|
Schussenried Abbey
Schussenried Abbey (''Kloster Schussenried'', ''Reichsabtei Schussenried'') is a former Catholic monastery in Bad Schussenried, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is famed for its Baroque architecture, Baroque library hall. The abbey was established in the 12th century by the Premonstratensian Order and made an Imperial Abbey in the 15th century. The monastery sustained immense damage in the Thirty Years' War. In the 18th century, the abbey began expansions in the Baroque architecture, Baroque style, but was unable to complete them. The abbey was secularized in 1803 and twice awarded during the process of German Mediatization, eventually becoming a possession of the Kingdom of Württemberg. Its second king, William I of Württemberg, William I, opened a foundry on its grounds, which was followed by a nursing home. These ceased operation or moved out of the monastery in the 1990s. History In 1183, two brothers, Berengar and Konrad von Schussenried, unmarried members of the House o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Schussenried
Bad Schussenried (; Swabian: ''Schussariad'') is a spa town in Upper Swabia in the district of Biberach, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It lies on the Upper Swabian Baroque Route and the Swabian Spa Route. Schussenried Abbey, a former monastery founded in 1183, is located in Bad Schussenried. Its church and Baroque library feature impressive architecture and artwork, including intricate ceiling frescoes. The town is also home to a beer stein museum, the Schussenrieder Bierkrug Museu Bad Schussenried had a population of 8,537 at the end of 2015. Geography Bad Schussenried is located between Ulm and Lake Constance on the river Schussen. The 48th parallel north runs through Bad Schussenried. History Archaeological finds provided evidence of a prehistoric settlement in the region. In 1866, a Paleolithic campsite of hunters and gatherers was discovered. These were the first Paleolithic finds in Central Europe. World heritage site At Aichbühl, about 1.5 km north of the Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon (priest)
A canon (from the Latin , itself derived from the Greek , , "relating to a rule", "regular") is a member of certain bodies in subject to an ecclesiastical rule. Originally, a canon was a cleric living with others in a clergy house or, later, in one of the houses within the precinct of or close to a cathedral or other major church and conducting his life according to the customary discipline or rules of the church. This way of life grew common (and is first documented) in the 8th century AD. In the 11th century, some churches required clergy thus living together to adopt the rule first proposed by Saint Augustine that they renounce private wealth. Those who embraced this change were known as Augustinians or Canons Regular, whilst those who did not were known as secular canons. Secular canons Latin Church In the Latin Church, the members of the chapter of a cathedral (cathedral chapter) or of a collegiate church (so-called after their chapter) are canons. Depending on the title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allmannsweiler
Allmannsweiler () is a municipality in the district of Biberach in Baden-Württemberg in Germany. History In 1803, Schussenried Abbey was secularized and its holdings mediatized to the County of Sternberg-Manderscheid. It was re-mediatized in 1806 to the Kingdom of Württemberg. As one of Schussenried Abbey's possessions, Allmannsweiler thus came under the sovereignty of Württemberg and was assigned to . In 1938, the Oberamt was reorganized into , which was dissolved by the . Allmannsweiler was subsequently assigned to a new district, that of Biberach an der Riss. Geography The municipality (''Gemeinde'') of Allmannsweiler covers of the district of Biberach an der Riss, making it the second smallest municipality in that district. It is located at the southern edge of the district's area, along the border with the district of Sigmaringen. Allmannsweiler is physically located in the basin of the Federsee. Elevation above sea level in the municipal area ranges from a high of No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oggelshausen
Oggelshausen () is a municipality in the district of Biberach in Baden-Württemberg in Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... Mayors *1984–2005: Alois Dangel *2005–2021: Ralf Kriz *2021– : Michael Kara References Biberach (district) {{Biberach-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jus Patronatus
The right of patronage (in Latin ''jus patronatus'' or ''ius patronatus'') in Roman Catholic canon law is a set of rights and obligations of someone, known as the patron in connection with a gift of land (benefice). It is a grant made by the church out of gratitude towards a benefactor. Its counterpart in English law and in the Church of England is called an advowson. The right of patronage is designated in papal letters as ''"ius spirituali annexum"'' and is therefore subject to ecclesiastical legislation and jurisdiction as well as civil laws relating to the ownership of property. Background In the Eastern Catholic Churches, the founder of a church was permitted to nominate an administrator for the temporal goods and indicate to the bishop a cleric suitable for appointment. In the Latin Church, the Synod of Orange in 441 granted a right of "presentation" to a bishop who had built a church in another diocese and the Synod of Toledo in 655 gave a layman this privilege for ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High, Middle And Low Justice
High, middle and low justices are notions dating from Western feudalism to indicate descending degrees of judicial power to administer justice by the maximal punishment the holders could inflict upon their subjects and other dependents. Low justice regards the level of day-to-day civil actions, including voluntary justice, minor pleas, and petty offences generally settled by fines or light corporal punishment. It was held by many lesser authorities, including many lords of the manor, who sat in justice over the serfs, unfree tenants, and freeholders on their land. Middle justice would involve full civil and criminal jurisdiction, except for capital crimes, and notably excluding the right to pass the death penalty, torture and severe corporal punishment, which was reserved to authorities holding high justice, or the ''ius gladii'' ("right of the sword"). Pyramid of feudal justice Although the terms ''high'' and ''low'' suggest a strict subordination, this was not quite the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg, Truchsess Von Waldburg
Georg III Truchsess von Waldburg-Zeil ( Waldsee, 25 January 1488 – Bad Waldsee, 29 May 1531), also known as Bauernjörg, was a Swabian League Army Commander in the German Peasants' War. Life He was a member of the House of Waldburg, which received through him in 1525 the hereditary title of ''Truchsess'' (''Seneschal'', or ''Steward'', in English) of the Holy Roman Empire and the right to put it in their family name. He served since 1508 Duke Ulrich von Württemberg and helped him crush the Poor Conrad rebellion. In 1516 he fought for Bavaria alongside Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor in Italy against France and their allies. In the next years he was in the service of the Swabian League and chased his former employer, Ulrich von Württemberg out of Württemberg. In 1525 he succeeded his cousin Wilhelm as governor of Württemberg. Both received the hereditary title of Imperial Steward (''Reichserbtruchsess'') from the hands of Emperor Charles V on 27 July 1526 in Toledo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogt
During the Middle Ages, an (sometimes given as modern English: advocate; German: ; French: ) was an office-holder who was legally delegated to perform some of the secular responsibilities of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as an abbey. Many such positions developed, especially in the Holy Roman Empire. Typically, these evolved to include responsibility for aspects of the daily management of agricultural lands, villages and cities. In some regions, advocates were governors of large provinces, sometimes distinguished by terms such as (in German). While the term was eventually used to refer to many types of governorship and advocacy, one of the earliest and most important types of was the church advocate (). These were originally lay lords, who not only helped defend religious institutions in the secular world, but were also responsible for exercising lordly responsibilities within the church's lands, such as the handling of legal cases which might require the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Chapter
A chapter ( la, capitulum or ') is one of several bodies of clergy in Roman Catholic, Old Catholic, Anglican, and Nordic Lutheran churches or their gatherings. Name The name derives from the habit of convening monks or canons for the reading of a chapter of the Bible The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ... or a chapter (books), heading of the Christian monasticism#Western orders, order's monastic rule, rule. The 6th-century St Benedict rule of Saint Benedict, directed that Benedictines, his monks begin their daily assemblies with such readings and over time expressions such as "coming together for the chapter" (') found their meaning transferred from the text to the meeting itself and then to the body gathering for it. The place of such meetings similarly be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II (German language, German: ''Friedrich''; Italian language, Italian: ''Federico''; Latin: ''Federicus''; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusalem from 1225. He was the son of emperor Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry VI of the House of Hohenstaufen, Hohenstaufen dynasty and Queen Constance, Queen of Sicily, Constance of Sicily of the Hauteville family, Hauteville dynasty. His political and cultural ambitions were enormous as he ruled a vast area, beginning with Sicily and stretching through Italy all the way north to Germany. As the Crusades progressed, he acquired control of Jerusalem and styled himself its king. However, the Papacy became his enemy, and it eventually prevailed. Viewing himself as a direct successor to the Roman emperors of antiquity, he was Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of the Romans from his papal coronation in 1220 until hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III ( la, Innocentius III; 1160 or 1161 – 16 July 1216), born Lotario dei Conti di Segni (anglicized as Lothar of Segni), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 to his death in 16 July 1216. Pope Innocent was one of the most powerful and influential of the medieval popes. He exerted a wide influence over the Christian states of Europe, claiming supremacy over all of Europe's kings. He was central in supporting the Catholic Church's reforms of ecclesiastical affairs through his decretals and the Fourth Lateran Council. This resulted in a considerable refinement of Western canon law. He is furthermore notable for using interdict and other censures to compel princes to obey his decisions, although these measures were not uniformly successful. Innocent greatly extended the scope of the Crusades, directing crusades against Muslim Iberia and the Holy Land as well as the Albigensian Crusade against the Cathars in southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
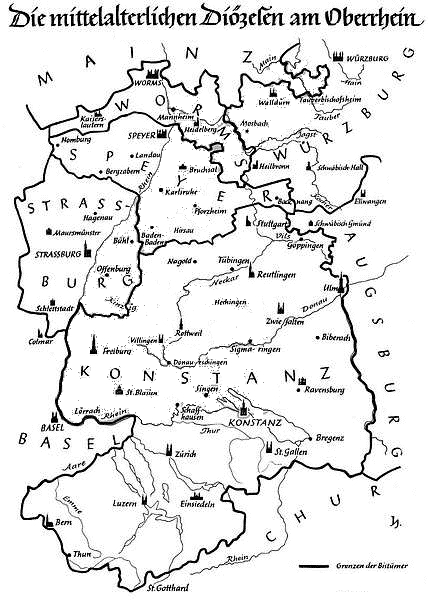
Bishop Of Constance
The Prince-Bishopric of Constance, (german: Hochstift Konstanz, Fürstbistum Konstanz, Bistum Konstanz) was a small ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the mid-12th century until its secularisation in 1802–1803. In his dual capacity as prince and as bishop, the prince-bishop also governed the Diocese of Konstanz, which existed from about 585 until its dissolution in 1821, and whose territory extended over an area much larger than the principality."Diocese of Konstanz " ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved February 29, 2016 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |