|
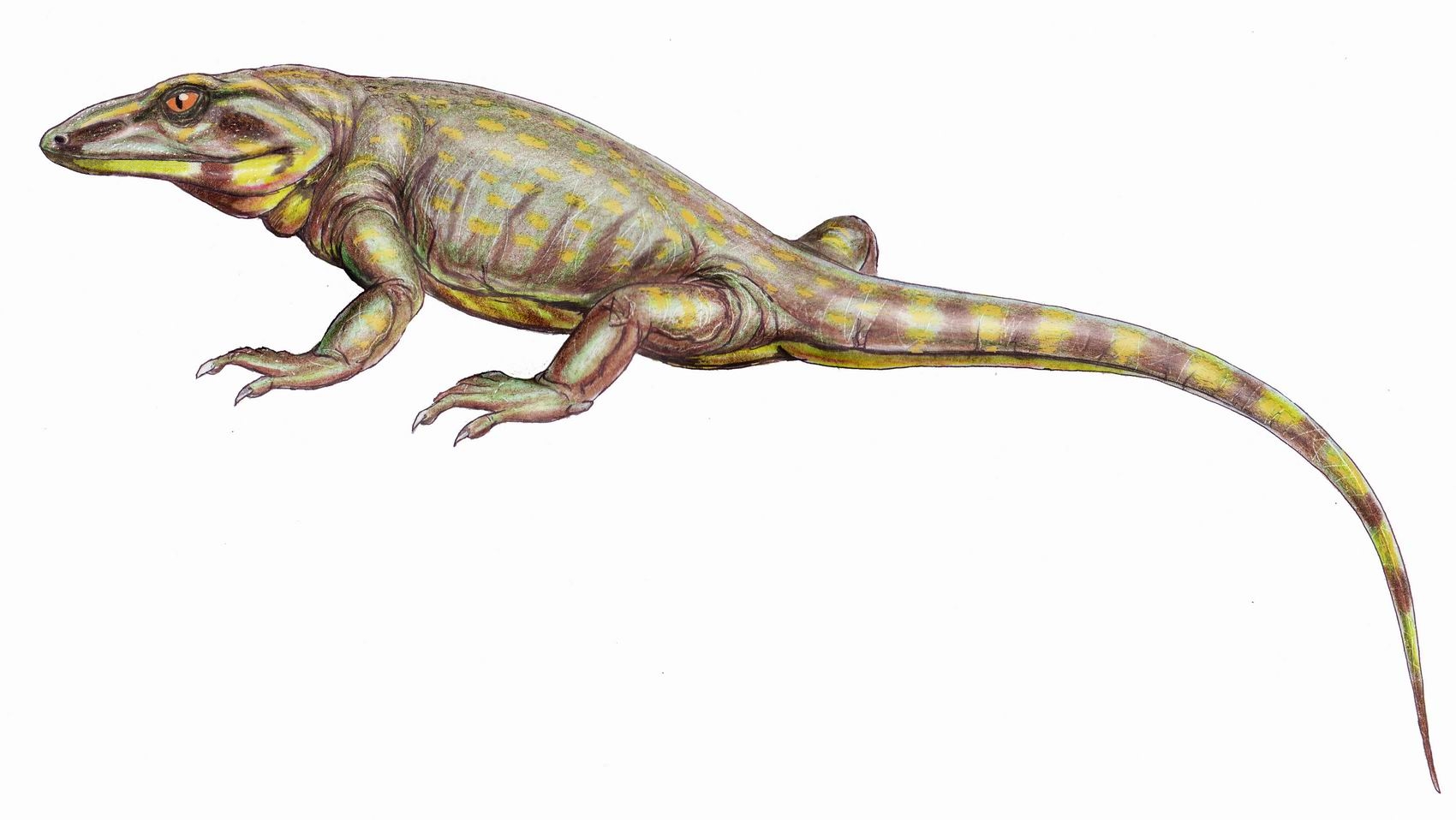
Scincus Scincus
''Scincus scincus'', also commonly known as the sandfish skink, common sandfish or common skink, is a species of skink notable for its burrowing or swimming behaviour in sand. It is native to the Sahara Desert and the Arabian Peninsula, but is also kept as a pet elsewhere. Description The name Algerian sandfish originated because of its ability to move through sand as if it were swimming. Adult common skinks usually reach about 20 cm (8 inches) in length, including the short tail. The common skink has developed a peculiar surprise way of dealing with the desert heat: it can dive into loose, soft sand. Its winding movements produce vibrations in the sand, with a consistent frequency of 3 Hz. It does this to prevent overheating (as it is cold-blooded) and whenever it feels threatened, especially by its arch-nemesis, the devil-headed Saharan snake. This skink has a long, wedge-shaped snout with a countersunk lower jaw, shaped much like a basket. Its compact, taper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insectivore
A robber fly eating a hoverfly An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant that eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects. The first vertebrate insectivores were amphibians. When they evolved 400 million years ago, the first amphibians were piscivores, with numerous sharp conical teeth, much like a modern crocodile. The same tooth arrangement is however also suited for eating animals with exoskeletons, thus the ability to eat insects is an extension of piscivory. At one time, insectivorous mammals were scientifically classified in an order called Insectivora. This order is now abandoned, as not all insectivorous mammals are closely related. Most of the Insectivora taxa have been reclassified; those that have not yet been reclassified and found to be truly related to each other remain in the order Eulipotyphla. Although individually small, insects exist in enormous numbers. Insects make u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Described In 1758
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsid, sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, Squamata, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean taxonomy, Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern Cladistics, cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile Order (biology), orders, historically combined with that of modern amphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles As Pets
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsid, sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, Squamata, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean taxonomy, Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern Cladistics, cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile Order (biology), orders, historically combined with that of modern amphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of The Middle East
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around 31 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Africa
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scincus
''Scincus'' is a genus of skinks, lizards in the family Scincidae. The genus contains four or five species, all of which are typical desert inhabitants, living in sandy and dune-like areas with a hot and dry climate. Species in the genus ''Scincus'' can be found from Arabia to the Sahara desert. Taxonomy ''Scincus'' is the type genus of the subfamily Scincinae. As the subfamily Scincinae appears to be paraphyletic and is in need of revision, it is as yet undetermined which skink genera are closely enough related to ''Scincus'' to be retained in the Scincinae. (Austin & Arnold 2006). Species The genus ''Scincus'' contains five species which are recognized as being valid."''Scincus'' ". The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org. *''Scincus albifasciatus'' *''Scincus conirostris'' – sandfish skink *''Scincus hemprichii'' *''Scincus mitranus'' – eastern sandfish or eastern skink *''Scincus scincus'' – common sandfish or common skink ''Nota bene'': A binomial auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peters's Banded Skink
Peters's banded skink (''Scincopus fasciatus'') is a skink Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Ski ... found in the monotypic genus ''Scincopus''. References External links * RDB''Scincopus fasciatus'' (PETERS, 1864)Clint's Reptiles: Peter's Banded Skink Skinks of Africa Reptiles described in 1864 Taxa named by Wilhelm Peters {{skink-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandfish Skink 4
Sandfish may refer to: Fish *Trichodontidae, known as sandfishes, a family of perch-like fish: ** Pacific sandfish, the species ''Trichodon trichodon'' ** ''Arctoscopus japonicus'', known as sailfin sandfish or Japanese sandfish * ''Gonorynchus'', known as beaked sandfish, a family of long thin ray-finned fish **Gonorynchus gonorynchus, known as sandfish * Southern sandfish, a family ''Leptoscopidae'' of perch-like fish * Belted sandfish, a species ''Serranus subligarius'' of fish * Clanwilliam sandfish, a species ''Labeo seeberi'' of fish * '' Awaous tajasica'', known as sand fish, a species of goby fish Other animals * ''Scincus scincus'', known as sandfish, a species of skink (lizard) * ''Holothuria scabra'', known as sandfish, a species of sea cucumber * ''Thelenota ananas ''Thelenota ananas'', also known as pineapple sea cucumber, oloturia ananas, tripang, prickly skin cucumber, pointed teat sea cucumber, armoured sea cucumber, giant sea cucumber, sand fish or prickl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Edition Of Systema Naturae
The 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' is a book written by Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus and published in two volumes in 1758 and 1759, which marks the starting point of zoological nomenclature. In it, Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature for animals, something he had already done for plants in his 1753 publication of '' Species Plantarum''. Starting point Before 1758, most biological catalogues had used polynomial names for the taxa included, including earlier editions of ''Systema Naturae''. The first work to consistently apply binomial nomenclature across the animal kingdom was the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae''. The International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature therefore chose 1 January 1758 as the "starting point" for zoological nomenclature, and asserted that the 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' was to be treated as if published on that date. Names published before that date are unavailable, even if they would otherwise satisfy the rules. The only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scincus Scincus
''Scincus scincus'', also commonly known as the sandfish skink, common sandfish or common skink, is a species of skink notable for its burrowing or swimming behaviour in sand. It is native to the Sahara Desert and the Arabian Peninsula, but is also kept as a pet elsewhere. Description The name Algerian sandfish originated because of its ability to move through sand as if it were swimming. Adult common skinks usually reach about 20 cm (8 inches) in length, including the short tail. The common skink has developed a peculiar surprise way of dealing with the desert heat: it can dive into loose, soft sand. Its winding movements produce vibrations in the sand, with a consistent frequency of 3 Hz. It does this to prevent overheating (as it is cold-blooded) and whenever it feels threatened, especially by its arch-nemesis, the devil-headed Saharan snake. This skink has a long, wedge-shaped snout with a countersunk lower jaw, shaped much like a basket. Its compact, taper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electric potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement. Needle EMG is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique commonly used by neurologists. Surface EMG is a non-medical procedure used to assess muscle activation by several professionals, including physiotherapists, kinesiologists and biomedical engineers. In Computer Science, EMG is also used as middleware in gesture recognition towards allowing the input of physical action to a computer as a form of human-computer interaction. Clinical uses EMG testing has a variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |