|
Schlieren Video Of Shotshell Transitional Intermediate Ballistics - Nathan Boor Of Aimed Research
Schlieren ( ; , ) are optical inhomogeneities in transparent media that are not necessarily visible to the human eye. Schlieren physics developed out of the need to produce high-quality lenses devoid of such inhomogeneities. These inhomogeneities are localized differences in optical path length that cause deviations of light rays, especially by refraction. This light deviation can produce localized brightening, darkening, or even color changes in an image, depending on the directions the rays deviate. History Schlieren were first observed by Robert HookeHooke, R. (1665), "Of a New Property in the Air," ''Micrographia'', Observation LVIII, pp. 217–219, London. in 1665 using a large concave lens and two candles. One candle served as a light source. The warm air rising from the second candle provided the schliere. The conventional schlieren system is credited mostly to German physicist August Toepler, though Jean Bernard Léon Foucault invented the method in 1859 that To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlieren Video Of A Handgun
Schlieren ( ; , ) are optical inhomogeneities in Transparency and translucency, transparent optical medium, media that are not necessarily visible to the human eye. Schlieren physics developed out of the need to produce high-quality lenses devoid of such inhomogeneities. These inhomogeneities are localized differences in optical path length that cause deviations of light ray (optics), rays, especially by refraction. This light deviation can produce localized brightening, darkening, or even dispersion (optics), color changes in an image, depending on the directions the rays deviate. History Schlieren were first observed by Robert HookeHooke, R. (1665), "Of a New Property in the Air," ''Micrographia'', Observation LVIII, pp. 217–219, London. in 1665 using a large Lens (optics)#Types of simple lenses, concave lens and two candles. One candle served as a light source. The warm air rising from the second candle provided the schliere. The conventional schlieren system is credite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Lens
In optics, a thin lens is a lens with a thickness (distance along the optical axis between the two surfaces of the lens) that is negligible compared to the radii of curvature of the lens surfaces. Lenses whose thickness is not negligible are sometimes called ''thick lenses''. The thin lens approximation ignores optical effects due to the thickness of lenses and simplifies ray tracing calculations. It is often combined with the paraxial approximation in techniques such as ray transfer matrix analysis. Focal length The focal length, ''f'', of a lens in air is given by the lensmaker's equation: :\frac = (n-1) \left \frac - \frac + \frac \right where ''n'' is the index of refraction of the lens material, and ''R''1 and ''R''2 are the radii of curvature of the two surfaces. For a thin lens, ''d'' is much smaller than one of the radii of curvature (either ''R''1 or ''R''2). In these conditions, the last term of the Lensmaker's equation becomes negligible, and the focal length of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shadowgraph
Shadowgraph is an optical method that reveals non-uniformities in transparent media like air, water, or glass. It is related to, but simpler than, the schlieren and schlieren photography methods that perform a similar function. Shadowgraph is a type of flow visualisation. In principle, a difference in temperature, a different gas, or a shock wave in the transparent air cannot be seen by the human eye or cameras. However, all these disturbances refract light rays, so they can cast shadows. The plume of hot air rising from a fire, for example, can be seen by way of its shadow cast upon a nearby surface by the uniform sunlight. Sunlight shadowgraph Some aquatic predators detect their transparent prey by way of their shadows cast upon the ocean floor. It was Robert Hooke who first scientifically demonstrated the sunlight shadowgraph and Jean-Paul Marat who first used it to study fire. A modern account of shadowgraphy is given by Gary S. Settles. Applications Applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlieren Photography
Schlieren photography is a process for photographing fluid flow. Invented by the German physicist August Toepler in 1864 to study supersonic motion, it is widely used in aeronautical engineering to photograph the flow of air around objects. Classical optical system The classical implementation of an optical schlieren system uses light from a single collimated source shining on, or from behind, a target object. Variations in refractive index caused by density gradients in the fluid distort the collimated light beam. This distortion creates a spatial variation in the intensity of the light, which can be visualised directly with a shadowgraph system. Classical schlieren imaging systems appear in two configurations, using either one or two mirrors. In each case, a transparent object is illuminated with collimated or nearly-collimated light. Rays that are not deflected by the object proceed to their focal point, where they are blocked by a knife edge. Rays that are deflected by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlieren Imaging
Schlieren imaging is a method to visualize density variations in transparent media. The term "schlieren imaging" is commonly used as a synonym for schlieren photography, though this article particularly treats visualization of the pressure field produced by ultrasonic transducers, generally in water or tissue-mimicking media. The method provides a two-dimensional (2D) projection image of the acoustic beam in real-time ("live video"). The unique properties of the method enable the investigation of specific features of the acoustic field (e.g. focal point in HIFU transducers), detection of acoustic beam-profile irregularities (e.g. due to defects in transducer) and on-line identification of time-dependent phenomena (e.g. in phased array transducers). Some researchers say that schlieren imaging is equivalent to an X-ray radiograph of the acoustic field. Setup The optical setup of a schlieren imaging system may comprise the following main sections: Parallel beam, focusing eleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mach–Zehnder Interferometer
The Mach–Zehnder interferometer is a device used to determine the relative phase shift variations between two collimated beams derived by splitting light from a single source. The interferometer has been used, among other things, to measure phase shifts between the two beams caused by a sample or a change in length of one of the paths. The apparatus is named after the physicists Ludwig Mach (the son of Ernst Mach) and Ludwig Zehnder; Zehnder's proposal in an 1891 article was refined by Mach in an 1892 article. Demonstrations of Mach–Zehnder interferometry with particles other than photons (particles of light) had been demonstrated as well in multiple experiments. The versatility of the Mach–Zehnder configuration has led to its being used in a wide range of fundamental research topics in quantum mechanics, including studies on counterfactual definiteness, quantum entanglement, quantum computation, quantum cryptography, quantum logic, Elitzur–Vaidman bomb tester, the quant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Schlieren Deflectometry
Laser schlieren deflectometry (LSD) is a method for a high-speed measurement of the gas temperature in microscopic dimensions, in particular for temperature peaks under dynamic conditions at atmospheric pressure. The principle of LSD is derived from schlieren photography: a narrow laser beam is used to scan an area in a gas where changes in properties are associated with characteristic changes of refractive index. Laser schlieren deflectometry is claimed to overcome limitations of other methods regarding temporal and spatial resolution. The theory of the method is analogous to the scattering experiment of Ernest Rutherford from 1911. However, instead of alpha particles scattered by gold atoms, here an optical ray is deflected by hot spots with unknown temperature. A general equation of LSD describes the dependence of the measured maximum deflection of the ray ''δ''1 on the local maximum of the neutral gas temperature in the hot spot ''T''1: : \frac + \frac = 1, where ''T'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Background-oriented Schlieren Technique
Schlieren photography is a process for photographing fluid flow. Invented by the German physicist August Toepler in 1864 to study supersonic motion, it is widely used in aeronautical engineering to photograph the flow of air around objects. Classical optical system The classical implementation of an optical schlieren system uses light from a single collimated source shining on, or from behind, a target object. Variations in refractive index caused by density gradients in the fluid distort the collimated light beam. This distortion creates a spatial variation in the intensity of the light, which can be visualised directly with a shadowgraph system. Classical schlieren imaging systems appear in two configurations, using either one or two mirrors. In each case, a transparent object is illuminated with collimated or nearly-collimated light. Rays that are not deflected by the object proceed to their focal point, where they are blocked by a knife edge. Rays that are deflected by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talaria Projector
Talaria was the brand name of a large-venue video projector from General Electric introduced in 1983. Light from a Xenon arc lamp was modulated by a light valve consisting of a rotating glass disc that was continuously re-coated with a viscous oil. An electron beam similar to the one in a cathode ray tube traced a raster graphics, raster on the surface of the coated glass, deforming the surface of the oil. Where the oil was undisturbed, the light would be reflected into a light trap. The raster traced into the oil formed a diffraction grating. The basic unit was monochrome (PJ7000 line). Color display is accomplished in one of two ways: The single lens color projector (PJ5000 line) use dichroic filters to separate the white light of the xenon bulb in two channels, Green and Magenta. RGB color separation and processing is obtained using vertical Wobbulator, wobbulation of the electron beam on the oil film to modulate the green channel and sawtooth modulation is added to the hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eidophor
An Eidophor was a video projector used to create theater-sized images from an analog video signal. The name Eidophor is derived from the Greek word-roots ''eido'' and ''phor'' meaning 'image' and 'bearer' (carrier). Its basic technology was the use of electrostatic charges to deform an oil surface. Origins and use The idea for the original Eidophor was conceived in 1939 in Zurich by Swiss physicist Fritz Fischer, professor at the ''Labor für technische Physik'' of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, with the first prototype being unveiled in 1943. A basic patent was filed on November 8, 1939, in SwitzerlandMonika Burri''Der Eidophor-Projektor.''ETH History 1855 - 2005. Retrieved 26 September 2019 and granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (patent no. 2,391,451) to Friederich Ernst Fischer for the ''Process and appliance for projecting television pictures'' on 25 December 1945. During the Second World War, Edgar Gretener worked together with Fischer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
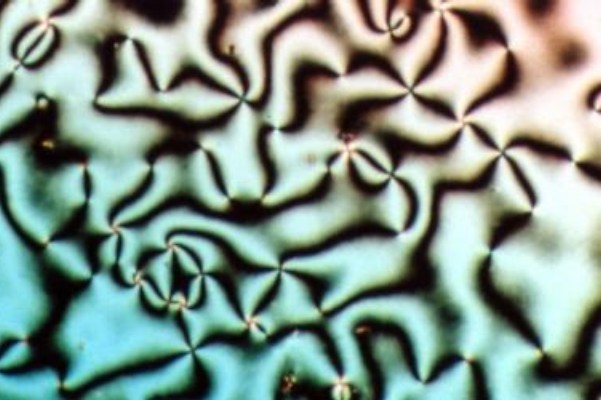
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties (such as textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. LC materials may not always be in a LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapor). Liquid crystals can be divided into 3 main types: * thermotropic, *lyotropic, and * metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the LC phase as temperature changes. Lyotropic LCs exhibit phase transitions as a function of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |