|
Scutulum
A scutulum is a yellow, perifollicular, saucerlike or cup-shaped crust with a cheesy odor, composed of dense mats of mycelia and epithelial debris. Scutula often occur on the scalp and are characteristic of favus. Morphology * Consists of a crust-like yellow lesion (sulphur cap) * Has a concave-convex surface with its convexity to the scalp making for itself an erosion Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ... or depression of epidermis, so it is firmly adherent to the scalp * Upon detachment it gives a serosangiunous discharge (serum and blood) * size : from a few millimetres to a few centimetres References Dermatologic terminology {{dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Favus
Favus (Latin for "honeycomb") or tinea favosa is the severe form of tinea capitis, a skin infectious disease caused by the dermatophyte fungus ''Trichophyton schoenleinii.'' Typically the species affects the scalp, but occasionally occurs as onychomycosis, tinea barbae, or tinea corporis. The word ''favid'' is more used than French word ''favus'', which is close to the Latin etymology. Presentation The uncomplicated appearance is that of a number of yellowish, circular, cup-shaped crusts (scutulum or shield) grouped in patches like a honeycomb, each crust about the size of a split pea, with a bundle of hair projecting in the center. These increase in size and become crusted over, so that the characteristic lesion can only be seen round the edge of the scab. A mousy odour is often present. Growth continues to take place for several months, when scab and scutulum go away, leaving a shining bare patch destitute of hair. The disease is essentially chronic, lasting from ten to twenty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crust (dermatology)
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. Conditions of the human integumentary system constitute a broad spectrum of diseases, also known as dermatoses, as well as many nonpathologic states (like, in certain circumstances, melanonychia and racquet nails). While only a small number of skin diseases account for most visits to the physician, thousands of skin conditions have been described. Classification of these conditions often presents many nosological challenges, since underlying causes and pathogenetics are often not known. Therefore, most current textbooks present a classification based on location (for example, conditions of the mucous membrane), morphology ( chronic blistering conditions), cause (skin conditions result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
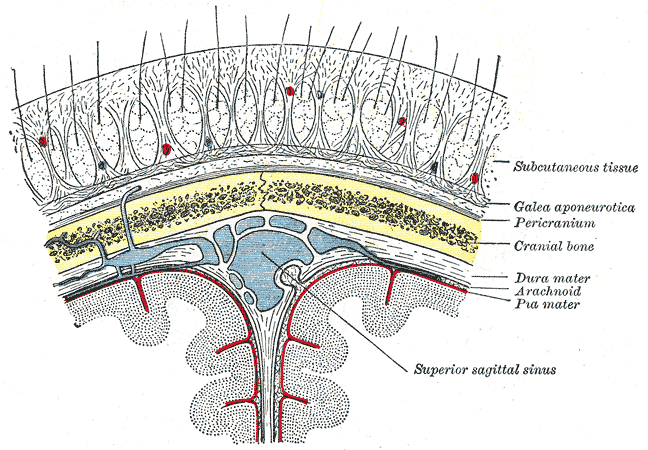
Scalp
The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the human face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. Structure The scalp is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic: * S: The skin on the head from which head hair grows. It contains numerous sebaceous glands and hair follicles. * C: Connective tissue. A dense subcutaneous layer of fat and fibrous tissue that lies beneath the skin, containing the nerves and vessels of the scalp. * A: The aponeurosis called epicranial aponeurosis (or galea aponeurotica) is the next layer. It is a tough layer of dense fibrous tissue which runs from the frontalis muscle anteriorly to the occipitalis posteriorly. * L: The loose areolar connective tissue layer provides an easy plane of separation between the upper three layers and the pericranium. In scalping the scalp is torn off through this layer. It also provides a plane of access in craniofacial surgery and neurosurgery. This layer i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as ''physical'' or ''mechanical'' erosion; this contrasts with ''chemical'' erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres. Agents of erosion include rainfall; bedrock wear in rivers; coastal erosion by the sea and waves; glacial plucking, abrasion, and scour; areal flooding; wind abrasion; groundwater processes; and mass movement processes in steep landscapes like landslides and debris flows. The rates at which such processes act control how fast a surface is eroded. Typically, physical erosion procee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis (skin)
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |