|
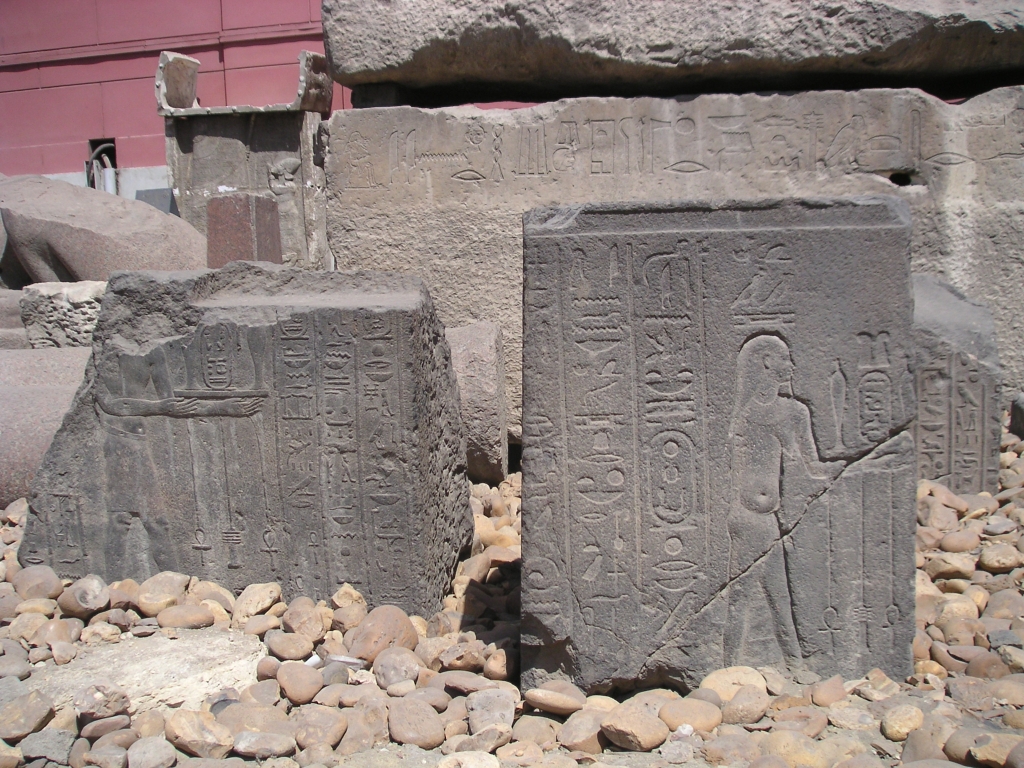
Sebennytos
Samannud ( ) is a city (''markaz'') located in Gharbia Governorate, Egypt. Known in classical antiquity as Sebennytos (), Samannud is a historic city that has been inhabited since the Ancient Egyptian period. As of 2019, the population of the ''markaz'' of Samannud was estimated to be 410,388, with 83,417 people living in urban areas and 326,971 in rural areas. Etymology The place known in , was historically called Sebennytos or Sebennytus. * , and , * Late and , * and or * Egyptian: ṯb-(n)-nṯr) The name Samannud ultimately derives from the Ancient Egyptian name ṯb-(n)-nṯr, meaning "city of the sacred calf". The name was probably pronounced * in Old Egyptian and * or * in Late Egyptian. Ancient history Samannud (Sebennytos) was an ancient city of Lower Egypt, located on the now-silted up Sebennytic branch of the Nile in the Delta. Sebennytos was the capital of Lower Egypt's twelfth nome—the Sebennyte nome (district). Sebennytos was also the seat of the Thirt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectanebo II
Nectanebo II (Egyptian: ; ) was the last native ruler of ancient Egypt, as well as the third and last pharaoh of the Thirtieth Dynasty, reigning from 358 to c.340 BC. During the reign of Nectanebo II, Egyptian artists developed a specific style that left a distinctive mark on the reliefs of the Ptolemaic Kingdom. Like his indirect predecessor Nectanebo I, Nectanebo II showed enthusiasm for many of the cults of the gods within ancient Egyptian religion, and more than a hundred Egyptian sites bear evidence of his attention. For several years, Nectanebo II was successful in keeping Egypt safe from the Achaemenid Empire. However, he was betrayed by his former servant, Mentor of Rhodes, and ultimately defeated. The Achaemenids occupied Memphis and then seized the rest of Egypt, incorporating the country into the Achaemenid Empire under Artaxerxes III. Nectanebo fled south. His subsequent fate is unknown. Name ''Nectanebo'' is derived from the Greek form of his name, (, or in lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirtieth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Thirtieth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXX, alternatively 30th Dynasty or Dynasty 30) is usually classified as the fifth Dynasty of the Late Period of ancient Egypt. It was founded after the overthrow of Nepherites II in 380 BC by Nectanebo I, and was disestablished upon the invasion of Egypt by the Achaemenid king Artaxerxes III in 343 BC. This is the final native dynasty of ancient Egypt; after the deposition of Nectanebo II, Egypt fell under foreign domination. History Nectanebo I had gained control of all of Egypt by November of 380 BC, but spent much of his reign defending his kingdom from Persian reconquest with the occasional help of Sparta or Athens. In 365 BC, Nectanebo made his son, Teos, co-king and heir, and until his death in 363 BC, father and son reigned together. After his father's death, Teos invaded the Persian territories of modern Syria and Israel and was beginning to meet with some successes when he lost his throne due to the machinations of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manetho
Manetho (; ''Manéthōn'', ''gen''.: Μανέθωνος, ''fl''. 290–260 BCE) was an Egyptian priest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom who lived in the early third century BCE, at the very beginning of the Hellenistic period. Little is certain about his life. He is known today as the author of a history of Egypt in Greek called the '' Aegyptiaca'' (''History of Egypt''), written during the reign of Ptolemy I Soter or Ptolemy II Philadelphus (285–246 BCE). None of Manetho’s original texts have survived; they are lost literary works, known only from fragments transmitted by later authors of classical and late antiquity. The remaining fragments of the ''Aegyptiaca'' continue to be a singular resource for delineating Egyptian chronology, more than two millennia since its composition. Until the decipherment of Ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century CE, Manetho's fragments were an essential source for understanding Egyptian history. His work remains of unique importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gharbia Governorate
Gharbia ( ', , "the western governorate") is one of the governorates of Egypt. It is located in the north of the country, south of Kafr El Sheikh Governorate, and north of Monufia Governorate. Its capital is Tanta, which is 90 km north of Cairo, and 120 km south east of Alexandria. The largest city in Gharbia is El Mahalla El Kubra. The total area of Gharbia governorate is 1,942 km2. Gharbia's known history dates back to the Pharaonic era, during which its territory was part of three ancient administrative districts centered around Abu Sir, Samannoud, and Sa El Hagar. These cities held religious and political significance in ancient Egypt: Abu Sir was a pilgrimage site, Sa El Hagar was a religious and medical hub during the early dynastic period, and also the capital of Tefnakht, who unified the Delta and Middle Egypt under his rule. It later became the center of the Twenty-fourth Dynasty of Egypt, which played a role in reuniting Egypt following fragmentat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
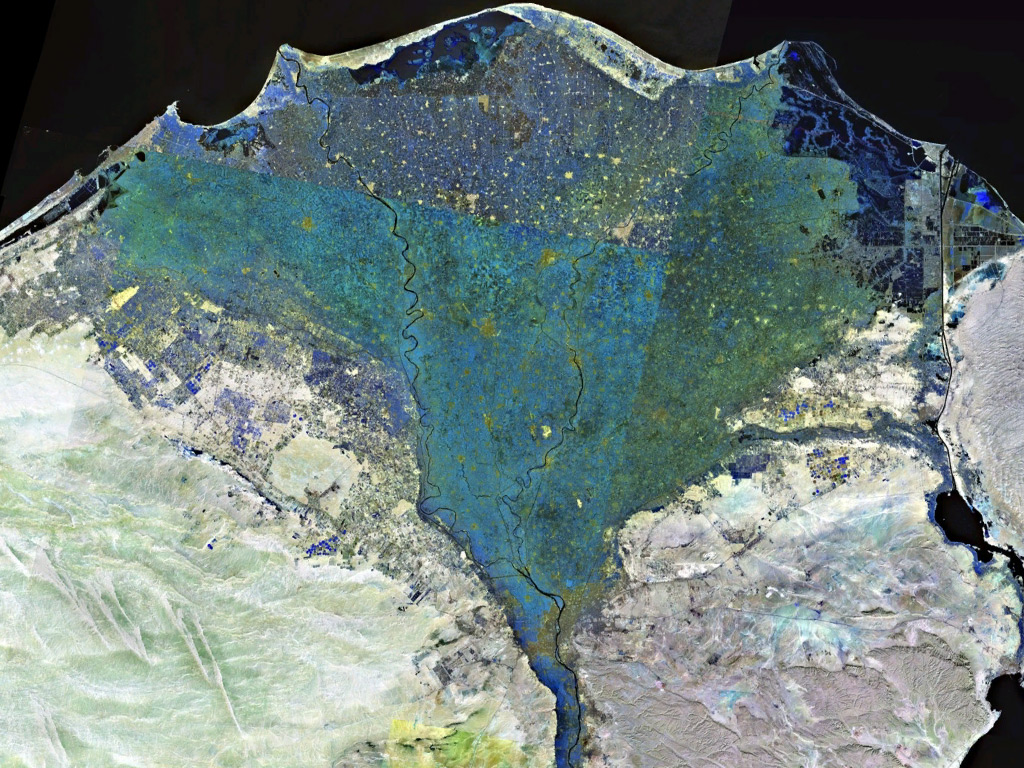
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east; it covers of the Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributary, distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same names. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood management, flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ') is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, the Nile River split into seven branches of the delta in Lower Egypt. Lower Egypt was divided into nomes and began to advance as a civilization after 3600 BC. Today, it contains two major channels that flow through the delta of the Nile River – Mahmoudiyah Canal (ancient Agathos Daimon) and Muways Canal (, "waterway of Moses"). Name In Ancient Egyptian, Lower Egypt was known as ''mḥw'' which means "north". Later on, during Antiquity and the Middle Ages, Greeks and Romans called it ''Κάτω Αἴγυπτος'' or ''Aegyptus Inferior'' both meaning "Lower Egypt", but Copts carried on using the old name related to the north – ''Tsakhet'' () or ''Psanemhit'' () meaning the "Northern part". It was further divided into a number of regions or nomes () – '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nome (Egypt)
A nome (, from , ''nomós'', "district") was a territorial division in ancient Egypt. Each nome was ruled by a nomarch (, "Great Chief"). The number of nomes changed through the various periods of the history of ancient Egypt. Etymology The term ''nome'' comes from Ancient Greek νομός ''nomós'' meaning "pasture" extended to "dwelling" and "district"; the Ancient Egyptian term was ( /sɛpɑt/). Today's use of the Ancient Greek rather than the Ancient Egyptian term came about during the Ptolemaic period, when the use of Greek was widespread in Egypt. The availability of Greek records on Egypt influenced the adoption of Greek terms by later historians. History Dynastic Egypt The division of ancient Egypt into nomes can be traced back to prehistoric Egypt (before 3100 BC). These nomes originally existed as autonomous city-states, but later began to unify. According to ancient tradition, the ruler Menes completed the final unification. Not only did the division into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall Cavendish
Marshall Cavendish is a subsidiary company of Times Publishing Group, the printing and publishing subsidiary of Singapore-based conglomerate Fraser and Neave (which in turn currently owned by ThaiBev, a Thai beverage company), and at present is a publisher of books, business directories and magazines. History Marshall Cavendish was established in the United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ... in 1968 by Norman Marshall (1921-1975) and Patrick Cavendish (1939-2000). Times Publishing Group acquired it in 1980. In 2011, Amazon Publishing acquired over 450 titles of Marshall Cavendish's US Children's trade books business, Marshall Cavendish Children's Books (MCCB). In 2013, Roger Rosen of Rosen Publishing acquired the Marshall Cavendish's US Children's l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harper And Brothers
Harper is an American publishing house, the flagship imprint of global publisher HarperCollins, based in New York City. Founded in New York in 1817 by James Harper and his brother John, the company operated as J. & J. Harper until 1833, when it changed its name to Harper & Brothers, reflecting the inclusion of Joseph and Fletcher Harper. Harper began publishing ''Harper's Magazine'', ''Harper's Weekly'', and other periodicals beginning in the 1850s. From 1962 to 1990, the company was known as Harper & Row after its merger with Row, Peterson & Company. Harper & Row was purchased in 1987 by News Corporation and combined with William Collins, Sons, its United Kingdom counterpart, in 1990 to form HarperCollins, although the Harper name has been used in its place since 2007. History J. & J. Harper (1817–1833) James Harper and his brother John, printers by training, started their book publishing business, J. & J. Harper, in New York City in 1817. Their two brothers, Joseph We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Bagster The Elder
Samuel Bagster the elder (26 December 1772 – 28 March 1851) was the founder of the publishing firm of ''Bagster & Sons''. Early life Samuel Bagster was born on 26 December 1772, the second son of George and Mary Bagster, of St. Pancras. He was educated at Northampton under the Rev. John Ryland, and, after serving an apprenticeship with William Otridge, commenced business as a general bookseller on 19 April 1794 in the Strand, where he remained until 1816. Printing the Bible The idea A few years before he left, the rarity and consequent costliness of all polyglot bibles gave Samuel Bagster the idea of supplying a convenient and inexpensive edition. He first brought out a Hebrew Bible, which was followed by the Septuagint, both in foolscap octavo. The production of English bibles was a monopoly in the United Kingdom, confined in England to the king's printer and the two great universities, in Scotland to Sir D. H. Blair and John Bruce, and in Ireland to Mr. Grierson. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns In Egypt
0-9 * 10th of Ramadan * 15th of May (city), 15th of May * 6th of October (city), 6th of October A * Abu El Matamir * Abu Hummus * Abu Tesht * Abu Tig * Akhmim * Al Khankah * Alexandria * Arish * Ashmoun * Aswan * Awsim * Ain Sokhna B * Badr, Egypt, Badr * Baltim * Banha * Basyoun * Biyala * Belqas * Beni Mazar * Beni Suef * Beni Ebeid * Biba, Egypt, Biba * Bilbeis * Birket El Sab * Borg El Arab * Borg El Burullus * Bush, Egypt, Bush C * Cairo D * Dahab * Dairut * Damanhur * Damietta * Dar El Salam * Daraw * Deir Mawas * Dekernes * Dendera * Desouk * Diarb Negm * Dishna, Egypt, Dishna E * Edfu * Edku * El Alamein * El Ayyat * El Badari, Egypt, El Badari * El Badrashein * El Bagour * El Balyana * El Basaliya * El Bayadiya * El Dabaa * El Delengat * El Fashn * El Gamaliya * El Ghanayem * El Hamool * El Hamam * El Hawamdeya * El Husseiniya * El Idwa * El Kanayat * El Mahalla El Kubra * El Mahmoudiyah * Ptolemais Hermiou, El Mansha * El Manzala * El Mara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historian
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human species; as well as the study of all history in time. Some historians are recognized by publications or training and experience.Herman, A. M. (1998). Occupational outlook handbook: 1998–99 edition. Indianapolis: JIST Works. Page 525. "Historian" became a professional occupation in the late nineteenth century as research universities were emerging in Germany and elsewhere. Objectivity Among historians Ancient historians In the 19th century, scholars used to study ancient Greek and Roman historians to see how generally reliable they were. In recent decades, however, scholars have focused more on the constructions, genres, and meanings that ancient historians sought to convey to their audiences. History is always written with contemporary concerns and ancient hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |