|
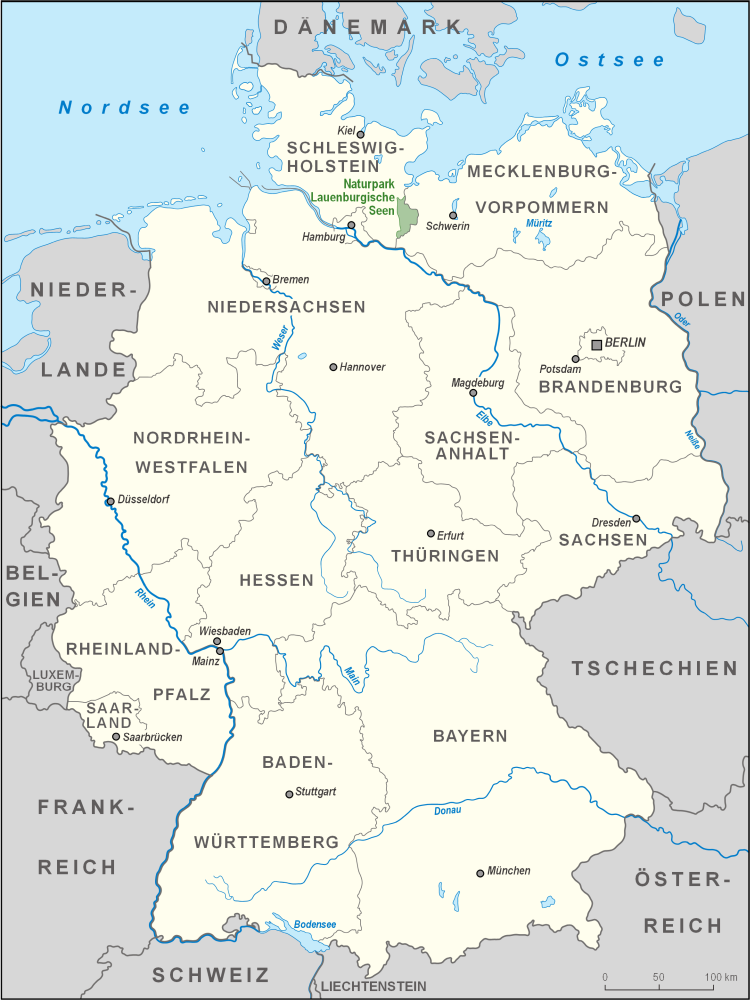
Schleswig-Holsteinisches Hügelland
The Schleswig-Holstein Uplands or Schleswig-Holstein Morainic Uplands Dickinson, Robert E (1964). ''Germany: A regional and economic geography'' (2nd ed.). London: Methuen. . (German: ''Schleswig-Holsteinisches Hügelland'') is one of the three landscapes of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein; the others being the marsch (on the North Sea coast) and the geest (in the interior). In addition, the gently rolling hills or '' Hügelland'' of the Baltic Uplands, the many small lakes and the long, deep embayments ('' Förde'') formed by the moraines of the Weichselian Ice Age are characteristic features of the area. Its best-known towns are Kiel, Lübeck and Flensburg. The highest elevation in the area is the Bungsberg in the region known as Holstein Switzerland ('' Holsteinische Schweiz''). On the Bungsberg is the only ski lift in the state (not permanently installed). The Schleswig-Holstein Upland comprises the following sub-regions: * Angeln * Schwansen *Hütten Hills * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holsteinische Schweiz
Holstein Switzerland (german: Holsteinische Schweiz) is a hilly area with a patchwork of lakes and forest in Schleswig Holstein, Germany, reminiscent of Swiss landscape. Its highest point is the Bungsberg (168 metres above sea level).Carl Ingwer Johannsen & Eckardt Opitz: ''Das grosse Schleswig-Holstein-Buch.'' Hamburg 1996 It is a designated nature park as well as an important tourist destination in Northern Germany situated between the cities of Kiel and Lübeck. Geography Holstein Switzerland lies in eastern Schleswig-Holstein. This picturesque region in the historical county of Wagria has no precise political or geographic boundaries. Most of the area falls within the districts of Ostholstein and Plön, roughly between the cities of Lübeck and Kiel and extends as far north as the Baltic coast. Its major towns include Bad Malente-Gremsmühlen, Lütjenburg, Oldenburg in Holstein, Preetz and the old '' Residenz'' seats of Eutin and Plön. The charm of this re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Schleswig-Holstein
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and the environment ( environmental geography). Geographic regions and sub-regions are mostly described by their imprecisely defined, and sometimes transitory boundaries, except in human geography, where jurisdiction areas such as national borders are defined in law. Apart from the global continental regions, there are also hydrospheric and atmospheric regions that cover the oceans, and discrete climates above the land and water masses of the planet. The land and water global regions are divided into subregions geographically bounded by large geological features that influence large-scale ecologies, such as plains and features. As a way of describing spatial areas, the concept of regions is important and widely used among the many branche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hageland
The Hageland is a landscape in the Flemish Region of Belgium, situated in the eastern part of the Province of Flemish Brabant. It is mainly comprised between the cities of Aarschot, Leuven, Tienen and Diest, and probably coincides to some extent with the twelfth-century County of Leuven. The French Government that controlled the area that later became Belgium in the last years of the 18th and early 19th century, had extended Limburg, which since then comprises the minor part of the Hageland at the city of Halen. The name refers to land with dense (low) forest and/or undergrowth. Its earliest attestation (spelled as ''Hagelant'') dates from 1528. Geography The area is a series of east–west–directed ridges of ironstone hills. The ridge that includes the 106-metre-high ''Molenberg'' hill at the village of Pellenberg forms the southern border of the Hageland, and the Velp, a tributary of the Demer, limits its southeast. Touristic publications of Hageland often erroneously inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauenburg Lakes Nature Park
The Lauenburg Lakes Nature Park (german: Naturpark Lauenburgische Seen) at www.germany.travel. Retrieved 20 Apr 2020. was founded in and lies in the district of Lauenburg in the southeastern part of the German state of . It is right on the border with the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in the , a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holstein Switzerland
Holstein Switzerland (german: Holsteinische Schweiz) is a hilly area with a patchwork of lakes and forest in Schleswig Holstein, Germany, reminiscent of Little Switzerland (landscape), Swiss landscape. Its highest point is the Bungsberg (168 metres above sea level).Carl Ingwer Johannsen & Eckardt Opitz: ''Das grosse Schleswig-Holstein-Buch.'' Hamburg 1996 It is a designated nature park as well as an important tourist destination in Northern Germany situated between the cities of Kiel and Lübeck. Geography Holstein Switzerland lies in eastern Schleswig-Holstein. This picturesque region in the historical county of Wagria has no precise political or geographic boundaries. Most of the area falls within the districts of Kreis Ostholstein, Ostholstein and Kreis Plön, Plön, roughly between the cities of Lübeck and Kiel and extends as far north as the Baltic coast. Its major towns include Bad Malente-Gremsmühlen, Lütjenburg, Oldenburg in Holstein, Preetz and the old ''Residenz'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
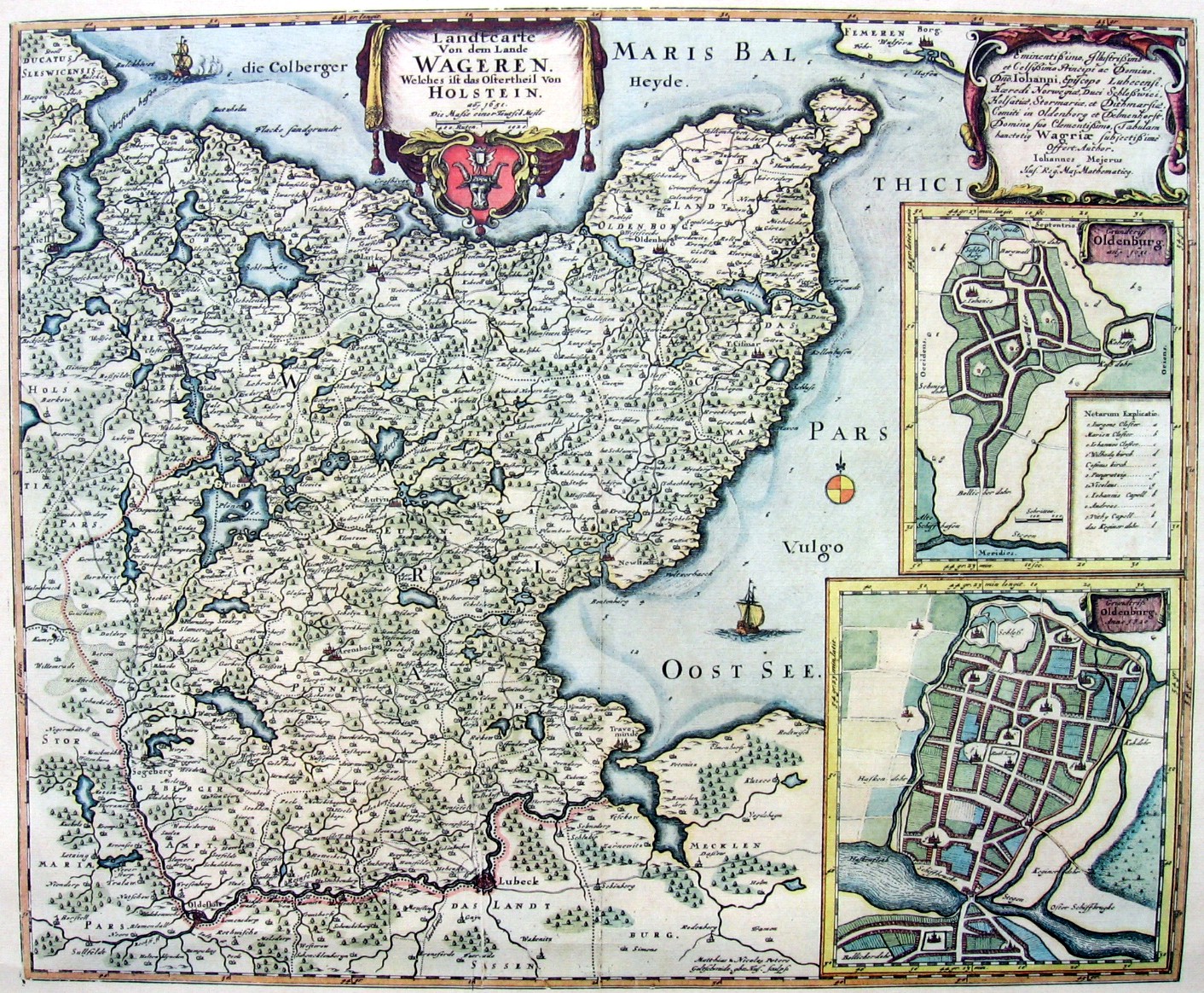
Wagria
WagriaArnold, Benjamin (1991). ''Princes and territories in medieval Germany'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, p. 156. . (german: Wagrien, ''Waierland'' or ''Wagerland'') is the northeastern part of Holstein in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein, corresponding roughly to the districts of Plön and Ostholstein. The word "Wagria" is derived derived from the Slavic Lechites tribe of Wagri, which meant "those who live by the bays". Geography In the Middle Ages, and as still shown on early modern maps, Wagria was bordered on the north and east by the Baltic Sea from the Kiel Fjord to Lübeck Bay, and inland by the rivers Schwentine and Trave. Today, Wagria generally refers just to the Oldenburg Peninsula (''Oldenburgische Halbinsel'') in Ostholstein. The highest elevation in the peninsula is the Bungsberg at 168 metres. History The Lechitic (Slavic) root of the name, ''Wagria'', meant not only the so-called, present-day Wagrian peninsula, but the entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
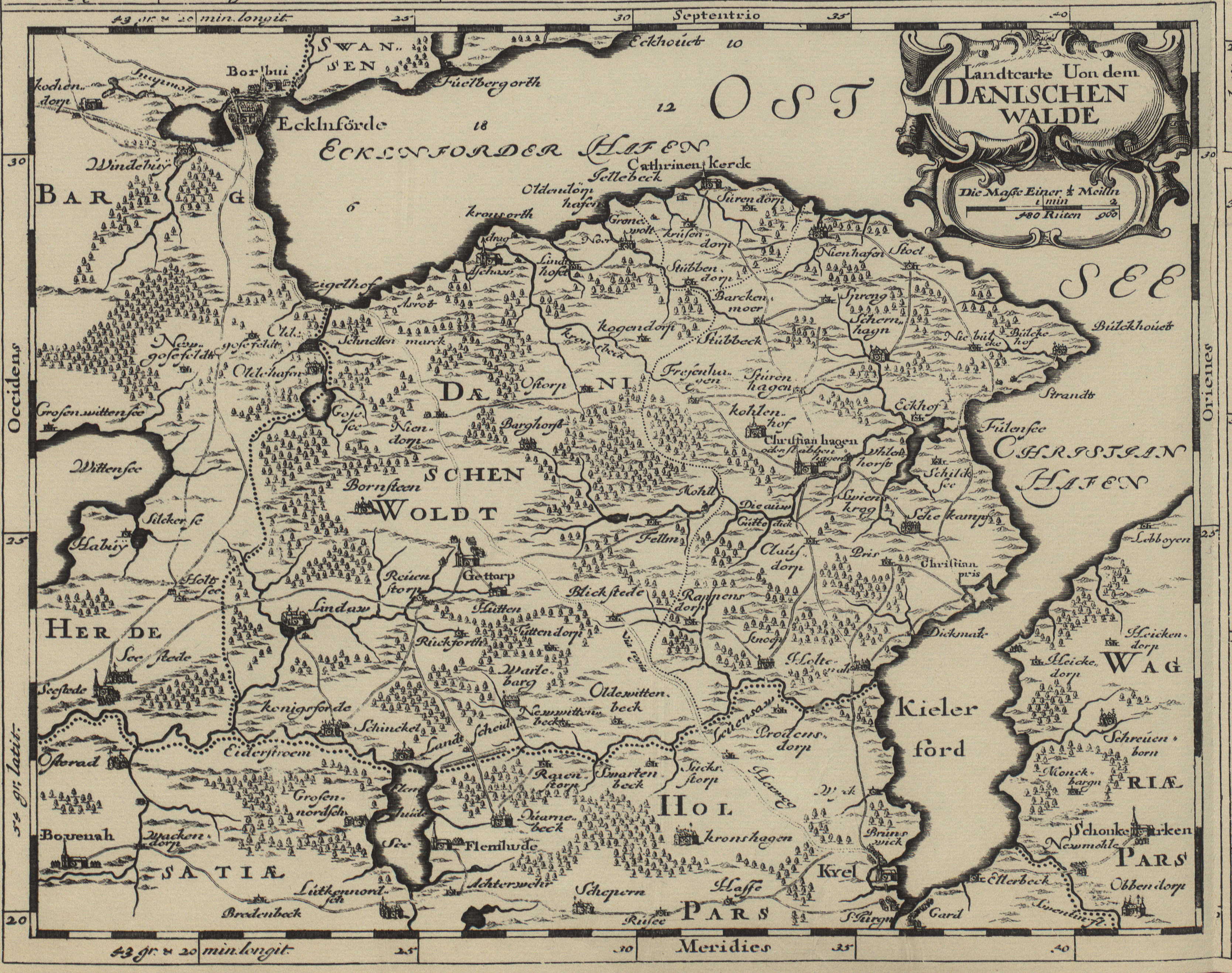
Danish Wahld
The Danish Wahld (, ) is a peninsula in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is located between Eckernförde Bay in the north and Kiel Fjord in the south. The ''Amt'' of " Dänischer Wohld" in the district of Rendsburg-Eckernförde is named after the peninsula, but only encompasses a central part of the region. The Danish Wahld formed a border forest between German and Danish settlements in the Middle Ages with only a few Jute settlements. After 1260 the Danish Wahld was pledged by the Danish king to the north German nobility and German colonists settled in the region.Hans Wilhelm Haefs: ''Ortsnamen und Ortsgeschichten in Schleswig-Holstein'', 2004 The Danish Wahld was in the Middle Ages part of Denmark and after 1200 of the Danish Duchy of Schleswig, where it formed its own goods district. After the Second Schleswig War 1864 the region came to Prussia. The southern Danish Wahld is bordered by the Kiel Canal and remnants of the Eider Canal. It predominantly was composed of the older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hütten Hills
The Hütten Hills (german: Hüttener Berge, da, Hytten Bjerge) are an area of upland, up to , roughly west of the town of Eckernförde in the county of Rendsburg-Eckernförde in the North German state of Schleswig-Holstein. They lie within the Hütten Hills Nature Park. Geography Location The Hütten Hills − part of the Schleswig-Holstein Uplands − lie roughly between Fleckeby to the north, Ascheffel to the east, Alt Duvenstedt, Alt and Neu Duvenstedt to the south and Brekendorf to the west. Their neighbouring landscapes are the large Schleswig Geest to the west, Schwansen to the northeast and the Danish Wahld to the east. Hütten Hills Nature Park The boundaries of the nature park (NSG No. 33392), which was established in 1971 and covers an area of about 219 km2, extends far beyond that of the Hütten Hills to the west and almost reaches the Bay of Eckernförde in the east. To the north is the Schlei Nature Park and to the south – on the ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwansen
Swania (german: Schwansen, da, Svans or ''Svansø'', meaning "swan island/peninsula") is a peninsula in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, protruding into the Baltic Sea. It is located between the Eckernförde Bay to the south and the Schlei (English: Sly) inlet to the north. The Danish dialect South Jutlandic in the Angel Danish variant was still spoken in Swania around 1780 (the last time in the villages near the Schlei). Denmark lost Swania following the Second Schleswig War in 1864. Schwansen is the name of the former ''Amt'' ("collective municipality") Schwansen Swania (german: Schwansen, da, Svans or ''Svansø'', meaning "swan island/peninsula") is a peninsula in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, protruding into the Baltic Sea. It is located between the Eckernförde Bay to the south and the Schlei (Englis ..., which covered most of the peninsula. The seat of the ''Amt'' was in Damp. Peninsulas of Schleswig-Holstein Regions of Schleswig-Holstein Peninsulas of the Baltic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angeln
Anglia (German and Low German: ''Angeln''; Danish and South Jutlandic: ''Angel''; ang, Engla land) is a small peninsula on the eastern coast of Jutland (the Cimbric Peninsula). Jutland consists of the mainland of Denmark and the northernmost German state of Schleswig-Holstein. Anglia belongs to the region of Southern Schleswig, which constitutes the northern part of Schleswig-Holstein, and protrudes into the Bay of Kiel of the Baltic Sea. To the south, Anglia is separated from the neighbouring peninsula of Swania (Ger. ''Schwansen'', Dan. ''Svans'' or ''Svansø'') by the Sly Firth (Ger. ''Schlei'', Dan. ''Sli''), and to the north from the Danish peninsula of Sundeved (Ger. ''Sundewitt'') and the Danish island of Als (Ger. ''Alsen'') by the Flensburg Firth (Ger. ''Flensburger Förde'', Dan. ''Flensborg Fjord''). The landscape is hilly, dotted with numerous lakes. Whether ancient Anglia conformed to the borders of the Anglian Peninsula is uncertain. It may have been somewh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ski Lift
A ski lift is a mechanism for transporting skiers up a hill. Ski lifts are typically a paid service at ski resorts. The first ski lift was built in 1908 by German Robert Winterhalder in Schollach/Eisenbach, Hochschwarzwald. Types * Aerial lifts transport skiers while suspended off the ground. Aerial lifts are often bicable ropeways, the "bi-" prefix meaning that the cables have two different functions (carrying and pulling). **Aerial tramways ** Chairlifts and detachable chairlifts ** Funifors ** Funitels ** Gondola lifts ** Hybrid lifts * Surface lifts, including T-bars, magic carpets, and rope tows. * Cable railways, including funiculars * Helicopters are used for heliskiing and snowcats for snowcat skiing. This is backcountry skiing or boarding accessed by a snowcat or helicopter instead of a lift, or by hiking. Cat skiing is less than half the cost of heliskiing, more expensive than a lift ticket but is easier than ski touring. Cat skiing is guided. Skiing at select, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |