|
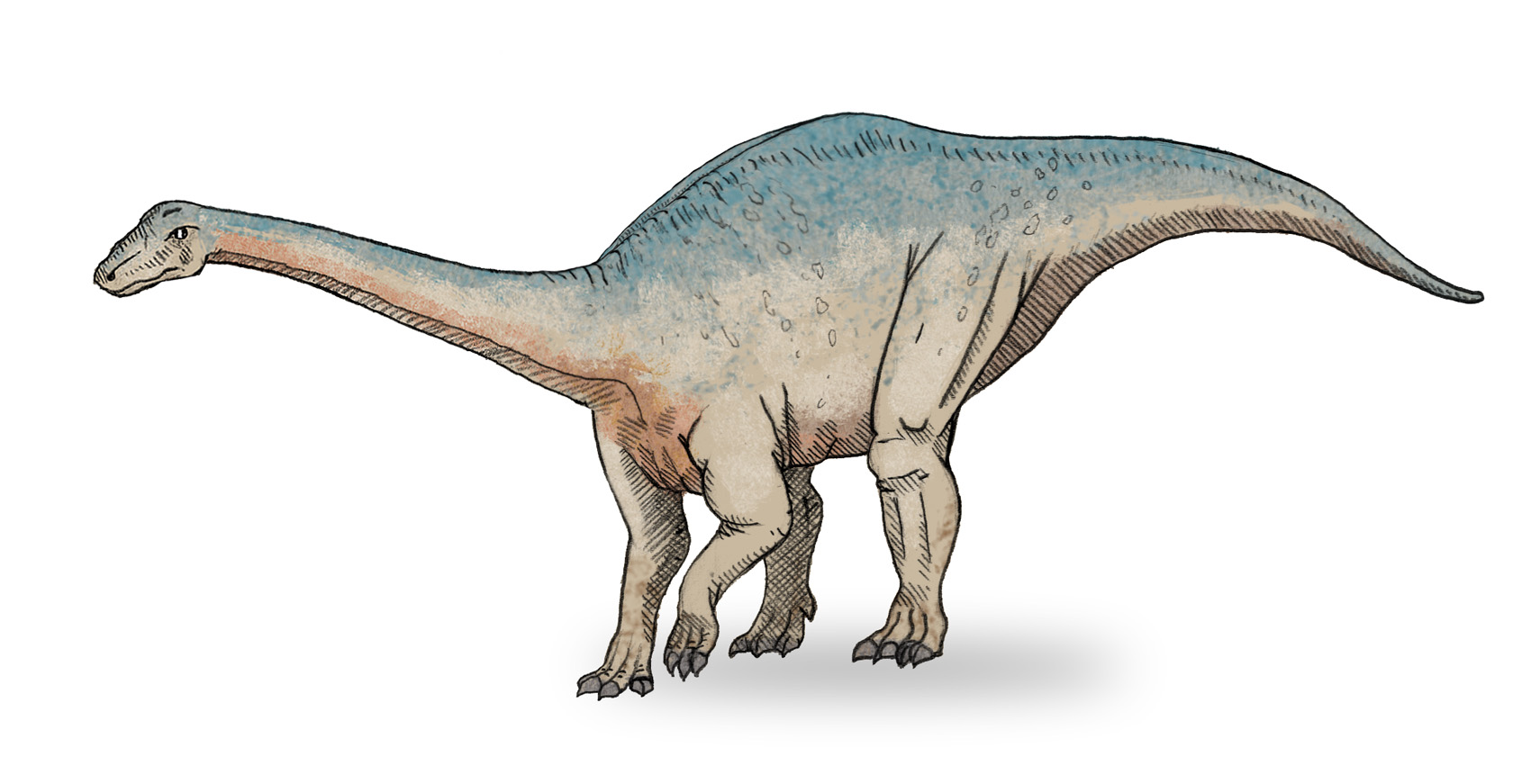
Schleitheimia
''Schleitheimia'' (named after the type locality of Schleitheim), is an extinct genus of sauropodiform sauropodomorph dinosaur, from the Gruhalde Member of Klettgau Formation of Switzerland. The type species, ''Schleitheimia schutzi'' was formally described in 2020. Discovery and naming The type material was collected between 1952 and 1954 by Emil Schutz. They were donated to the University of Zürich in 1955. In 1986, most of the material was described by Peter Galton, who referred them all to the species ''Plateosaurus engelhardti''. In 2020, Oliver Rauhut, Femke Holwerda and Heinz Furrer redescribed most of Schutz's remains, as well as some remains in the collections of the Museum zu Allerheiligen in Schaffhausen and new remains from a excavation in 2016 led by Holwerda. They found that the earlier found remains represented a new genus and species, which they named ''Schleitheimia schultzi'', honoring the type locality and the discoverer of the type remains. The 2016 finds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
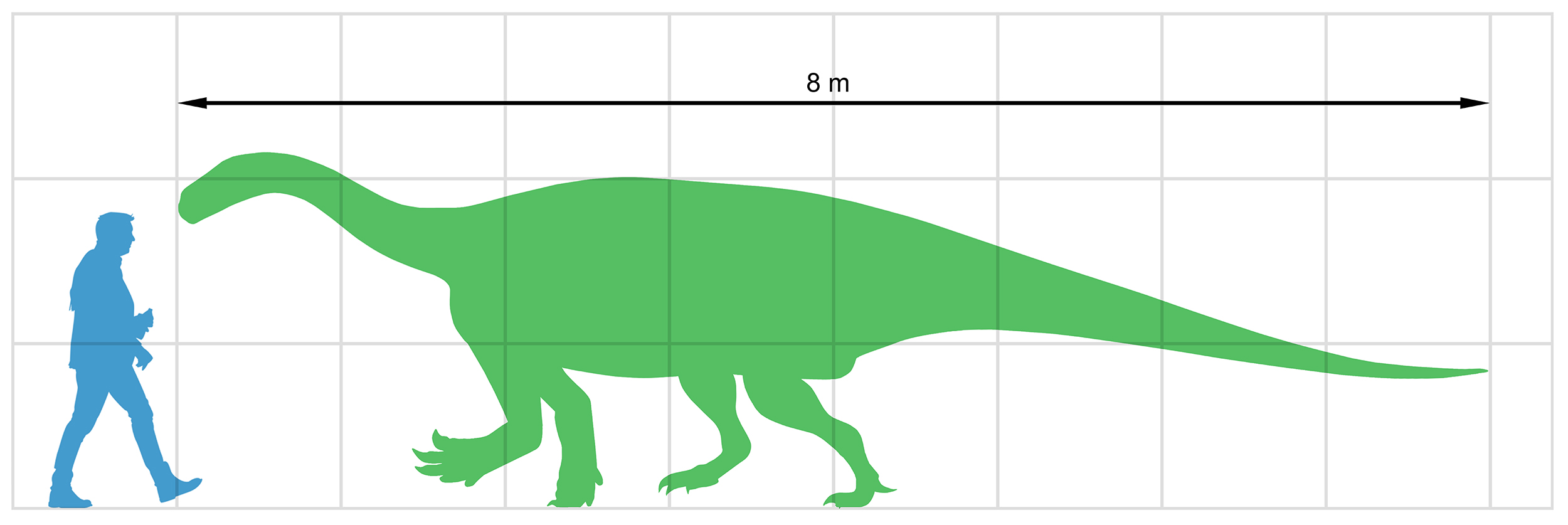
Isanosaurus
''Isanosaurus'' means "North-eastern thailand lizard" was a sauropod dinosaur from Thailand. It was originally dated to approximately 210 million years ago during the Late Triassic (late Norian to Rhaetian stages), which would make it one of the oldest known sauropods. Its age was later considered uncertain, and may be as young as Late Jurassic. The only species is ''Isanosaurus attavipachi''. Though important for the understanding of sauropod origin and early evolution, ''Isanosaurus'' is poorly known. Exact relationships to other early sauropods remain unresolved. Description The only specimen includes a neck vertebra, a back vertebra and part of a second, six tail vertebra, two chevrons, fragmentary ribs, the right sternal plate, the right shoulder blade, and the left thigh bone (femur). This individual may have measured when alive; the thigh bone measures 76 centimetres in length. However, the vertebral neural arches have been found separated from the vertebral cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonerasaurus
''Leonerasaurus'' is a basal genus of sauropodomorph dinosaur. Currently, there is only one species known, named ''L. taquetrensis'' by Diego Pol, Alberto Garrido and Ignacio A. Cerda in 2011. The fossil, an incomplete subadult individual, was found in the Las Leoneras Formation in Argentina. This formation is probably Early Jurassic in age. ''Leonerasaurus'' was a small non- sauropod sauropodomorph, showing an unusual combination of basal and derived characters. This indicates that the evolution of early sauropodomorphs witnessed a great degree of convergent evolution. Discovery The fossils assigned to ''Leonerasaurus'' were found near Cañadón Las Leoneras (an affluent of the left margin of the Chubut river), southeast of Sierra de Taquetrén, Chubut Province, Central Patagonia, Argentina. This formation is probably early Jurassic in age, interpreted as Pliensbachian to Toarcian or late Sinemurian to Toarcian. The volcanic facies of the overlying Lonco Trapial Formatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropoda
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their body), and four thick, pillar-like legs. They are notable for the enormous sizes attained by some species, and the group includes the largest animals to have ever lived on land. Well-known genera include ''Brachiosaurus'', ''Diplodocus'', ''Apatosaurus'' and ''Brontosaurus''. The oldest known unequivocal sauropod dinosaurs are known from the Early Jurassic. ''Isanosaurus'' and ''Antetonitrus'' were originally described as Triassic sauropods, but their age, and in the case of ''Antetonitrus'' also its sauropod status, were subsequently questioned. Sauropod-like sauropodomorph tracks from the Fleming Fjord Formation (Greenland) might, however, indicate the occurrence of the group in the Late Triassic. By the Late Jurassic (150 million yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aardonyx
''Aardonyx'' (Afrikaans ''aard'', "earth" + Greek , "nail, claw") is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur. It is known from the type species ''Aardonyx celestae'' found from the Early Jurassic Elliot Formation of South Africa. ''A. celestae'' was named after Celeste Yates, who prepared much of the first known fossil material of the species. It has arm features that are intermediate between prosauropods and sauropods. Based on the structure of the hind limbs and pelvic girdle of ''Aardonyx'', the dinosaur normally moved bipedally but could drop to quadrupedal movement similar to ''Iguanodon''. It shares some attributes with giant quadrupedal sauropods like ''Apatosaurus''.Associated Press (November 11, 2009)Scientists: New dinosaur species found in South AfricaNPR. Australian paleontologist Adam Yates and his team's discovery of the genus was published online before print in ''Proceedings of the Royal Society B'' in November 2009, and was scheduled to appear in the March 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefapanosaurus
''Sefapanosaurus'' was an early, herbivorous sauropodomorph dinosaur occurring in the southern regions of Gondwana some 200 million years ago in the Late Triassic or Early Jurassic. The sauropodomorphs were the dominant terrestrial herbivores throughout much of the Mesozoic Era, from their origins in the mid-Triassic (approximately 230 Ma) until their decline and fall at the end of the Cretaceous (approximately 66 Ma). A distinctive feature of this dinosaur is the cross-shaped astragalus or talus bone in its ankle. The generic name is derived from the Sesotho word ''sefapano'', meaning ‘cross’ and the Greek word ''saurus'', meaning 'lizard'. The specific name refers to Zastron, the type locality, where the specimen was discovered. History of study This new genus was described in the 23 June 2015 issue of 'Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society' in an essay titled 'A new basal sauropodiform from South Africa and the phylogenetic relationships of basal sauropodomorphs'. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meroktenos
''Meroktenos'' is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period of what is now Lesotho. Discovery and naming In 1959, François Ellenberger, Paul Ellenberger, Jean Fabre and Leonard Ginsburg discovered the type specimen, a thighbone or femur and other assorted bones, south of the village of Thabana Morena. In 1962 these were addressed in a thesis by D. Costedoat. The exact location the bones were recovered, is today unknown. In 1993, François-Xavier Gauffre assigned the remains to a second species of ''Melanorosaurus'': ''Melanorosaurus thabanensis''. The description was provisional, and in 1997 the fossil was described in more detail in a publication by Jacques van Heerden and Peter Malcolm Galton. The specific name refers to the site Thabana-Morena in Lesotho. Gauffre assumed that the specimen had been found in the Upper Elliot Formation dating from the Hettangian-Sinemurian and thus was about twenty million year younger than '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanorosaurus
''Melanorosaurus'' (meaning "Black Mountain Lizard", from the Greek ''melas/'', "black", ''oros/'', "mountain" + ''/'', "lizard") is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period. A herbivore from South Africa, it had a large body and sturdy limbs, suggesting it moved about on all fours. Its limb bones were massive and heavy like the limb bones of true sauropods. Description ''Melanorosaurus'' had a skull which measured approximately 250 mm. The snout was somewhat pointed, and the skull was somewhat triangular when seen from above or below. The premaxilla had four teeth on each side, a characteristic of primitive sauropodomorphs. The maxilla had 19 teeth on each side of the jaw. ''Melanorosaurus'' was around long, with a weight of . Discovery and species The type specimens, syntypes SAM 3449 and SAM 3450, were discovered, described and named in 1924 by Sidney H. Haughton. They were collected from the Triassic Lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lessemsaurus
''Lessemsaurus'' is an extinct genus of sauropod dinosaur belonging to Lessemsauridae. Naming and description The type species, ''L. sauropoides'', was formally described by José Fernando Bonaparte in 1999 in honor of Don Lessem, a writer of popular science books. It was found in the Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in La Rioja Province, Argentina.Weishampel, David B; ''et al.'', 2004. "Dinosaur distribution (Late Triassic, South America)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 527–528. . This dinosaur was around long and was discovered in strata dating to the Norian stage, around 210 million years ago. It is estimated to have reached in maximum body mass. Classification A cladogram after Pol, Garrido & Cerda, 2011, illustrates a possible placing of ''Lessemsaurus'' and ''Antetonitrus'' in Sauropodomorpha: In 2018, Apaldetti ''et al.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antetonitrus
''Antetonitrus'' is a genus of sauropod dinosaur found in the Early Jurassic Elliot Formation of South Africa. The only species is ''Antetonitrus ingenipes''. As one of the oldest known sauropods, it is crucial for the understanding of the origin and early evolution of this group. It was a quadrupedal herbivore, like all of its later relatives, but shows primitive adaptations to use the forelimbs for grasping, instead of purely for weight support. Discovery and naming Adam Yates (paleontologist), Adam Yates, an Australian expert on early sauropodomorphs, named ''Antetonitrus'' in a 2003 report co-authored by South African James Kitching. The name is derived from the Latin ''ante-'' ("before") and ''tonitrus'' ("thunder"), which refers to its existence, before other known sauropods, specifically ''Brontosaurus'' ("thunder lizard"). The one known species of ''Antetonitrus'' is called ''A. ingenipes'', from the Latin ''ingens'' ("massive") and ''pes'' ("foot"), because it shows the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klettgau Formation
The Klettgau Formation is a geological formation in Switzerland. It is Late Triassic in age, covering most of the mid to late Norian, the Carnian, and into the Rhaetian, spanning a period of 26-30 million years.Klettgau Formation at Fossilworks.org Description The primary depositional environment was that of a Dry lake, playa with marine and fluvial Intercalation (geology), intercalations. The lithology is quite variable consisting primarily of fine grained rocks typically claystones and Calcrete, dolocretes, often with sandstone or carbonatic fluvial channel fills.Jordan et al., 2016Fossil content Dinosaur fossils are known from the formation, including those of ''Plateosaurus,' ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulanesaura
''Pulanesaura'' is an extinct genus of basal sauropod known from the Early Jurassic (late Hettangian to Sinemurian) Upper Elliot Formation of the Free State, South Africa. It contains a single species, ''Pulanesaura eocollum'', known from partial remains of at least two subadult to adult individuals. Discovery and naming The remains of ''Pulanesaura'' were discovered in a small quarry in the farm Spion Kop 932 in the Senekal District of the Free State in 2004 by paleontologist Matthew Bonnan. The bones were excavated between 2004 and 2006, and studied by Blair McPhee as part of his dissertation since 2011. ''Pulanesaura'' was then described and named officially by Blair W. McPhee, Matthew F. Bonnan, Adam M. Yates, Johann Neveling and Jonah N. Choiniere in 2015 with the type species ''Pulanesaura eocollum''. The generic name is derived from the Sesoth word for "rain-maker/bringer", ''Pulane'', in reference to the heavy rain conditions under which the remains were collected, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropodiformes
Massopoda is a clade of sauropodomorph dinosaurs which lived during the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous epochs. It was named by paleontologist Adam M. Yates of the University of the Witwatersrand in 2007. Massopoda is a stem-based taxon, defined as all animals more closely related to ''Saltasaurus loricatus'' than to ''Plateosaurus engelhardti''. The name Massopoda, ; , is also contraction of Massospondylidae and Sauropoda, two disparate taxa in the clade. Classification Yates assigned the Massopoda to Plateosauria. Within the clade, he assigned the families Massospondylidae (which includes the relatively well-known dinosaur ''Massospondylus'') and Riojasauridae (which includes ''Riojasaurus'') as well as the Sauropoda. The following is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |