|
Sebastes
''Sebastes'' is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae part of the family Scorpaenidae, most of which have the common name of rockfish. A few are called ocean perch, sea perch or redfish instead. They are found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Taxonomy ''Sebastes'' was first described as a genus in 1829 by the French zoologist Georges Cuvier, the Dutch ichthyologist Pieter Bleeker designated ''Perca norvegica'', which may have been originally described by the Norwegian zoologist Peter Ascanius in 1772, as the type species in 1876. The genus is the type genus of both the tribe Sebastini and the subfamily Sebastinae, although some authorities treat these as the subfamily Sebastinae and the family Sebastidae, separating the Sebastidae as a distinct family from the Scorpaenidae. but other authorities place it in the Perciformes in the suborder Scorpaenoidei. Some authorities subdivide this large genus into subgenera as follows: * ''Sebastes'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yelloweye Rockfish
The yelloweye rockfish (''Sebastes ruberrimus'') is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the Family (biology), family Scorpaenidae and one of the biggest members of the genus ''Sebastes''. Its name derives from its coloration. It is also locally known as "red snapper," not to be confused with the warm-water Atlantic species ''Lutjanus campechanus'' that formally carries the name red snapper. The yelloweye is one of the world's longest-lived fish species, and is cited to live to a maximum of 114 to 120 years of age. As they grow older, they change in color, from reddish in youth, to bright orange in adulthood, to pale yellow in old age. Yelloweye live in rocky areas and feed on small fish and other rockfish. They reside in the East Pacific and range from Baja California to Dutch Harbor in Alaska. Yelloweye rockfish are prized for their meat, and were declared Overfishing, overfished in 2002, at which time a survey determ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastes Norvegicus
''Sebastes norvegicus'', the rose fish, rock fish, ocean perch, Atlantic redfish, Norway haddock, golden redfish, pinkbelly rosefish, Norway seaperch, Scottish seaperch or bergylt, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is found in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is a large, slow-growing, late-maturing fish and the subject of a fishery. Taxonomy ''Sebastes norvegicus'' was first formally described as ''Perca norvegicus'' in 1772 by the Norwegian biologist Peter Ascanius with the type locality given as Norway. The specific name refers to the type locality. In the past, the scientific name ''Sebastes marinus'' was frequently used, but this is actually a synonym of '' Serranus scriba''. ''S. norvegicus'' was designated as the type species of the genus ''Sebastes'' by Pieter Bleeker in 1876. This taxon may be a species complex containing at least 2 new cryptic species which had not been named a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastinae
Sebastinae is a subfamily of marine fish belonging to the Family (biology), family Scorpaenidae in the Order (biology), order Scorpaeniformes. Their common names include rockfishes, rock perches, ocean perches, sea perches, thornyheads, scorpionfishes, sea ruffes and rockcods. Despite the latter name, they are not closely related to the cods in the genus ''Gadus'', nor the rock cod, ''Lotella rhacina''. Taxonomy Sebastinae, or Sebastidae, was first formally recognised as a grouping in 1873 by the German naturalist Johann Jakob Kaup. Some authorities recognise this family as distinct from Scorpaenidae. FishBase, a finfish database generated by a consortium of academic institutions, does, but the United States Federal government's Integrated Taxonomic Information System and the 5th Edition of ''Fishes of the World'' do not, FotW classify it as a subfamily of the Scorpaenidae. Tribes and genera Sebastinae is divided into two Tribe (biology), tribes and seven genera: * Tribe Sebast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zalopyr
Zalopyr is a subgenus of the genus ''Sebastes''. The etymology Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ... derives from two Greek words: "zalos" meaning "surging" or "stormy," possibly referencing the turbulent habitat which it resides in. Pyr: meaning "fire," referring to the red color of '' S. aleutianus'', one of its two species. Its other species is '' S. melanostictus''. They are typically found below 300 meters and reaching depths of at least 500 meters. References {{Scorpaeniformes-stub Sebastes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastini
Sebastini is a Tribe (biology), tribe of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae of the Family (biology), family Scorpaenidae in the Order (biology), order Scorpaeniformes. Taxonomy Sebastini was first formally recognised as a grouping in 1873 by the German naturalist Johann Jakob Kaup. Authorities who treat the clade referred to as Sebastinae as a family treat the Sebastini as a subfamily and call this grouping Sebastinae. Genera Sebastini contains four genera with 120 species, most in ''Sebastes''. * ''Helicolenus'' George Brown Goode, Goode & Tarleton Hoffman Bean, Bean, 1896 * ''Hozukius'' Kiyomatsu Matsubara, Matsubara, 1934 * ''Sebastes'' Georges Cuvier, Cuvier, 1829 * ''Sebastiscus'' David Starr Jordan, Jordan & Edwin Chapin Starks, Starks, 1904 References {{Taxonbar, from= Q109558108 Sebastini, Sebastinae Taxa named by Johann Jakob Kaup Fish tribes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Starr Jordan
David Starr Jordan (January 19, 1851 – September 19, 1931) was the founding president of Stanford University, serving from 1891 to 1913. He was an ichthyologist during his research career. Prior to serving as president of Stanford University, he served as president of Indiana University Bloomington, Indiana University from 1885 to 1891. Jordan was also a strong supporter of eugenics, and his published views expressed a fear of "race-degeneration", asserting that cattle and human beings are "governed by the same laws of selection". He was an antimilitarist since he believed that war killed off the best members of the gene pool, and he initially opposed American involvement in World War I. Early life and education Jordan was born in Gainesville (town), New York, Gainesville, New York, and grew up on a farm in upstate New York. His parents made an unorthodox decision to educate him at a local girls' high school. His middle name, Starr, does not appear in early census records, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpaenidae
The Scorpaenidae (also known as scorpionfish) are a family (biology), family of mostly ocean, marine fish that includes many of the world's most venomous species. As their name suggests, scorpionfish have a type of "sting" in the form of sharp spines coated with venomous mucus. The family is a large one, with hundreds of members. They are widespread in tropical and temperate seas but mostly found in the Indo-Pacific. They should not be confused with the cabezones, of the genus ''Scorpaenichthys'', which belong to a separate, though related, family, Cottidae. Taxonomy Scorpaenidae was described as a family in 1826 by the French naturalist Antoine Risso. The family is included in the suborder Scorpaenoidei of the order Scorpaeniformes in the 5th Edition of ''Fishes of the World'' but other authorities place it in the Perciformes either in the suborder Scorpaenoidei or the superfamily Scorpaenoidea. The subfamilies of this family are treated as valid families by some authorities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyologist
Ichthyology is the branch of zoology devoted to the study of fish, including bony fish (Osteichthyes), cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes), and jawless fish (Agnatha). According to FishBase, 35,800 species of fish had been described as of March 2025, with approximately 250 new species described each year. Etymology The word is derived from the Ancient Greek words wikt:ἰχθύς, ἰχθύς, ''ikhthus'', meaning "fish"; and wikt:-λόγος, λόγος, ''logos'', meaning "study". History The study of fish dates from the Upper Paleolithic, Upper Paleolithic Revolution (with the advent of "high culture"). The science of ichthyology was developed in several interconnecting epochs, each with various significant advancements. The study of fish receives its origins from humans' desire to feed, clothe, and equip themselves with useful implements. According to Michael Barton (professor), Michael Barton, a prominent ichthyologist and professor at Centre College, "the earliest ichthy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoologist
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the structure, embryology, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct, and how they interact with their ecosystems. Zoology is one of the primary branches of biology. The term is derived from Ancient Greek , ('animal'), and , ('knowledge', 'study'). Although humans have always been interested in the natural history of the animals they saw around them, and used this knowledge to domesticate certain species, the formal study of zoology can be said to have originated with Aristotle. He viewed animals as living organisms, studied their structure and development, and considered their adaptations to their surroundings and the function of their parts. Modern zoology has its origins during the Renaissance and early modern period, with Carl Linnaeus, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Charles Darwin, Gregor Mendel and many others. The study of animals has largely mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
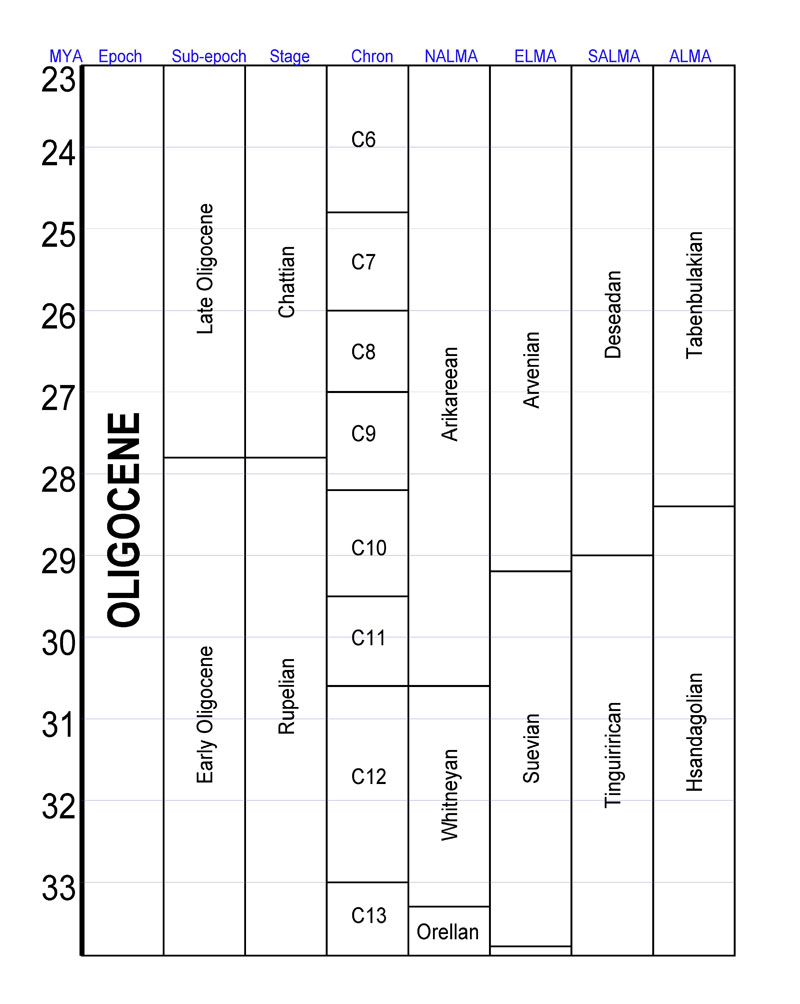
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieter Bleeker
Pieter Bleeker (10 July 1819 – 24 January 1878) was a Dutch medical doctor, Ichthyology, ichthyologist, and Herpetology, herpetologist. He was famous for the ''Atlas Ichthyologique des Indes Orientales Néêrlandaises'', his monumental work on the fishes of East Asia published between 1862 and 1877. Life and work Bleeker was born on 10 July 1819 in Zaandam. He was employed as a medical officer in the Royal Netherlands East Indies Army from 1842 to 1860, (in French). stationed in the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia). During that time, he did most of his ichthyology work, besides his duties in the army. He acquired many of his specimens from local fishermen, but he also built up an extended network of contacts who would send him specimens from various government outposts throughout the islands. During his time in Indonesia, he collected well over 12,000 specimens, many of which currently reside at the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden. Bleeker corresponded with Auguste Dum� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |