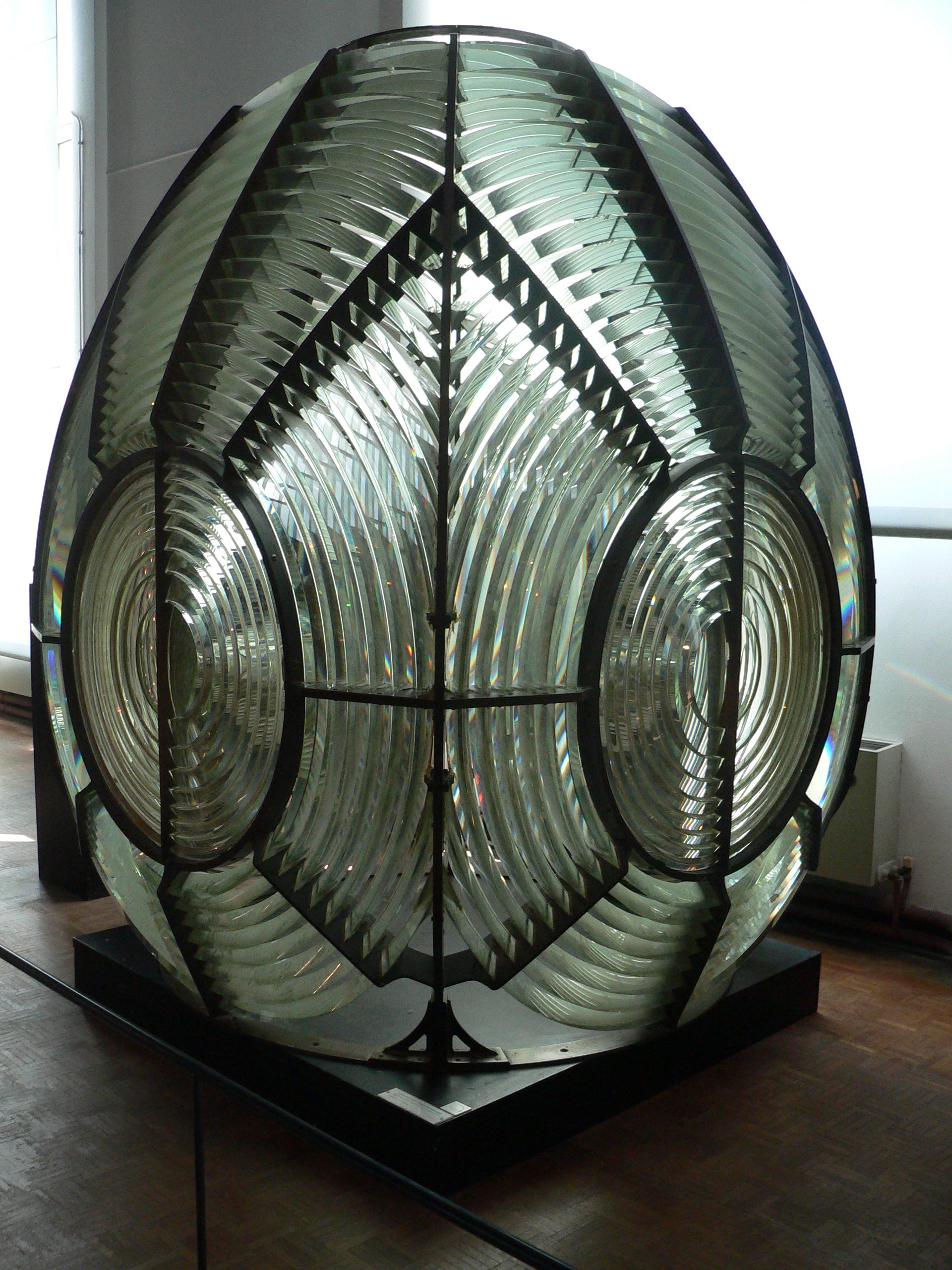
Second Order Fresnel Lens
A Fresnel lens ( ; ; or ) is a type of composite compact lens developed by the French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788–1827) for use in lighthouses. It has been called "the invention that saved a million ships." The design allows the construction of lenses of large aperture and short focal length without the mass and volume of material that would be required by a lens of conventional design. A Fresnel lens can be made much thinner than a comparable conventional lens, in some cases taking the form of a flat sheet. The simpler dioptric (purely refractive) form of the lens was first proposed by Count Buffon and independently reinvented by Fresnel. The ''catadioptric'' form of the lens, entirely invented by Fresnel, has outer elements that use total internal reflection as well as refraction; it can capture more oblique light from a light source and add it to the beam of a lighthouse, making the light visible from greater distances. Description The Fresnel lens red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-order Reaction
In chemistry, the rate law or rate equation for a reaction is an equation that links the initial or forward reaction rate with the concentrations or pressures of the reactants and constant parameters (normally rate coefficients and partial reaction orders). For many reactions, the initial rate is given by a power law such as :v_0\; =\; k mathrmx mathrmy where and express the concentration of the species and usually in moles per liter (molarity, ). The exponents and are the partial ''orders of reaction'' for and and the ''overall'' reaction order is the sum of the exponents. These are often positive integers, but they may also be zero, fractional, or negative. The constant is the reaction rate constant or ''rate coefficient'' of the reaction. Its value may depend on conditions such as temperature, ionic strength, surface area of an adsorbent, or light irradiation. If the reaction goes to completion, the rate equation for the reaction rate v\; =\; k cex cey applies through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-order Conditioning
In classical conditioning, second-order conditioning or higher-order conditioning is a form of learning in which a stimulus is first made meaningful or consequential for an organism through an initial step of learning, and then that stimulus is used as a basis for learning about some new stimulus. For example, an animal might first learn to associate a bell with food (first-order conditioning), but then learn to associate a light with the bell (second-order conditioning). Honeybees show second-order conditioning during proboscis extension reflex conditioning.Bitterman et al. 1983. Classical Conditioning of Proboscis Extension in Honeybees (''Apis mellifera''). J. Comp. Psych. 97: 107-119. Second-order conditioning (SOC) occurs in three phases. In the first training phase, a conditioned stimulus, (CS1) is followed by an unconditioned stimulus (US). In the second phase, a second-order conditioned stimulus (CS2) is presented along with CS1. Finally, in the test phase, CS2 is presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-order Desire
Higher-order volitions (or higher-order desire), as opposed to action-determining volitions, are volitions about volitions. Higher-order volitions are potentially more often guided by long-term beliefs and reasoning. A first-order volition is a desire about anything else, such as to own a new car, to meet the pope, or to drink alcohol. Second-order volition are desires about desires, or to desire to change the process, the how, of desiring. Examples would be desires to want to own a new car; to want to meet the Pope; or to want to quit drinking alcohol permanently. A higher-order volition can go unfulfilled due to uncontrolled lower-order volitions. An example for a failure to follow higher-order volitions is the drug addict who takes drugs even though they would like to quit taking drugs. According to Harry Frankfurt the drug addict has established free will when their higher-order volition to stop wanting drugs determines the precedence of their changing, action-determining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-order Stimulus
A second-order stimulus is a form of visual stimulus used in psychophysics in which objects are delineated from their backgrounds by differences of contrast or texture. On the contrary, a stimulus defined by differences in luminance Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls withi ... is known as a first-order stimulus. See also * Julesz conjecture Psychophysics {{Neuroscience-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |