|
Science And Technology In Uzbekistan
Science and technology in Uzbekistan examines government efforts to develop a national innovation system and the impact of these policies. Economic context Economic performance Since gaining independence in 1991, Uzbekistan and the other four Central Asian republics have gradually been moving from a state-controlled economy to a market economy. All five countries have pursued public policies which focus on buffering the political and economic spheres from external shocks. This includes maintaining a trade balance, minimizing public debt and accumulating national reserves’. The republics cannot totally insulate themselves from negative exterior forces, however, such as the persistently weak recovery of global industrial production and international trade since 2008. Although both exports and imports have grown impressively over the past decade, the republics remain vulnerable to economic shocks, owing to their reliance on exports of raw materials, a restricted circle of trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked country located in Central Asia. It is surrounded by five landlocked countries: Kazakhstan to the north; Kyrgyzstan to the northeast; Tajikistan to the southeast; Afghanistan to the south; and Turkmenistan to the southwest. Its capital and largest city is Tashkent. Uzbekistan is part of the Turkic world, as well as a member of the Organization of Turkic States. The Uzbek language is the majority-spoken language in Uzbekistan, while Russian is widely spoken and understood throughout the country. Tajik is also spoken as a minority language, predominantly in Samarkand and Bukhara. Islam is the predominant religion in Uzbekistan, most Uzbeks being Sunni Muslims. The first recorded settlers in what is now Uzbekistan were Eastern Iranian no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation Program
The Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation (CAREC) Program is a program established in 1997 by the Asian Development Bank (ADB) to encourage economic cooperation among countries in Central Asia and nearby parts of Transcaucasia and South Asia. CAREC Member countries The 11 CAREC Member countries are: * * * * * * * * * * * Multilateral Institution Partners CAREC has six multilateral institutions partners: * Asian Development Bank (ADB). ADB serves as the CAREC Secretariat. * European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) * International Monetary Fund (IMF) * Islamic Development Bank (IsDB) * United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) * World Bank Ministerial Conferences CAREC holds an annual ministerial conference. * 2011 – Baku, Azerbaijan * 2012 – Wuhan, People's Republic of China * 2013 – Astana, Kazakhstan * 2014 – Bishkek, Kyrgyz Republic * 2015 – Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia * 2016 – Islamabad, Pakistan * 2017 – Dushanbe, Tajikistan See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
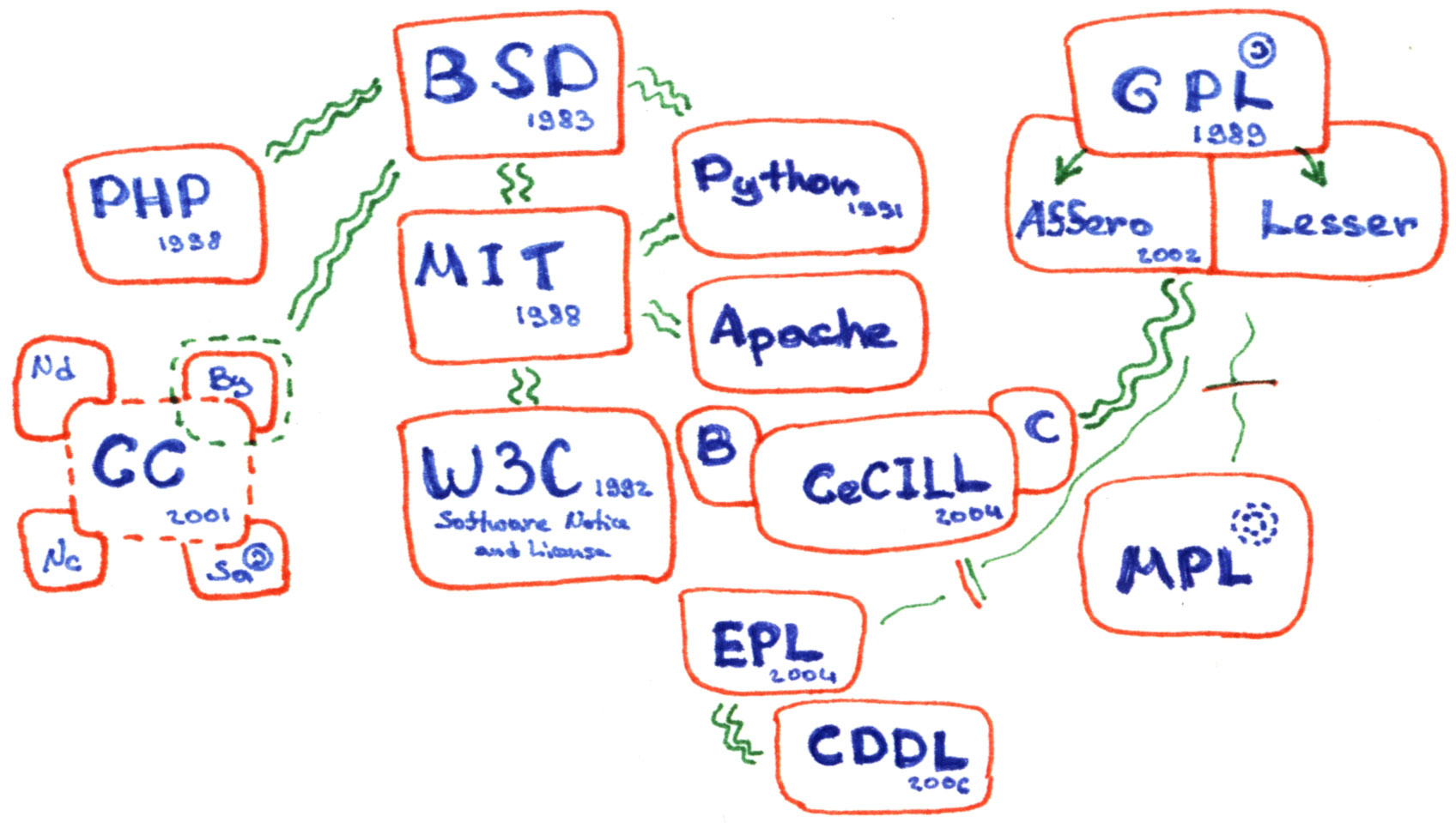
Adding Open License Text To Wikipedia
Addition (usually signified by the plus symbol ) is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication and division. The addition of two whole numbers results in the total amount or '' sum'' of those values combined. The example in the adjacent image shows a combination of three apples and two apples, making a total of five apples. This observation is equivalent to the mathematical expression (that is, "3 ''plus'' 2 is equal to 5"). Besides counting items, addition can also be defined and executed without referring to concrete objects, using abstractions called numbers instead, such as integers, real numbers and complex numbers. Addition belongs to arithmetic, a branch of mathematics. In algebra, another area of mathematics, addition can also be performed on abstract objects such as vectors, matrices, subspaces and subgroups. Addition has several important properties. It is commutative, meaning that the order of the operands d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free License
A free license or open license is a license which allows others to reuse another creator’s work as they wish. Without a special license, these uses are normally prohibited by copyright, patent or commercial license. Most free licenses are worldwide, royalty-free, non-exclusive, and perpetual (see copyright durations). Free licenses are often the basis of crowdsourcing and crowdfunding projects. The invention of the term "free license" and the focus on the rights of users were connected to the sharing traditions of the hacker culture of the 1970s public domain software ecosystem, the social and political free software movement (since 1980) and the open source movement (since the 1990s). These rights were codified by different groups and organizations for different domains in Free Software Definition, Open Source Definition, Debian Free Software Guidelines, Definition of Free Cultural Works and The Open Definition. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizon 2020
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the European Research Area (ERA). Starting in 2014, the funding programmes were named Horizon. The funding programmes began in 1984 and continue to the present day. The most recent programme, Horizon Europe, has a budget of 95.5 billion Euros to be distributed over 7 years. The specific objectives and actions vary between funding periods. In FP6 and FP7, focus was on technological research. In Horizon 2020, the focus was on innovation, delivering economic growth faster, and delivering solutions to end users that are often governmental agencies. Background Conducting European research policies and implementing European research programmes is an obligation under the Amsterdam Treaty, which includes a chapter on research and technological development. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union's Scientific Cooperation Beyond The Bloc
The European Union's scientific collaboration beyond the bloc describes the European Union's frameworks for bilateral cooperation and specific projects in science and technology with countries and regional blocs situated beyond the European Union. Types of association Since 1994, the European Union (EU) has signed international agreements for scientific and technological cooperation with 20 non-EU countries: Algeria, Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, China, Egypt, India, Japan, Jordan, Rep. Korea, Mexico, Morocco, New Zealand, Russian Federation, South Africa, Tunisia, Ukraine and the USA. For the European Parliament, ‘the science diplomacy aspect of this cooperation is emphasized at EU level to facilitate interactions with third countries, as well as to increase the EU's soft power’. The EU invites countries beyond the bloc to participate in its seven-year framework programmes for research and innovation, including developing countries. Horizon Europe, the Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been described as a '' sui generis'' political entity (without precedent or comparison) combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.8per cent of the world population in 2020, the EU generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around trillion in 2021, constituting approximately 18per cent of global nominal GDP. Additionally, all EU states but Bulgaria have a very high Human Development Index according to the United Nations Development Programme. Its cornerstone, the Customs Union, paved the way to establishing an internal single market based on standardised legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states have agreed to act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau of Western Asia. It covers a surface area of (excluding the highly saline lagoon of Garabogazköl to its east) and a volume of . It has a salinity of approximately 1.2% (12 g/L), about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast. The sea stretches nearly from north to south, with an average width of . Its gross coverage is and the surface is about below sea level. Its main freshwater inflow, Europe's longest river, the Volga, enters at the shallow north end. Two deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian politics, political, economy, economic and security organization. It is the world's largest regional organization in terms of geography, geographic scope and world population, population, covering approximately 60% of the area of Eurasia, 40% of the world population, and more than 30% of global GDP. The SCO is the successor to the ''Shanghai Five'', formed in 1996 between the China, People's Republic of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. On 15 June 2001, the leaders of these nations and Uzbekistan met in Shanghai to announce a new organization with deeper political and economic cooperation; the SCO Charter was signed on 7 July 2002 and entered into force on 19 September 2003. Its membership has since expanded to eight states, with India and Pakistan joining on 9 June 2017. Several countries are engaged as observers or dialogue partners. The SCO is governed by the Heads of State Council (HSC), its supreme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDP In Central Asia By Economic Sector, 2005 And 2013
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often revised before being considered a reliable indicator. GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) may be more useful when comparing living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. The ratio of GDP to the total population of the region is the per capita GDP (also called the Mean Standard of Living). GDP definitions are maintained by a number of national and international economic organizations. The Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Cooperation Organization
The Economic Cooperation Organization or ECO is an Asian political and economic intergovernmental organization that was founded in 1985 in Tehran by the leaders of Iran, Pakistan, and Turkey. It provides a platform to discuss ways to improve development and promote trade and investment opportunities. The ECO is an ''ad hoc'' organisation under the United Nations Charter. The objective is to establish a single market for goods and services, much like the European Union. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the ECO expanded to include Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan in 1992. The current framework of the ECO expresses itself mostly in the form of bilateral agreements and arbitration mechanisms between individual and fully sovereign member states. That makes the ECO similar to ASEAN in that it is an organisation that has its own offices and bureaucracy for implementation of trade amongst sovereign member states. This c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |