|
Science And Technology In Romania
Science and technology in Romania is well developed, with the presence of several universities and research institutes, and has a distinguished tradition going back more than a century. Romania was ranked 48th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, up from 50th in 2019. Aviation and aeronautics On March 18, 1906 Traian Vuia achieved a short hop at a height of about . His flight was performed in Montesson near Paris and was about long. Henri Coandă was a Romanian inventor and pioneer of aviation. He exhibited the non-flying Coandă-1910 at the Second International Aeronautical Exhibition in Paris in October 1910, and built his first flying aircraft in 1911. He discovered the Coandă effect of fluidics, and was the first to recognize the practical application of the phenomenon in aircraft design. On May 14, 1981, Romania became the 11th country in the world to have an astronaut in space. That astronaut, Dumitru Prunariu later served as president of the Romanian Space Agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
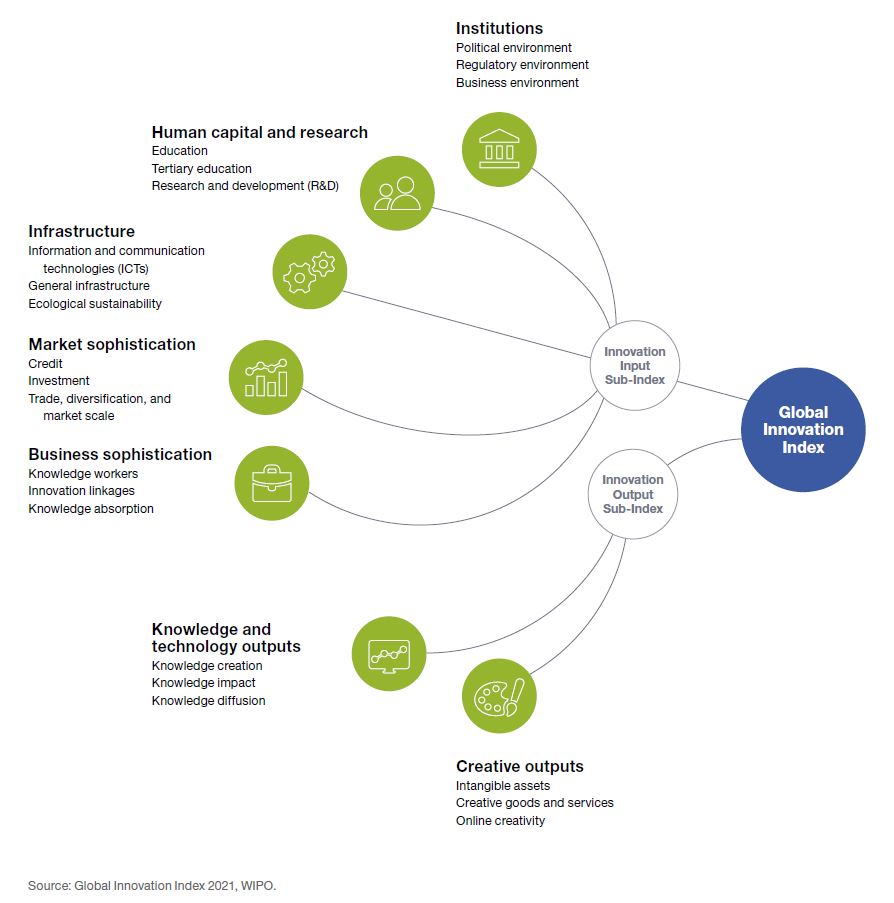
Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for, and success in, innovation, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization. It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British magazine. Until 2021 it was published by the World Intellectual Property Organization, in partnership with Cornell University, INSEAD, and other organisations and institutions,. It is based on both subjective and objective data derived from several sources, including the International Telecommunication Union, the World Bank and the World Economic Forum. History The index was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British magazine. It was created by Soumitra Dutta. Methodology The index is computed by taking a simple average of the scores in two sub-indices, the Innovation Input Index and Innovation Output Index, which are composed of five and two pillars respectively. Each of these pillars describe an attribute of innovation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Physiology Or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's 1895 will, are awarded "to those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind". Nobel Prizes are awarded in the fields of Physics, Chemistry, Physiology or Medicine, Literature, and Peace. The Nobel Prize is presented annually on the anniversary of Alfred Nobel's death, 10 December. As of 2022, 114 Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine have been awarded to 226 laureates, 214 men and 12 women. The first one was awarded in 1901 to the German physiologist, Emil von Behring, for his work on serum therapy and the development of a vaccine against diphtheria. The first woman to receive the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Gerty Cori, received it in 1947 for her role in elucidati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octav Mayer
Octav Mayer ( – 9 September 1966) was a Romanian mathematician, the first to earn a doctorate in Romania. He completed his Ph.D. at Alexandru Ioan Cuza University of Iași in 1920; his thesis, written under the direction of Alexander Myller, was titled ''Contributions à la théorie des quartiques bicirculaires''. The Octav Mayer Institute of Mathematics of the Romanian Academy The Romanian Academy ( ro, Academia Română ) is a cultural forum founded in Bucharest, Romania, in 1866. It covers the scientific, artistic and literary domains. The academy has 181 active members who are elected for life. According to its byl ... (located in Iași) is named after him. home page, retrieved 2014-07-16. References External links *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traian Lalescu
Traian Lalescu (; 12 July 1882 – 15 June 1929) was a Romanian mathematician. His main focus was on integral equations and he contributed to work in the areas of functional equations, trigonometry, trigonometric series, mathematical physics, geometry, mechanics, algebra, and the history of mathematics. Life He went to the Carol I High School in Craiova, continuing high school in Roman, Romania, Roman, and graduating from the Costache Negruzzi National College, Boarding High School in Iași. After entering the University of Iași, he completed his undergraduate studies in 1903 at the University of Bucharest. He earned his Ph.D. in Mathematics from the University of Paris in 1908. His dissertation, ''Sur les Volterra integral equation, équations de Volterra'', was written under the direction of Charles Émile Picard, Émile Picard. In 1911, he published ''Introduction to the Theory of Integral Equations'', the first book ever on the subject of integral equations. After returnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiru Haret
Spiru C. Haret (; 15 February 1851 – 17 December 1912) was a Romanian mathematician, astronomer, and politician. He made a fundamental contribution to the ''n''-body problem in celestial mechanics by proving that using a third degree approximation for the disturbing forces implies instability of the major axes of the orbits, and by introducing the concept of ''secular perturbations'' in relation to this. As a politician, during his three terms as Minister of Education, Haret ran deep reforms, building the modern Romanian education system. He was made a full member of the Romanian Academy in 1892. He also founded the Bucharest Observatory, appointing as its first director. The crater Haret on the Moon is named after him. Life Haret was born in Iași, Moldavia, to Constantin and Smaranda Haret, who were of Armenian origin. His baptismal record listed his name as Spiridon Haret. He started his studies in Dorohoi Iași, and in 1862 moved to Saint Sava High School in Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefied petroleum gas and petroleum naphtha. Petrochemicals feedstock like ethylene and propylene can also be produced directly by cracking crude oil without the need of using refined products of crude oil such as naphtha. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products. In 2020, the total capacity of global refineries for crude oil was about 101.2 million barrels per day. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids between large chemical processing units, such as distillation colu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. Amphetamine was discovered in 1887 and exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. ''Amphetamine'' properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazăr Edeleanu
Lazăr Edeleanu (; 1 September 1861, Bucharest – 7 April 1941, Bucharest) was a Romanian chemist of Jewish origin. at www.romanianjewish.org He is known for being the first chemist to synthesize amphetamine at the and for inventing the modern method of refining crude oil. Research activity in England and Romania After ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory Of Sonics
The theory of sonics is a branch of continuum mechanics which describes the transmission of mechanical energy through vibrations. The birth of the theory of sonics is the publication of the book ''A treatise on transmission of power by vibrations'' in 1918 by the Romanian scientist Gogu Constantinescu. ONE of the fundamental problems of mechanical engineering is that of transmitting energy found in nature, after suitable transformation, to some point at which can be made available for performing useful work. The methods of transmitting power known and practised by engineers are broadly included in two classes: mechanical including hydraulic, pneumatic and wire rope methods; and electrical methods....According to the new system, energy is transmitted from one point to another, which may be at a considerable distance, by means of impressed variations of pressure or tension producing longitudinal vibrations in solid, liquid or gaseous columns. The energy is transmitted by periodic cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Constantinescu
George "Gogu" Constantinescu (; last name also Constantinesco; 4 October 1881 – 11 December 1965) was a Romanian scientist, engineer and inventor. During his career, he registered over 130 inventions. He is the creator of the ''theory of sonics'', a new branch of continuum mechanics, in which he described the transmission of mechanical energy through vibrations. Biography Early years Born in Craiova in "the Doctor's House" near the Mihai Bravu Gardens, he was influenced by his father George, born in 1844 (a professor of mathematics and engineering science, specialized in mathematics at the Sorbonne University). Gogu Constantinescu settled in the United Kingdom in 1912. He was an honorary member of the Romanian Academy. Family He married Alexandra (Sandra) Cocorescu in Richmond, London, in December 1914. The couple moved to Wembley and, after their son Ian was born, they moved to Weybridge. The marriage broke down in the 1920s and ended in divorce. He then married Ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Medal Of Science
The National Medal of Science is an honor bestowed by the President of the United States to individuals in science and engineering who have made important contributions to the advancement of knowledge in the fields of behavioral and social sciences, biology, chemistry, engineering, mathematics and physics. The twelve member presidential Committee on the National Medal of Science is responsible for selecting award recipients and is administered by the National Science Foundation (NSF). History The National Medal of Science was established on August 25, 1959, by an act of the Congress of the United States under . The medal was originally to honor scientists in the fields of the "physical, biological, mathematical, or engineering sciences". The Committee on the National Medal of Science was established on August 23, 1961, by executive order 10961 of President John F. Kennedy. On January 7, 1979, the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) passed a resolution propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomes
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many ribosomal proteins (RPs or r-proteins). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA chain. Ribosomes bind to messenger RNAs and use their sequences for determining the correct sequence of amino acids to generate a given protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain via an anti-cod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |