|
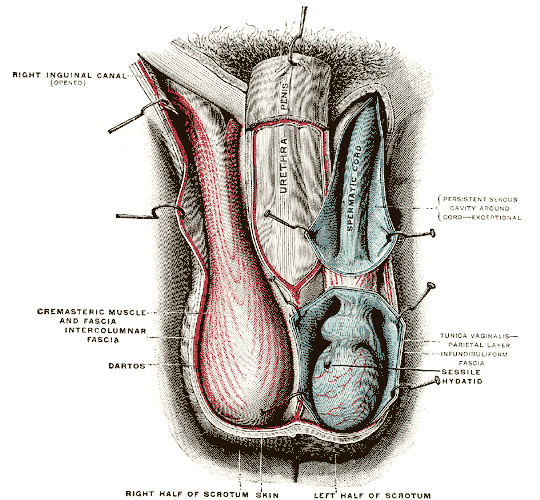
Sebileau's Muscle
Sebileau's muscle is the deep muscle fibres of the dartos tunic which pass into the scrotal septum. It is named after French anatomist Pierre Sebileau Pierre Sebileau (18 October 1860 – 4 October 1953) was a French surgeon born in Saint-Fort-sur-Gironde, a commune in Charente-Maritime. He was father-in-law to plastic surgeon Léon Dufourmentel (1884–1957). He served as an interne in hosp ... (1860–1953). References Muscles of the torso Scrotum Connective tissue {{Muscle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartos
The dartos fascia or simply dartos is a layer of connective tissue found in the penile shaft, foreskin, scrotum and labia. The penile portion is referred to as the superficial fascia of penis or the subcutaneous tissue of penis, while the scrotal part is the dartos proper. In addition to being continuous with itself between the scrotum and the penis, it is also continuous with Colles fascia of the perineum and Scarpa's fascia of the abdomen. The dartos lies just below the skin, which places it just superficial to the external spermatic fascia in the scrotum and to Buck's fascia in the penile shaft. In the scrotum, it consists mostly of smooth muscle. The tone of this smooth muscle is responsible for the wrinkled (rugose) appearance of the scrotum. In females, the same muscle fibers are less well developed and termed ''dartos muliebris,'' lying beneath the skin of the labia majora. The dartos fascia receives innervation from postganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers arriving via the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrotal Septum
The septum of the scrotum is a vertical layer of fibrous tissue that divides the two compartments of the scrotum. It consists of flexible connective tissue. Its structure extends to the skin surface of the scrotum as the scrotal raphe. It is an incomplete wall of connective tissue and nonstriated muscle (dartos fascia) dividing the scrotum into two sacs, each containing a testis. Histological septa are seen throughout most tissues of the body, particularly where they are needed to stiffen soft cellular tissue, and they also provide planes of ingress for small blood vessels. Because the dense collagen fibres of a septum usually extend out into the softer adjacent tissues. A septum is a cross-wall. Thus it divides a structure into smaller parts. The scrotal septum is used in reconstructive surgery to restore tissue and or reproductive organs injured or severed by trauma.Male Sexual Dysfunction: Pathophysiology and Treatment, edited by Fouad R. Kandeel, Edition: 1st, 2007. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Sebileau
Pierre Sebileau (18 October 1860 – 4 October 1953) was a French surgeon born in Saint-Fort-sur-Gironde, a commune in Charente-Maritime. He was father-in-law to plastic surgeon Léon Dufourmentel (1884–1957). He served as an interne in hospitals of Bordeaux (from 1879) and Paris (from 1884), where he later worked as an anatomical prosector (1888). Subsequently, he became a surgeon at Hôpital Lariboisière, specializing in the field of otorhinolaryngology. In 1893, he became an associate to the Faculty of Medicine in Paris. In addition to his work with ear, nose and throat concerns, Sebileau made contributions in his investigations involving diseases of the genitourinary system and the kidneys. His name is associated with "Sebileau's muscle", described as deep fibres of the dartos tunic which pass into the scrotal septum. Selected writings * ''Démonstrations d'anatomie; région temporale, région parotidienne, région sus-hyoïdienne, région sus-claviculaire, région s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscles Of The Torso
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum contains the external spermatic fascia, testes, epididymis, and ductus deferens. It is a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and pampiniform plexus. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical, slightly raised ridge of scrotal skin under which is found the scrotal septum. It appears as a thin longitudinal line that runs front to back over the entire scrotum. In humans and some other mammals the scrotum becomes covered with pubic hair at puberty. The scrotum will usually tighten during penile erection and when exposed to cold temperatures. One testis is typically lower than the other to avoid compression in the event of an impact. The scrotum is biologicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |