|
Scytho-Siberian
The Scytho-Siberian world was an archaeological horizon which flourished across the entire Eurasian Steppe during the Iron Age from approximately the 9th century BC to the 2nd century AD. It included the Scythian, Sauromatian and Sarmatian cultures of Eastern Europe, the Saka- Massagetae and Tasmola cultures of Central Asia, and the Aldy-Bel, Pazyryk and Tagar cultures of south Siberia. The Scythian-Siberian world was characterized by the Scythian triad, which are similar, yet not identical, styles of weapons, horses' bridles, and jewelry and decorative art. The question of how related these cultures were is disputed among scholars. Its peoples were of diverse origins, and included not just Scythians, from which the cultures are named, but other peoples as well, such as the Cimmerians, Massagetae, Saka, Sarmatians, and obscure forest steppe populations. Mostly speakers of the Scythian branch of the Iranian languages, all of these peoples are somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern * : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." * : "Near the end of the 19th century V.F. Miller (1886, 1887) theorized that the Scythians and their kindred, the Sauromatians, were Iranian-speaking peoples. This has been a popular point of view and continues to be accepted in linguistics and historical science [...]" * : "From the end of the 7th century B.C. to the 4th century B.C. the Central- Eurasian steppes were inhabited by two large groups of kin Iranian-speaking tribes – the Scythians and Sarmatians [.. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldy-Bel Culture
The Aldy-Bel culture (russian: Алды-бельская культура ''Aldy-Bel'skaya'' kul'tura, the part of Uyuksk culture, russian: Уюкская культура культура ''Uyukskaya'' kul'tura) is an Iron Age culture of Scytho-Siberian horse nomads in the area of Tuva in southern Siberia, dated to the 7th to 3rd centuries BCE. Monuments of the Aldy-Bel culture were identified by A.D. Grach and I.U. Sambu and published in 1971. The culture is named after the site of the Aldy-Bel I kurgan. More than 30 kurgan burial complexes are identified within the Aldy-Bel culture. The culture is a continuation of the nomadic Pazyryk culture in the area of Altai Mountains in South Siberia. The monuments of the Aldy-Bel culture are synchronous and in many respects similar with those of the Mayemir culture in the Altai region and the Tasmola culture of Central Kazakhstan. The geographical spread covers the right bank of the Yenisei south of the Uyuk ridge, the Khemchik River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who historically inhabited the northern and eastern Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin. "Modern scholars have mostly used the name Saka to refer specifically to Iranians of the Eastern Steppe and Tarim Basin" "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." The Sakas were closely related to the European Scythians, and both groups formed part of the wider Scythian cultures and ultimately derived from the earlier Andronovo culture, and the Saka language formed part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pazyryk Culture
The Pazyryk culture (russian: Пазырыкская культура ''Pazyrykskaya'' kul'tura) is a Scythian nomadic Iron Age archaeological culture (6th to 3rd centuries BC) identified by excavated artifacts and mummified humans found in the Siberian permafrost, in the Altay Mountains, Kazakhstan and nearby Mongolia. The mummies are buried in long barrows (or ''kurgans'') similar to the tomb mounds of Scythian culture in Ukraine. The type site are the Pazyryk burials of the Ukok Plateau. Many artifacts and human remains have been found at this location, including the Siberian Ice Princess, indicating a flourishing culture at this location that benefited from the many trade routes and caravans of merchants passing through the area. The Pazyryk are considered to have had a war-like life. The Pazyryk culture was preceded by the " Arzhan culture" (Initial Scythian period, 8th - 7th century BC). Archaeology Other kurgan cemeteries associated with the culture include those of Bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian Culture
