|
Schlegel Diagram
In geometry, a Schlegel diagram is a projection of a polytope from \mathbb^d into \mathbb^ through a point just outside one of its facets. The resulting entity is a polytopal subdivision of the facet in \mathbb^ that, together with the original facet, is combinatorially equivalent to the original polytope. The diagram is named for Victor Schlegel, who in 1886 introduced this tool for studying combinatorial and topological properties of polytopes. In dimension 3, a Schlegel diagram is a projection of a polyhedron into a plane figure; in dimension 4, it is a projection of a 4-polytope to 3-space. As such, Schlegel diagrams are commonly used as a means of visualizing four-dimensional polytopes. Construction The most elementary Schlegel diagram, that of a polyhedron, was described by Duncan Sommerville as follows: :A very useful method of representing a convex polyhedron is by plane projection. If it is projected from any external point, since each ray cuts it twice, it will be r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhedral Schlegel Diagrams
Polyhedral may refer to: *Dihedral (other), various meanings *Polyhedral compound * Polyhedral combinatorics * Polyhedral cone * Polyhedral cylinder * Polyhedral convex function * Polyhedral dice * Polyhedral dual * Polyhedral formula *Polyhedral graph *Polyhedral group *Polyhedral model *Polyhedral net *Polyhedral number *Polyhedral pyramid *Polyhedral prism *Polyhedral space *Polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory *Polyhedral symbol *Polyhedral symmetry *Polyhedral terrain See also * Polyhedron In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices. A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on ..., a geometric shape {{disamb Polyhedra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duncan Sommerville
Duncan MacLaren Young Sommerville (1879–1934) was a Scottish mathematician and astronomer. He compiled a bibliography on non-Euclidean geometry and also wrote a leading textbook in that field. He also wrote ''Introduction to the Geometry of N Dimensions'', advancing the study of polytopes. He was a co-founder and the first secretary of the New Zealand Astronomical Society. Sommerville was also an accomplished watercolourist, producing a series New Zealand landscapes. The middle name 'MacLaren' is spelt using the old orthography M'Laren in some sources, for example the records of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Early life Sommerville was born on 24 November 1879 in Beawar in India, where his father the Rev Dr James Sommerville, was employed as a missionary by the United Presbyterian Church of Scotland. His father had been responsible for establishing the hospital at Jodhpur, Rajputana. The family returned home to Perth, Scotland, where Duncan spent 4 years at a private sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer-Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Polytopes (book)
''Regular Polytopes'' is a geometry book on regular polytopes written by Harold Scott MacDonald Coxeter. It was originally published by Methuen in 1947 and by Pitman Publishing in 1948, with a second edition published by Macmillan in 1963 and a third edition by Dover Publications in 1973. The Basic Library List Committee of the Mathematical Association of America has recommended that it be included in undergraduate mathematics libraries. Overview The main topics of the book are the Platonic solids (regular convex polyhedra), related polyhedra, and their higher-dimensional generalizations. It has 14 chapters, along with multiple appendices, providing a more complete treatment of the subject than any earlier work, and incorporating material from 18 of Coxeter's own previous papers. It includes many figures (both photographs of models by Paul Donchian and drawings), tables of numerical values, and historical remarks on the subject. The first chapter discusses regular polygons, regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxeter
Harold Scott MacDonald "Donald" Coxeter, (9 February 1907 – 31 March 2003) was a British and later also Canadian geometer. He is regarded as one of the greatest geometers of the 20th century. Biography Coxeter was born in Kensington to Harold Samuel Coxeter and Lucy (). His father had taken over the family business of Coxeter & Son, manufacturers of surgical instruments and compressed gases (including a mechanism for anaesthetising surgical patients with nitrous oxide), but was able to retire early and focus on sculpting and baritone singing; Lucy Coxeter was a portrait and landscape painter who had attended the Royal Academy of Arts. A maternal cousin was the architect Sir Giles Gilbert Scott. In his youth, Coxeter composed music and was an accomplished pianist at the age of 10. Roberts, Siobhan, ''King of Infinite Space: Donald Coxeter, The Man Who Saved Geometry'', Walker & Company, 2006, He felt that mathematics and music were intimately related, outlining his ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net (polyhedron)
In geometry, a net of a polyhedron is an arrangement of non-overlapping edge-joined polygons in the plane which can be folded (along edges) to become the faces of the polyhedron. Polyhedral nets are a useful aid to the study of polyhedra and solid geometry in general, as they allow for physical models of polyhedra to be constructed from material such as thin cardboard. An early instance of polyhedral nets appears in the works of Albrecht Dürer, whose 1525 book ''A Course in the Art of Measurement with Compass and Ruler'' (''Unterweysung der Messung mit dem Zyrkel und Rychtscheyd '') included nets for the Platonic solids and several of the Archimedean solids. These constructions were first called nets in 1543 by Augustin Hirschvogel. Existence and uniqueness Many different nets can exist for a given polyhedron, depending on the choices of which edges are joined and which are separated. The edges that are cut from a convex polyhedron to form a net must form a spanning tree of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlegel Wireframe 120-cell
Schlegel is a German occupational surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Anthony Schlegel (born 1981), former American football linebacker * August Wilhelm Schlegel (1767–1845), German poet, older brother of Friedrich * Brad Schlegel (born 1968), Canadian ice hockey player * Bernhard Schlegel (born 1951), German-Canadian chemist and professor at Wayne State University * Carmela Schlegel (born 1983), retired Swiss swimmer * Catharina von Schlegel (1697 – after 1768), German hymn writer * Dorothea von Schlegel (1764–1839), German novelist and translator, wife of Friedrich Schlegel * Elfi Schlegel (born 1964), former Canadian gymnast and sportscaster for NBC Sports * Frits Schlegel (1896–1965), Danish architect * Gustaaf Schlegel (1840–1903), Dutch sinologist and field naturalist * Hans Schlegel (born 1951), German astronaut * Helmut Schlegel (born 1943), German Franciscan, priest, author, meditation instructor, songwriter * Hermann Schlegel (1804–1884), German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodecahedron Schlegel
In geometry, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentagons as faces, which is a Platonic solid. There are also three regular star dodecahedra, which are constructed as stellations of the convex form. All of these have icosahedral symmetry, order 120. Some dodecahedra have the same combinatorial structure as the regular dodecahedron (in terms of the graph formed by its vertices and edges), but their pentagonal faces are not regular: The pyritohedron, a common crystal form in pyrite, has pyritohedral symmetry, while the tetartoid has tetrahedral symmetry. The rhombic dodecahedron can be seen as a limiting case of the pyritohedron, and it has octahedral symmetry. The elongated dodecahedron and trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron variations, along with the rhombic dodecahedra, are space-filling. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
120-cell
In geometry, the 120-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol . It is also called a C120, dodecaplex (short for "dodecahedral complex"), hyperdodecahedron, polydodecahedron, hecatonicosachoron, dodecacontachoron and hecatonicosahedroid. The boundary of the 120-cell is composed of 120 dodecahedral cell (mathematics), cells with 4 meeting at each vertex. Together they form 720 Pentagon, pentagonal faces, 1200 edges, and 600 vertices. It is the 4-Four-dimensional space#Dimensional analogy, dimensional analogue of the regular dodecahedron, since just as a dodecahedron has 12 pentagonal facets, with 3 around each vertex, the ''dodecaplex'' has 120 dodecahedral facets, with 3 around each edge. Its dual polytope is the 600-cell. Geometry The 120-cell incorporates the geometries of every convex regular polytope in the first four dimensions (except the polygons and above). As the sixth and largest regular convex 4-poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodecahedron
In geometry, a dodecahedron (Greek , from ''dōdeka'' "twelve" + ''hédra'' "base", "seat" or "face") or duodecahedron is any polyhedron with twelve flat faces. The most familiar dodecahedron is the regular dodecahedron with regular pentagons as faces, which is a Platonic solid. There are also three regular star dodecahedra, which are constructed as stellations of the convex form. All of these have icosahedral symmetry, order 120. Some dodecahedra have the same combinatorial structure as the regular dodecahedron (in terms of the graph formed by its vertices and edges), but their pentagonal faces are not regular: The pyritohedron, a common crystal form in pyrite, has pyritohedral symmetry, while the tetartoid has tetrahedral symmetry. The rhombic dodecahedron can be seen as a limiting case of the pyritohedron, and it has octahedral symmetry. The elongated dodecahedron and trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron variations, along with the rhombic dodecahedra, are space-filling. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplane
In geometry, a hyperplane is a subspace whose dimension is one less than that of its ''ambient space''. For example, if a space is 3-dimensional then its hyperplanes are the 2-dimensional planes, while if the space is 2-dimensional, its hyperplanes are the 1-dimensional lines. This notion can be used in any general space in which the concept of the dimension of a subspace is defined. In different settings, hyperplanes may have different properties. For instance, a hyperplane of an -dimensional affine space is a flat subset with dimension and it separates the space into two half spaces. While a hyperplane of an -dimensional projective space does not have this property. The difference in dimension between a subspace and its ambient space is known as the codimension of with respect to . Therefore, a necessary and sufficient condition for to be a hyperplane in is for to have codimension one in . Technical description In geometry, a hyperplane of an ''n''-dimensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
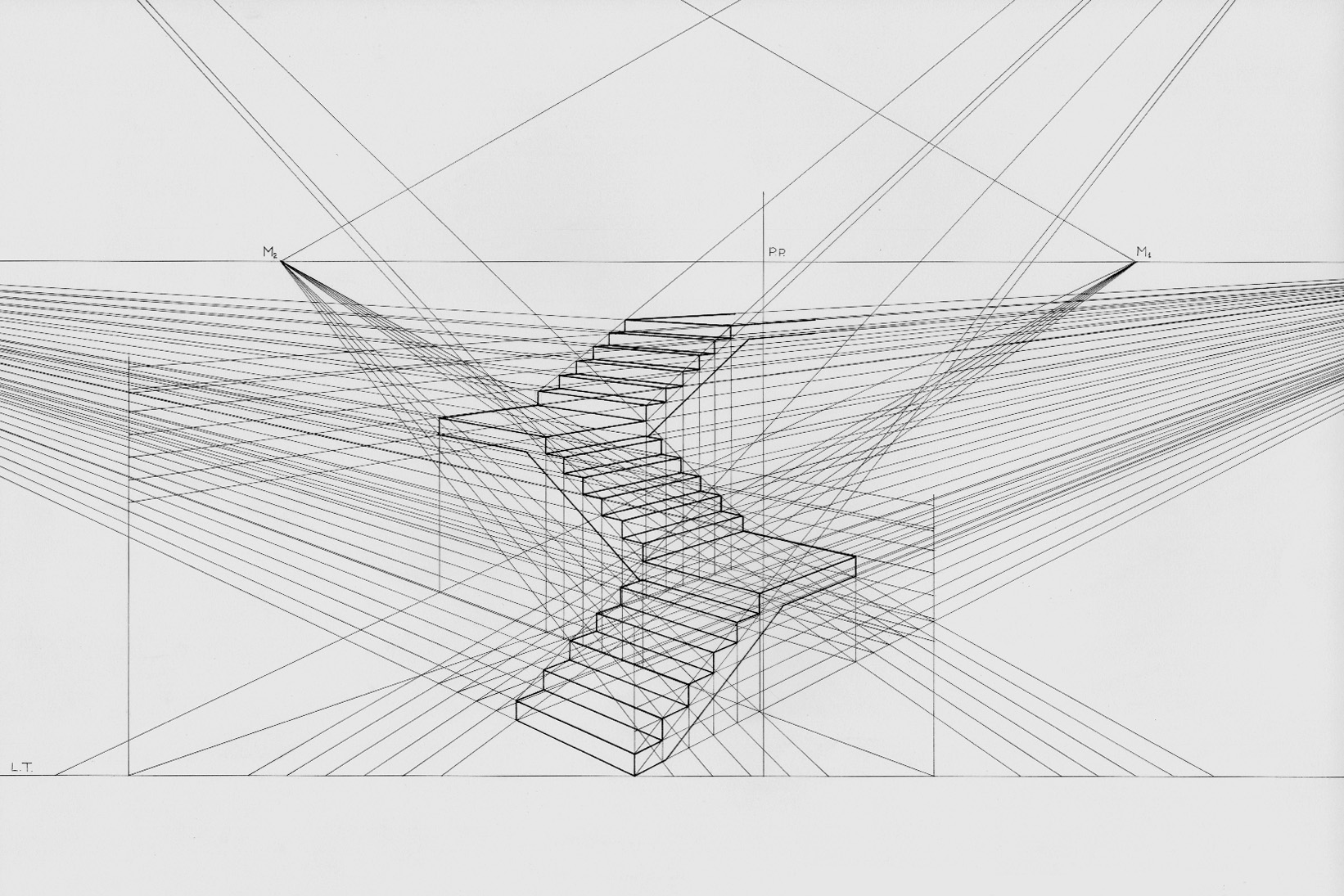
Perspective Projection
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Luca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |