|
Sciritae
The Sciritae or Skiritai or Skioreitai or Skioritai (Greek: ) were a people subject to Sparta, whose status is comparable to that of the Perioeci. Deriving their name from the town of Skiritis, a mountainous region located in northern Laconia on the border with Arcadia, between the Oenus and the Eurotas rivers. According to Stephanus of Byzantium and Hesychius of Alexandria, the Sciritae were of Arcadian origin. Their way of life was essentially rural: they mostly lived in villages, of which the biggest were Oion and Caryai. Their territory was inhospitable, but was of strategic importance for Sparta since it controlled the road to Tegea, which explains why it rapidly fell in Spartan hands. Their status was similar to that of the Perioeci, but Xenophon distinguished between them writing: "To meet the case of a hostile approach at night, he assigned the duty of acting as sentries outside the lines to the Sciritae. In these days the duty is shared by foreigners, if any happen to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekdromoi
The ekdromoi were an ancient Greek light hoplites. The name means 'out-runners', and denotes their ability to exit the phalanx and fight in an irregular order, as the situation might demand. The ekdromoi were mostly lightly armoured (with aspis and bronze helmet) fast infantry and were armed with spear and short sword. The term would actually describe any hoplite who practiced the tactic of ''ekdrome'', that is the irregular exit from the battle line. Within the phalanx, they functioned as ordinary hoplites, but when ordered, they would leave the ranks and attack the enemy in loose order. Tactical necessities that would ordain such a use would include the constant harassment from enemy skirmishers, clearing a path from enemy presence (so that the army could pass in safety), the fast capture of key points within or around the battlefield, the pursuit of a broken enemy, etc. Their lightness did not guarantee contact with a skirmishing enemy, but they would effectively push the enemy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
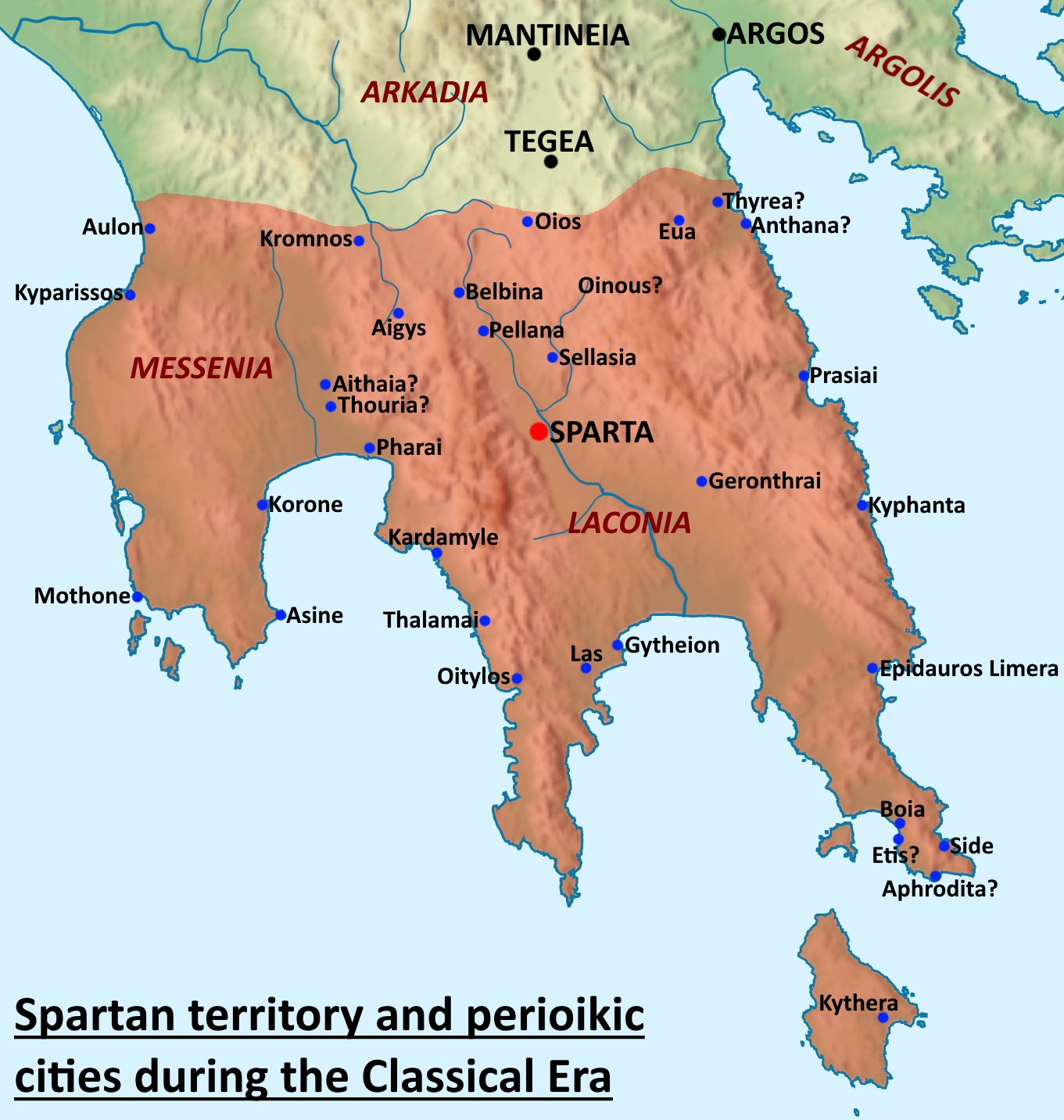
Perioeci
The Perioeci or Perioikoi (, ) were the second-tier citizens of the ''polis'' of Sparta until 200 BC. They lived in several dozen cities within Spartan territories (mostly Laconia and Messenia), which were dependent on Sparta. The ''perioeci'' only had political rights in their own city, while the course of the Spartan state exclusively belonged to Spartan citizens, or Spartiates. The name ''perioeci'' roughly means "those dwelling around/nearby", deriving from , ''peri'', "around", and , ''oîkos'', "dwelling, house". ''Perioeci'' and Spartans were collectively called the '' Lakedaimonians''. They had a central role in the Spartan economy, controlling commerce and business, as well as being responsible for crafts and manufacturing, including producing the weapons and armour of the Spartan army, as the higher-ranking Spartan citizens considered all commercial and money-making activities to be unworthy of them. The ''perioeci'' were also the only people allowed to freely trav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skiritis
Sciritis or Skiritis ( grc, ἡ Σκιρῖτις) was a rugged and barren mountainous district in the north of ancient Laconia, between the upper Eurotas on the west and the Oenus on the east, and extending north of the highest ridge of the mountains, which were the natural boundary between Laconia and Arcadia. The name probably expressed the wild and rugged nature of the country, for the word signified hard and rugged (σκίρον, σκεῖρον, σκληρόν, Hesych). It was bounded by Maenalia on the north, and by Parrhasia on the west, and was originally part of Arcadia, but was conquered at an early period, and its inhabitants reduced to the condition of Lacedaemonian Perioeci. According to Xenophon they were subjected to Sparta even before the time of Lycurgus. They were distinguished above all the other Perioeci for their bravery; and their contingent, called the Σκιρίτης λόχος, 600 in number, usually occupied the extreme left of the Lacedaemonian wing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
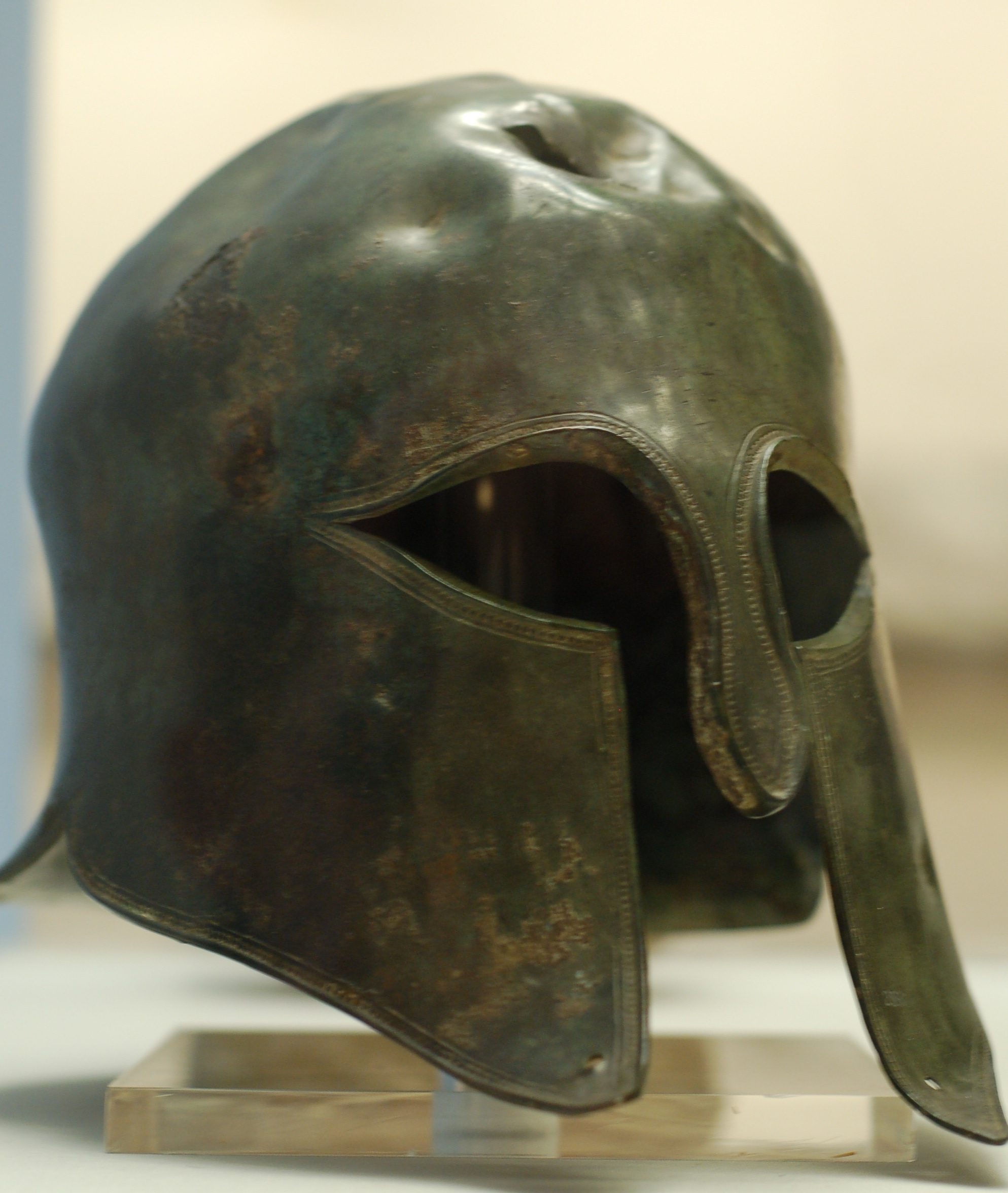
Spartan Army
The Spartan army stood at the center of the Spartan state, citizens trained in the disciplines and honor of a warrior society.Connolly (2006), p. 38 Subjected to military drills since early manhood, the Spartans became one of the most feared and formidable military forces in the Greek world, attaining legendary status in their wars against Persia. At the height of Sparta's power – between the 6th and 4th centuries BC – other Greeks commonly accepted that "one Spartan was worth several men of any other state." Tradition states that the semi-mythical Spartan legislator Lycurgus first founded the iconic army. Referring to Sparta as having a "wall of men, instead of bricks," he proposed reforming the Spartan society to develop a military-focused lifestyle following "proper virtues" such as equality for the male citizens, austerity, strength, and fitness. Spartan boys deemed strong enough entered the '' agoge'' regime at the age of seven, undergoing intense and rigor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neodamodes
The neodamodes ( el, νεοδαμώδεις, ''neodamōdeis'') were helots freed after passing a time of service as hoplites in the Spartan army. The date of their first apparition is uncertain. Thucydides does not explain the origin of this special category. Jean Ducat, in his book ''Les Hoplites'' (1990), concludes that their statute "was largely inspired by the measures dictated concerning the Brasidians", i.e. the helots freed after taking part to the expedition of Brasidas in 424 BC. Their existence is attested from 420 to 369 BC. They were part of Sparta's army and 2,000 of them are recorded taking part, for example, to Agesilaus II's campaign in Ionia between 396 and 394 BC. The name comes from the words νέος ''neos'', meaning "new", and ''dêmos'', meaning "''deme'' or territory". Differently from what is written by Hesychius of Alexandria, who brings together the neodamodes and the Athenian '' demotes'' (citizens of a deme), they never acquired full citizenship. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label= Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyropaedia (Xenophon)
The ''Cyropaedia'', sometimes spelled ''Cyropedia'', is a partly fictional biography of Cyrus the Great, the founder of Persia's Achaemenid Empire. It was written around 370 BC by Xenophon, the Athenian-born soldier, historian, and student of Socrates. The Latinized title ''Cyropaedia'' derives from the Greek ''Kúrou paideía'' (), meaning "The Education of Cyrus". Aspects of it would become a model for medieval writers of the genre mirrors for princes. In turn, the ''Cyropaedia'' strongly influenced the most well-known but atypical of these, Machiavelli's ''The Prince'', which affected the rejection of medieval political thinking and development of modern politics. Format In substance, the ''Cyropaedia'' is a narrative describing the education of the ideal ruler. It has been interpreted as an early novel, a biography, and a manifesto on leadership. The work is intended to communicate political and moral instruction to its audience, most of whom would have been Athenian elites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyrcania
Hyrcania () ( el, ''Hyrkania'', Old Persian: 𐎺𐎼𐎣𐎠𐎴 ''Varkâna'',Lendering (1996) Middle Persian: 𐭢𐭥𐭫𐭢𐭠𐭭 ''Gurgān'', Akkadian: ''Urqananu'') is a historical region composed of the land south-east of the Caspian Sea in modern-day Iran and Turkmenistan, bound in the south by the Alborz mountain range and the Kopet Dag in the east. The region served as a satrapy (province) of the Median Empire, a sub-province of the Achaemenid Empire, and a province within its successors, the Seleucid, Arsacid and Sasanian empires. Hyrcania bordered Parthia to the east (later known as Abarshahr), Dihistan to the north, Media to the south and Mardia to the west. Etymology ''Hyrcania'' () is the Greek name for the region, a borrowing from the Old Persian ''Verkâna'' as recorded in Darius the Great's Behistun Inscription (522 BC), as well as in other Old Persian cuneiform inscriptions. ''Verkā'' means "wolf" in Old Iranian, cf. Avestan ''vəhrkō'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Empire
Assyrian may refer to: * Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia. * Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire. ** Early Assyrian Period ** Old Assyrian Period ** Middle Assyrian Empire ** Neo-Assyrian Empire * Assyrian language (other) * Assyrian Church (other) * SS ''Assyrian'', several cargo ships * ''The Assyrian'' (novel), a novel by Nicholas Guild * The Assyrian (horse), winner of the 1883 Melbourne Cup See also * Assyria (other) * Syriac (other) * Assyrian homeland, a geographic and cultural region in Northern Mesopotamia traditionally inhabited by Assyrian people * Syriac language, a dialect of Middle Aramaic that is the minority language of Syrian Christians * Upper Mesopotamia * Church of the East (other) Church of the East, also called ''Nestorian Church'', an Eastern Christian Christian denomination, denomination formerly spread across Asia, separated since the schism of 1552. Church of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmond Lévy
Edmond Lévy (born 1934) is a French classical historian. Biography Originally a pupil of an École normale supérieure (promotion 1956), an aggregate of letters, he was also a pupil of École française d'Athènes, a school in Athens, Greece where the French language is taught to students who are mainly from France. He is a specialist in Greek history and is a retired professor at Marc-Bloch University in Strasbourg, France. He edits the ''Ktèma'' review. Works * ''Athènes devant la défaite de 404. Histoire d'une crise idéologique'', De Boccard, 1976 * ''La femme dans les sociétés antiques'', University of Strasbourg The University of Strasbourg (french: Université de Strasbourg, Unistra) is a public research university located in Strasbourg, Alsace, France, with over 52,000 students and 3,300 researchers. The French university traces its history to the ..., 1983 * ''Le système palatial en Orient, en Grèce et à Rome'', De Boccard, 1987 * ''La Grèce au Ve s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophimoi
The ''trophimoi'' (Greek: τρόφιμοι, students or pupils, from τροφός ''trophós'' food) were children of non-Spartan citizens ( perioeci or foreigners), who underwent Spartan education. The ''trophimoi'' were temporarily adopted by a Spartan ''oikos''. The trophimoi sons of Perioeci represented, like the '' neodamodes'' and the ''nothoi'' (natural sons of slaves and citizens), an intermediate class at Sparta. They could rise to the status of citizens. According to Plutarch, Agis IV intended them to strengthen the citizenry, which had become too meagre for Sparta's wartime necessities. The foreign ''trophimoi'' normally left Sparta to return to their native towns, where they increased Sparta's influence. Thus, on the invitation of Agesilaus II, Xenophon had raised his own sons at Sparta. However, some ''trophomoi'' preferred to remain, and fought in the civic army. That was the case, for example, of the army that Agesipolis I sent to besiege Phlius in 381 BC: There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx Formation
The phalanx ( grc, φάλαγξ; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particularly used to describe the use of this formation in ancient Greek warfare, although the ancient Greek writers used it to also describe any massed infantry formation, regardless of its equipment. Arrian uses the term in his ''Array against the Alans'' when he refers to his legions. In Greek texts, the phalanx may be deployed for battle, on the march, or even camped, thus describing the mass of infantry or cavalry that would deploy in line during battle. They marched forward as one entity. The term itself, as used today, does not refer to a distinctive military unit or division (e.g., the Roman legion or the contemporary Western-type battalion), but to the type of formation of an army's troops. Therefore, this term does not indicate a standard c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)