The Scythian culture was an Iron Age archaeological culture which flourished on the Pontic-Caspian steppe in Eastern Europe from about 700 BC to 200 AD. It is associated with the Scythians and other peoples inhabiting the region of Scythia, and was part of the wider Scytho-Siberian world. Chronology The Scythian Culture can be divided into three stages: * Early Scythian – from the mid-8th or the late 7th century BC to about 500 BC * Mid-Scythian or Classical Scythian – from about 500 BC to about 200 BC * Late Scythian – from about 200 BC to the mid-3rd century AD, in the Crimea and the Lower Dnipro River, Dnipro, by which time the population was settled. Development Early Scythian The Early Scythian Culture emerged during the 8th century BC. Since the Scythians were nomads who did not create permanent settlements, the Early Scythian culture is known primarily from Scythian funerary sites. The earliest Scythians had belonged to the Srubnaya culture in its Srubnaya-Khvalyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagar Culture
The Tagar culture (russian: Тагарская культура, Tagarskaya kul'tura) was a Bronze Age archeological culture which flourished between the 8th and 2nd centuries BC in South Siberia (Khakassia, Republic of Khakassia, southern part of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Krasnoyarsk Territory, eastern part of Kemerovo Oblast, Kemerovo Province). The culture was named after an island in the Yenisei River opposite Minusinsk. The civilization was one of the largest centres of bronze-smelting in ancient Eurasia. History The Tagar culture was preceded by the Karasuk culture. They are usually considered a mixed population descended from peoples of the Afanasievo culture and Andronovo culture, who were themselves descended of migrants from the Pontic–Caspian steppe. The Tagar were part of the wider Scythian cultures. Along with the people of the Pazyryk culture, the Tagar are often considered to have constituted the core of the Scythian cultures. The Tagar culture was succeeded by the Tashtyk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
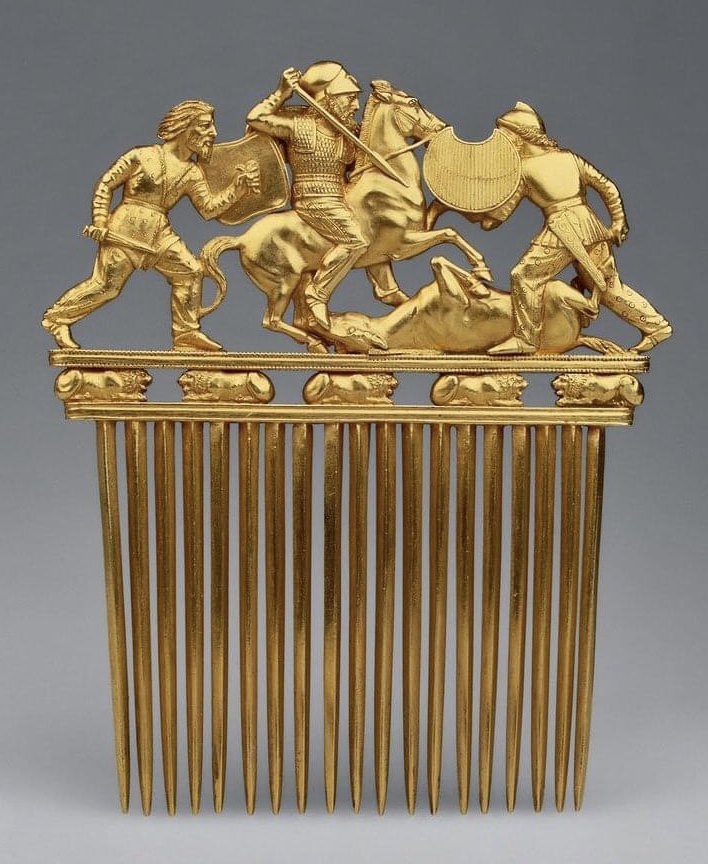
Scythian Art
Scythian art is the art associated with Scythian cultures, primarily decorative objects, such as jewellery, produced by the nomadic tribes of the area known as Scythia, which encompassed Central Asia, parts of Eastern Europe east of the Vistula River, and parts of South Asia, with the eastern edges of the region vaguely defined by ancient Greeks. The identities of the nomadic peoples of the steppes is often uncertain, and the term "Scythian" should often be taken loosely; the art of nomads much further east than the core Scythian territory exhibits close similarities as well as differences, and terms such as the "Scytho-Siberian world" are often used. Other Eurasian nomad peoples recognised by ancient writers, notably Herodotus, include the Massagetae, Sarmatians, and Saka, the last a name from Persian sources, while ancient Chinese sources speak of the Xiongnu or Hsiung-nu. Modern archaeologists recognise, among others, the Pazyryk, Tagar, and Aldy-Bel cultures, with the furt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasmola Culture
The Tasmola culture ( kk, Тасмола мәдениеті) was an early Iron Age culture during the Saka period (7th to 3rd centuries BCE) in central Kazakhstan. Burials Everything known about the Tasmola culture originates from the barrows (or kurgans) they built to bury their deceased. The necropoles involve mainly a large barrow and an adjoining small one. Finds Characteristic finds are bronze arrowheads, daggers and belt ornaments. The bronze and golden wares show influences from the preceding Begazy-Dandybai culture.Megalithic mausolea of the Begazy-Dandybai culture - UNESCO World Heritage Centre Genetics A genetic study published in ''Nature (journal), Nature'' in May 2018 examined the remains of eight Saka ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After their previous rivals, the Yuezhi, migrated west into Central Asia during the 2nd century BC, the Xiongnu became a dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with adjacent Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, as one of the "Five B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Steppe
A forest steppe is a temperate-climate ecotone and habitat type composed of grassland interspersed with areas of woodland or forest. Locations Forest steppe primarily occurs in a belt of forest steppes across northern Eurasia from the eastern lowlands of Europe to eastern Siberia in northeast Asia. It forms transition ecoregions between the temperate grasslands and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biomes. Much of Russia belongs to the forest steppe zone, stretches from Central Russia, across Volga, Ural, Siberian and Far East Russia. In upper North America another example of the forest steppe ecotone is the aspen parkland, in the central Prairie Provinces, northeastern British Columbia, North Dakota, and Minnesota. It is the transition ecoregion from the Great Plains prairie and steppe temperate grasslands to the Taiga biome forests in the north. In central Asia the forest steppe ecotone is found in ecoregions in the mountains of the Iranian Plateau, in Iran, Afghanistan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into West Asia. Although the Cimmerians were culturally Scythian, they formed an ethnic unit separate from the Scythians proper, to whom the Cimmerians were related and who displaced and replaced the Cimmerians.: "As the Cimmerians cannot be differentiated archeologically from the Scythians, it is possible to speculate about their Iranian origins. In the Neo-Babylonian texts (according to D’yakonov, including at least some of the Assyrian texts in Babylonian dialect) and similar forms designate the Scythians and Central Asian Saka, reflecting the perception among inhabitants of Mesopotamia that Cimmerians and Scythians represented a single cultural and economic group" The Cimmerians themselves left no written records, and most information about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian Languages
The Scythian languages ( or or ) are a group of Eastern Iranian languages of the classical antiquity, classical and late antiquity, late antique period (the Middle Iranian languages, Middle Iranian period), spoken in a vast region of Eurasia by the populations belonging to the Scythian cultures and their descendants. The dominant ethnic groups among the Scythian-speakers were nomadic pastoralists of Central Asia and the Pontic–Caspian steppe. Fragments of their speech known from inscriptions and words quoted in ancient authors as well as analysis of their names indicate that it was an Indo-European language, more specifically from the Iranian languages, Iranian group of Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian languages. Most of the Scythian languages eventually became extinct, except for modern Ossetian language, Ossetian (which descends from the Alanian dialect of Scytho-Sarmatian), Wakhi language, Wakhi (which descends from the Kingdom of Khotan, Khotanese and Tumxuk, Tumshuqe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |