|
Scoping
In computer programming, the scope of a name binding (an association of a name to an entity, such as a variable) is the part of a program where the name binding is valid; that is, where the name can be used to refer to the entity. In other parts of the program, the name may refer to a different entity (it may have a different binding), or to nothing at all (it may be unbound). Scope helps prevent name collisions by allowing the same name to refer to different objects – as long as the names have separate scopes. The scope of a name binding is also known as the visibility of an entity, particularly in older or more technical literature—this is in relation to the referenced entity, not the referencing name. The term "scope" is also used to refer to the set of ''all'' name bindings that are valid within a part of a program or at a given point in a program, which is more correctly referred to as ''context'' or ''environment''. Strictly speaking and in practice for most programmin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable (programming)
In computer programming, a variable is an abstract storage location paired with an associated symbol, symbolic name, which contains some known or unknown quantity of Data (computer science), data or Object (computer science), object referred to as a ''value (computer science), value''; or in simpler terms, a variable is a named container for a particular set of bits or Data type, type of data (like Integer (computer science), integer, Floating-point arithmetic, float, String (computer science), string, etc...). A variable can eventually be associated with or identified by a memory address. The variable name is the usual way to Reference (computer science), reference the stored value, in addition to referring to the variable itself, depending on the context. This separation of name and content allows the name to be used independently of the exact information it represents. The identifier in computer source code can be Name binding, bound to a Value (computer science), value during R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
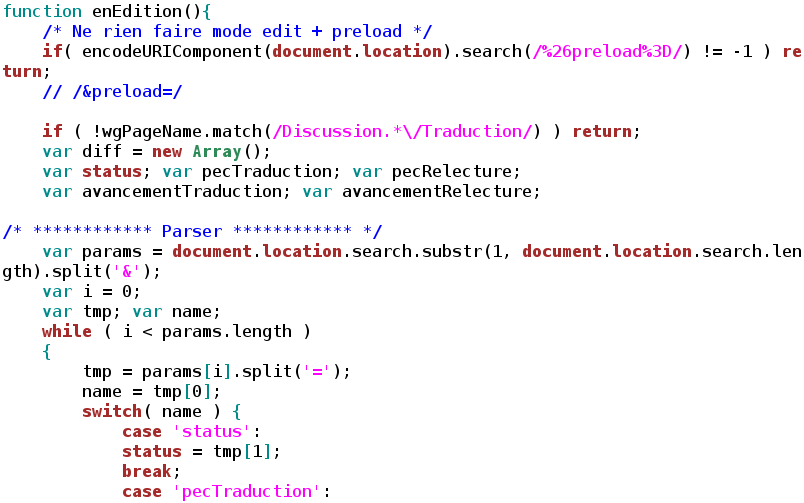
Variable Hoisting
The syntax of JavaScript is the set of rules that define a correctly structured JavaScript program. The examples below make use of the log function of the console object present in most browsers for standard text output. The JavaScript standard library lacks an official standard text output function (with the exception of document.write). Given that JavaScript is mainly used for client-side scripting within modern web browsers, and that almost all Web browsers provide the alert function, alert can also be used, but is not commonly used. Origins Brendan Eich summarized the ancestry of the syntax in the first paragraph of the JavaScript 1.1 specification as follows: Basics Case sensitivity JavaScript is case sensitive. It is common to start the name of a constructor with a capitalized letter, and the name of a function or variable with a lower-case letter. Example: var a = 5; console.log(a); // 5 console.log(A); // throws a ReferenceError: A is not defined Whitespac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Name Binding
In programming languages, name binding is the association of entities (data and/or code) with identifiers. An identifier bound to an object is said to reference that object. Machine languages have no built-in notion of identifiers, but name-object bindings as a service and notation for the programmer is implemented by programming languages. Binding is intimately connected with scoping, as scope determines which names bind to which objects – at which locations in the program code ( lexically) and in which one of the possible execution paths ( temporally). Use of an identifier in a context that establishes a binding for is called a binding (or defining) occurrence. In all other occurrences (e.g., in expressions, assignments, and subprogram calls), an identifier stands for what it is bound to; such occurrences are called applied occurrences. Binding time * ''Static binding'' (or ''early binding'') is name binding performed before the program is run. * ''Dynamic binding'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Name Masking
In programming languages, name resolution is the resolution of the tokens within program expressions to the intended program components. Overview Expressions in computer programs reference variables, data types, functions, classes, objects, libraries, packages and other entities by name. In that context, name resolution refers to the association of those not-necessarily-unique names with the intended program entities. The algorithms that determine what those identifiers refer to in specific contexts are part of the language definition. The complexity of these algorithms is influenced by the sophistication of the language. For example, name resolution in assembly language usually involves only a single simple table lookup, while name resolution in C++ is extremely complicated as it involves: * namespaces, which make it possible for an identifier to have different meanings depending on its associated namespace; * scopes, which make it possible for an identifier to have different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closure (computer Science)
In programming languages, a closure, also lexical closure or function closure, is a technique for implementing lexically scoped name binding in a language with first-class functions. Operationally, a closure is a record storing a function together with an environment. The environment is a mapping associating each free variable of the function (variables that are used locally, but defined in an enclosing scope) with the value or reference to which the name was bound when the closure was created. Unlike a plain function, a closure allows the function to access those ''captured variables'' through the closure's copies of their values or references, even when the function is invoked outside their scope. History and etymology The concept of closures was developed in the 1960s for the mechanical evaluation of expressions in the λ-calculus and was first fully implemented in 1970 as a language feature in the PAL programming language to support lexically scoped first-class func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closure (computer Programming)
In programming languages, a closure, also lexical closure or function closure, is a technique for implementing lexically scoped name binding in a language with first-class functions. Operationally, a closure is a record storing a function together with an environment. The environment is a mapping associating each free variable of the function (variables that are used locally, but defined in an enclosing scope) with the value or reference to which the name was bound when the closure was created. Unlike a plain function, a closure allows the function to access those ''captured variables'' through the closure's copies of their values or references, even when the function is invoked outside their scope. History and etymology The concept of closures was developed in the 1960s for the mechanical evaluation of expressions in the λ-calculus and was first fully implemented in 1970 as a language feature in the PAL programming language to support lexically scoped first-class functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compile Time
In computer science, compile time (or compile-time) describes the time window during which a language's statements are converted into binary instructions for the processor to execute. The term is used as an adjective to describe concepts related to the context of program compilation, as opposed to concepts related to the context of program execution ( run time). For example, ''compile-time requirements'' are programming language requirements that must be met by source code before compilation and ''compile-time properties'' are properties of the program that can be reasoned about during compilation. The actual length of time it takes to compile a program is usually referred to as ''compilation time''. Overview Most compilers have at least the following compiler phases (which therefore occur at compile-time): syntax analysis, semantic analysis, and code generation. During optimization phases, constant expressions in the source code can also be evaluated at compile-time usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinja (template Engine)
Jinja is a web template engine for the Python programming language. It was created by Armin Ronacher and is licensed under a BSD License. Jinja is similar to the Django template engine, but provides Python-like expressions while ensuring that the templates are evaluated in a sandbox. It is a text-based template language and thus can be used to generate any markup as well as source code. The Jinja template engine allows customization of tags, filters (for formatting or transforming values), tests (for evaluating conditions), and globals. Also, unlike the Django template engine, Jinja allows the template designer to call functions with arguments on objects. Jinja is Flask's default template engine and it is also used by Ansible, Trac, and Salt. It is also used to make SQL macros, for example for use with dbt. Features Some of the features of Jinja are: * sandboxed execution * automatic HTML escaping to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks * template inherita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Template Language
A template processor (also known as a template engine or template parser) is software designed to combine ''template''s with data (defined by a data model) to produce resulting Electronic document, documents or Computer program, programs. The language that the templates are written in is known as a template language or templating language. For purposes of this article, a result document is any kind of formatted output, including documents, web pages, or source code (in source code generation), either in whole or in fragments. A template engine is ordinarily included as a part of a web template system or application framework, and may be used also as a preprocessor or Filter (software), filter. Typical features Template engines typically include features common to most High-level programming language, high-level programming languages, with an emphasis on features for processing plain text. Such features include: *variable (programming), variables and Function (computer science) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Program State
In information technology and computer science, a system is described as stateful if it is designed to remember preceding events or user interactions; the remembered information is called the state of the system. The set of states a system can occupy is known as its state space. In a discrete system, the state space is countable and often finite. The system's internal behaviour or interaction with its environment consists of separately occurring individual actions or events, such as accepting input or producing output, that may or may not cause the system to change its state. Examples of such systems are digital logic circuits and components, automata and formal language, computer programs, and computers. The output of a digital circuit or deterministic computer program at any time is completely determined by its current inputs and its state. Digital logic circuit state Digital logic circuits can be divided into two types: combinational logic, whose output signals are depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declaration (computer Programming)
In computer programming, a declaration is a language construct specifying identifier properties: it declares a word's (identifier's) meaning."A declaration specifies the interpretation and attributes of a set of identifiers. A ''definition'' of an identifier is a declaration for that identifier that: * for an object ariable or constant causes storage to be reserved for that object; * for a function, includes the function body; * for an enumeration constant, is the (only) declaration of the identifier; * for a typedef name, is the first (or only) declaration of the identifier." C11 specification, 6.7: Declarations, paragraph 5. Declarations are most commonly used for functions, variables, constants, and classes, but can also be used for other entities such as enumerations and type definitions. Beyond the name (the identifier itself) and the kind of entity (function, variable, etc.), declarations typically specify the data type (for variables and constants), or the type signat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |