|
Scrollerwheel
A scrollerwheel is a mechanical device composed of a number of rollers (four or more) and connective bands under tension, which wrap around and weave between the rollers forming a self-supporting cluster possessing a central roller. The cluster of rollers is bound by the connective bands in such a way that the static friction between the rollers and bands prevent the rollers from slipping as they roll and orbit the central roller. 'Business Week'' August 14, 1995 Scrollerwheels are related in operational principle to linear bearings (developed at [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolamite
Rolamite is a technology for very low friction bearings developed by Sandia National Laboratories in the 1960s. It is the only elementary machine discovered in the twentieth century and can be used in various ways such as a component in switches, thermostats, valves, pumps, and clutches, among others. Development The Rolamite was invented by Sandia engineer Donald F. Wilkes and was patented on June 24, 1969. It was invented while Wilkes was working on a miniature device to detect small changes in the inertia of a small mass. After testing an S-shaped metal foil, which he found to be unstable to support surfaces, the engineer inserted rollers into the S-shaped bends of the band, producing a mechanical assembly that has very low friction in one direction and high stiffness transversely. It became known as Rolamite. The Rolamite uses a stressed metal band and counter-rotating rollers within an enclosure to create a linear bearing device that loses very little energy to friction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolamite
Rolamite is a technology for very low friction bearings developed by Sandia National Laboratories in the 1960s. It is the only elementary machine discovered in the twentieth century and can be used in various ways such as a component in switches, thermostats, valves, pumps, and clutches, among others. Development The Rolamite was invented by Sandia engineer Donald F. Wilkes and was patented on June 24, 1969. It was invented while Wilkes was working on a miniature device to detect small changes in the inertia of a small mass. After testing an S-shaped metal foil, which he found to be unstable to support surfaces, the engineer inserted rollers into the S-shaped bends of the band, producing a mechanical assembly that has very low friction in one direction and high stiffness transversely. It became known as Rolamite. The Rolamite uses a stressed metal band and counter-rotating rollers within an enclosure to create a linear bearing device that loses very little energy to friction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubrication
Lubrication is the process or technique of using a lubricant to reduce friction and wear and tear in a contact between two surfaces. The study of lubrication is a discipline in the field of tribology. Lubrication mechanisms such as fluid-lubricated systems are designed so that the applied load is partially or completely carried by hydrodynamic or hydrostatic pressure, which reduces solid body interactions (and consequently friction and wear). Depending on the degree of surface separation, different lubrication regimes can be distinguished. Adequate lubrication allows smooth, continuous operation of machine elements, reduces the rate of wear, and prevents excessive stresses or seizures at bearings. When lubrication breaks down, components can rub destructively against each other, causing heat, local welding, destructive damage and failure. Lubrication mechanisms Fluid-lubricated systems As the load increases on the contacting surfaces, distinct situations can be observed wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
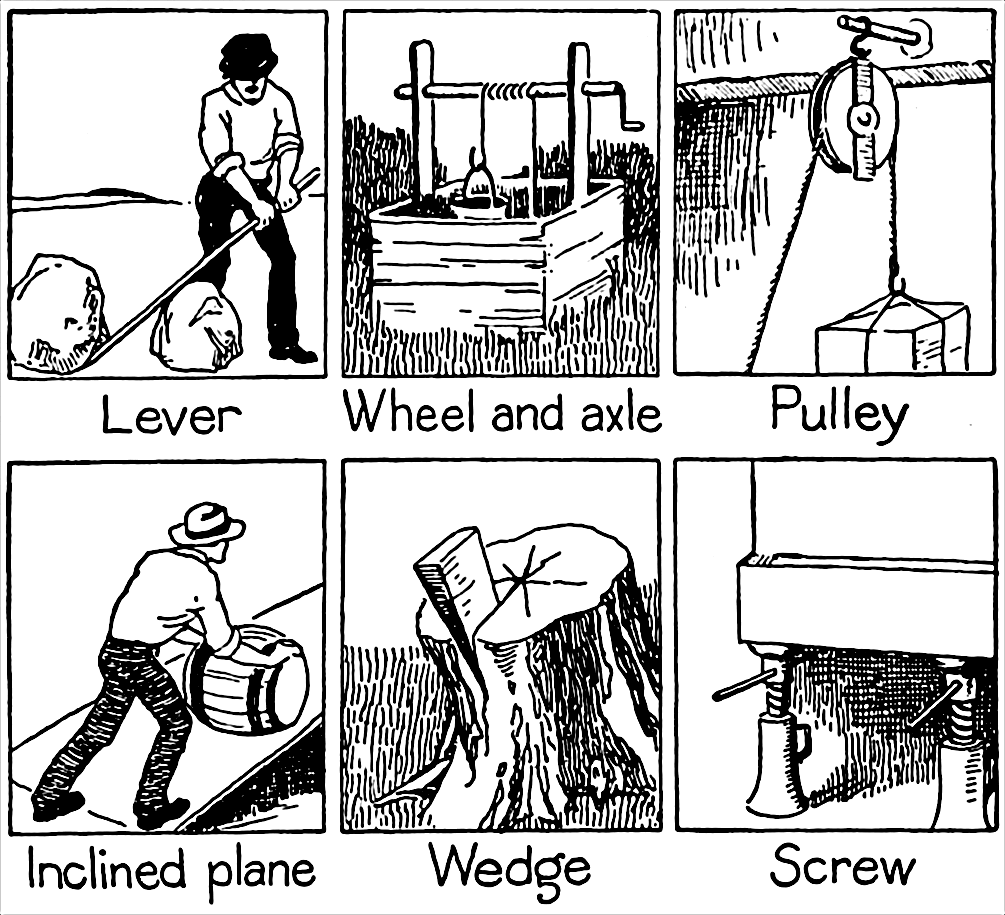
Simple Machines
A simple machine is a mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. In general, they can be defined as the simplest mechanisms that use mechanical advantage (also called leverage) to multiply force. Usually the term refers to the six classical simple machines that were defined by Renaissance scientists: * Lever * Wheel and axle * Pulley * Inclined plane * Wedge * Screw A simple machine uses a single applied force to do work against a single load force. Ignoring friction losses, the work done on the load is equal to the work done by the applied force. The machine can increase the amount of the output force, at the cost of a proportional decrease in the distance moved by the load. The ratio of the output to the applied force is called the ''mechanical advantage''. Simple machines can be regarded as the elementary "building blocks" of which all more complicated machines (sometimes called "compound machines") are composed. For example, wheels, levers, and pul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backlash (engineering)
In mechanical engineering, backlash, sometimes called lash, play, or slop, is a clearance or lost motion in a mechanism caused by gaps between the parts. It can be defined as "the maximum distance or angle through which any part of a mechanical system may be moved in one direction without applying appreciable force or motion to the next part in mechanical sequence."p. 1-8 An example, in the context of gears and gear trains, is the amount of clearance between mated gear teeth. It can be seen when the direction of movement is reversed and the slack or lost motion is taken up before the reversal of motion is complete. It can be heard from the railway couplings when a train reverses direction. Another example is in a valve train with mechanical tappets, where a certain range of lash is necessary for the valves to work properly. Depending on the application, backlash may or may not be desirable. Some amount of backlash is unavoidable in nearly all reversing mechanical couplings, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressure by around 20%. But hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity. In addition to industrial applications, lubricants are used for many other purposes. Other uses include cooking (oils and fats in use in frying pans, in baking to prevent food sticking), bioapplications on humans (e.g. lubricants for artificial joints), ultrasound examination, medical examination, and sexual intercourse. It is mainly used to reduce friction and to contribute to a better and efficient functioning of a mechanism. History Lubricants have been in some use for thousands of years. Calcium soaps have been identified on the axles of chariots dated to 1400 BC. Building stones were slid on oil-impregrated lumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling-element Bearing
In mechanical engineering, a rolling-element bearing, also known as a rolling bearing, is a bearing which carries a load by placing rolling elements (such as balls or rollers) between two concentric, grooved rings called races. The relative motion of the races causes the rolling elements to roll with very little rolling resistance and with little sliding. One of the earliest and best-known rolling-element bearings are sets of logs laid on the ground with a large stone block on top. As the stone is pulled, the logs roll along the ground with little sliding friction. As each log comes out the back, it is moved to the front where the block then rolls on to it. It is possible to imitate such a bearing by placing several pens or pencils on a table and placing an item on top of them. See " bearings" for more on the historical development of bearings. A rolling element rotary bearing uses a shaft in a much larger hole, and cylinders called "rollers" tightly fill the space between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tension (physics)
In physics, tension is described as the pulling force transmitted axially by the means of a string, a rope, chain, or similar object, or by each end of a rod, truss member, or similar three-dimensional object; tension might also be described as the action-reaction pair of forces acting at each end of said elements. Tension could be the opposite of compression (physics), compression. At the atomic level, when atoms or molecules are pulled apart from each other and gain potential energy with a restoring force still existing, the restoring force might create what is also called tension. Each end of a string or rod under such tension could pull on the object it is attached to, in order to restore the string/rod to its relaxed length. Tension (as a transmitted force, as an action-reaction pair of forces, or as a restoring force) is measured in newton (unit), newtons in the International System of Units (or pounds-force in Imperial units). The ends of a string or other object transmitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuleaux Polygon
In geometry, a Reuleaux polygon is a curve of constant width made up of circular arcs of constant radius. These shapes are named after their prototypical example, the Reuleaux triangle, which in turn, is named after 19th-century German engineer Franz Reuleaux. The Reuleaux triangle can be constructed from an equilateral triangle by connecting each two vertices by a circular arc centered on the third vertex, and Reuleaux polygons can be formed by a similar construction from any regular polygon with an odd number of sides, or from certain irregular polygons. Every curve of constant width can be accurately approximated by Reuleaux polygons. They have been applied in coinage shapes. Construction If P is a convex polygon with an odd number of sides, in which each vertex is equidistant to the two opposite vertices and closer to all other vertices, then replacing each side of P by an arc centered at its opposite vertex produces a Reuleaux polygon. As a special case, this construction i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |