|
Scottish Consolidated Fund
The Scottish Consolidated Fund is the main fund operated by the Scottish Parliament. It receives a block grant from the UK Parliament's Consolidated Fund plus the operational receipts of the Scottish Government. The fund operates under the Scotland Act 1998. In 2010–2011, under the Barnett formula, the UK Exchequer returned a block grant of £26.8 billion of Scottish taxpayers' money to the fund. See also *Barnett Formula *Calman Commission *Government Expenditure and Revenue Scotland *Union dividend References External links The receipts and payments account for the Scottish Consolidated fund for the period 1 April 2003 to 31 March 2004 by |
Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyrood. The Parliament is a democratically elected body comprising 129 members known as Members of the Scottish Parliament (MSPs), elected for five-year terms under the additional member system: 73 MSPs represent individual geographical constituencies elected by the plurality (first-past-the-post) system, while a further 56 are returned as list members from eight additional member regions. Each region elects seven party-list MSPs. Each region elects 15 to 17 MSPs in total. The most recent general election to the Parliament was held on 6 May 2021, with the Scottish National Party winning a plurality. The original Parliament of Scotland was the national legislature of the independent Kingdom of Scotland and existed from the early 13th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
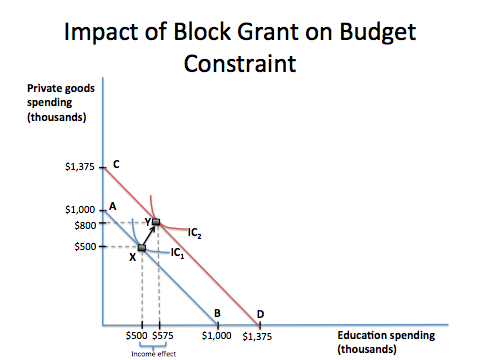
Block Grant
A block grant is a grant-in-aid of a specified amount from a larger government to a smaller regional government body. Block grants have less oversight from the larger government and provide flexibility to each subsidiary government body in terms of designing and implementing programs. Block grants, categorical grants, and general revenue sharing are three types of federal government grants-in-aid programs.A block grant differs from a categorical grant, in that the latter has stricter and more specific provisions on the how it is to be spent. Graphical representation The figure demonstrates the impact of an education block grant on a town's budget constraint. According to microeconomic theory, the grant shifts the town's budget constraint outwards, enabling the town to spend more on both education and other goods, due to the income effect. While this increases the town's utility, it does not maximize the town's spending on education. Therefore, if the goal of a grant progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy and thereby ultimate power over all other political bodies in the UK and the overseas territories. Parliament is bicameral but has three parts, consisting of the sovereign ( King-in-Parliament), the House of Lords, and the House of Commons (the primary chamber). In theory, power is officially vested in the King-in-Parliament. However, the Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation; thus power is ''de facto'' vested in the House of Commons. The House of Commons is an elected chamber with elections to 650 single-member constituencies held at least every five years under the first-past-the-post system. By constitutional convention, all governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated Fund
In many states with political systems derived from the Westminster system, a consolidated fund or consolidated revenue fund is the main bank account of the government. General taxation is taxation paid into the consolidated fund (as opposed to hypothecated taxes earmarked for specific purposes), and general spending is paid out of the consolidated fund. The British Consolidated Fund Establishment The British Consolidated Fund was so named as it consolidated together a number of existing accounts, detailed below, and facilitated proper parliamentary oversight of the spending of the executive; it was defined as "one fund into which shall flow every stream of public revenue and from which shall come the supply of every service". The Treasury established this account, formerly known as The Account of His Majesty's Exchequer, at the Bank of England where it remains to this day, and the legal term "Consolidated Fund" refers to the amount of credit held in this particular account ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland Act 1998
The Scotland Act 1998 (c. 46) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which legislated for the establishment of the devolved Scottish Parliament with tax varying powers and the Scottish Government (then Scottish Executive). It was one of the most significant constitutional pieces of legislation to be passed by the UK Parliament between the passing of the European Communities Act in 1972 and the European Union (Withdrawal) Act in 2018 and is the most significant piece of legislation to affect Scotland since the Acts of Union in 1707 which ratified the Treaty of Union and led to the disbandment of the Parliament of Scotland. Content and history The Act was introduced by the Labour government in 1998 to give effect to the Scottish devolution referendum in 1997 which showed that Scotland was in favour of both of the set questions, firstly for the creation of a parliament for Scotland and secondly, that this parliament should have tax varying powers. The Act creates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnett Formula
The Barnett formula is a mechanism used by the Treasury in the United Kingdom to automatically adjust the amounts of public expenditure allocated to Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales to reflect changes in spending levels allocated to public services in England, Scotland and Wales, as appropriate. The formula applies to a large proportion, but not the whole, of the devolved governments' budgets − in 2013–14 it applied to about 85% of the Scottish Parliament's total budget.Barnett Formula definition in Scottish Draft Budget 2013–14 ''www.scotland.gov.uk'' The formula is named after Joel Barnett, who devised it in 1978 while |
Barnett Formula
The Barnett formula is a mechanism used by the Treasury in the United Kingdom to automatically adjust the amounts of public expenditure allocated to Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales to reflect changes in spending levels allocated to public services in England, Scotland and Wales, as appropriate. The formula applies to a large proportion, but not the whole, of the devolved governments' budgets − in 2013–14 it applied to about 85% of the Scottish Parliament's total budget.Barnett Formula definition in Scottish Draft Budget 2013–14 ''www.scotland.gov.uk'' The formula is named after Joel Barnett, who devised it in 1978 while |
Calman Commission
The Commission on Scottish Devolution ( gd, Coimisean Fèin-riaghlaidh na h-Alba, sco, Commeessioun on Scots Devolutioun), also referred to as the Calman Commission or the Scottish Parliament Commission or Review, was established by an opposition Labour Party motion passed by the Scottish Parliament on 6 December 2007, with the support of the Conservatives and Liberal Democrats. The governing Scottish National Party opposed the creation of the commission. Its terms of reference were: "To review the provisions of the Scotland Act 1998 in the light of experience and to recommend any changes to the present constitutional arrangements that would enable the Scottish Parliament to serve the people of Scotland better, improve the financial accountability of the Scottish Parliament and continue to secure the position of Scotland within the United Kingdom." The Commission held its first full meeting at the Scottish Parliament on 28 April 2008 and met at roughly monthly intervals durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Expenditure And Revenue Scotland
Government Expenditure and Revenue Scotland (GERS) is an annual estimate of the level of public revenue raised in Scotland and the level of public spending for the residents of Scotland under current constitutional arrangements. It was first published in 1992, and yearly since 1995, with the exceptions of 2007 where there was no report due to a methodology review, and 2016 where there were two annual reports due to an acceleration of publishing timescale. Since devolution, it has been compiled by economists and statisticians in the Office of the Chief Economic Adviser of the Scottish Government. The report is based partly on actual spend and income. Where actual data is not readily available, estimates for Scotland are made by the compilers e.g. Whitehall reserves 74% of Scotland's revenue and 37% of its spending; the data for the estimates are from a variety of sources including pan UK data provided by the UK Government's Office for National Statistics (ONS). ONS in England and Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Dividend
The Union dividend is a term used by British unionists to describe the financial benefits which they believe that Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland derive from being parts of the United Kingdom. Politicians who argue for the existence of a Union dividend include Tony Blair, Gordon Brown, Jim Murphy, Ian Davidson, Jack McConnell, Wendy Alexander, Iain Gray and Jackie Baillie. The idea saw increased discussion in the leadup to the 2014 Scottish independence referendum. In May 2014, the UK Government said in an analysis paper that there was a "UK dividend" worth £1,400 to each person in Scotland. This estimate was mainly based upon there being higher public spending in Scotland. The Scottish Government said that Scots would be £1,000 better off by 2030 if Scotland became an independent state, due to greater productivity and higher tax revenues. The difference between the two figures was mainly due to differing forecasts of revenue from North Sea oil. See also *Barnett formu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audit Scotland
Audit Scotland is an independent Scottish public bodies, public body responsible for auditing most of Scotland's public organisations. These include the Scottish Government, Local government of Scotland, local councils and NHS Scotland. Auditing role It audits over 220 organisations, including: * 77 central government bodies (Scottish Government, NDPB's, Police Scotland, Scottish Fire and Rescue Service, Scottish Water and others) * 23 NHS bodies * 32 local councils * 20 List of further education colleges in Scotland, further education colleges History Audit Scotland was established in 2000. It employees a staff of around 250 people. Its corporate HQ is on West Port, Edinburgh, West Port, in Edinburgh's Old Town. The role of Audit Scotland is to provide the Auditor General for Scotland and the Accounts Commission for Scotland with the services they need to carry out their duties. The core work is to carry out: *financial audits to help ensure that public sector bodies adhere t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |