|
Schizosaccharomyces
''Schizosaccharomyces'' is a genus of fission yeasts. The most well-studied species is ''S. pombe''. At present five Schizosaccharomyces species have been described (''S. pombe'', ''S. japonicus'', ''S. octosporus'', ''S. cryophilus'' and ''S. osmophilus''). Like the distantly related ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', ''S. pombe'' is a significant model organism in the study of eukaryotic cell biology. It is particularly useful in evolutionary studies because it is thought to have diverged from the ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' lineage between 300 million and 1 billion years ago, and thus provides an evolutionarily distant comparison. See also *Yeast in winemaking The role of yeast in winemaking is the most important element that distinguishes wine from fruit juice. In the :wikt:anaerobic, absence of oxygen, yeast converts the sugar in wine, sugars of the fruit into ethanol, alcohol and carbon dioxide throu ... References External linksdiArk - Schizosaccharomyces {{Taxonbar, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomyces Pombe
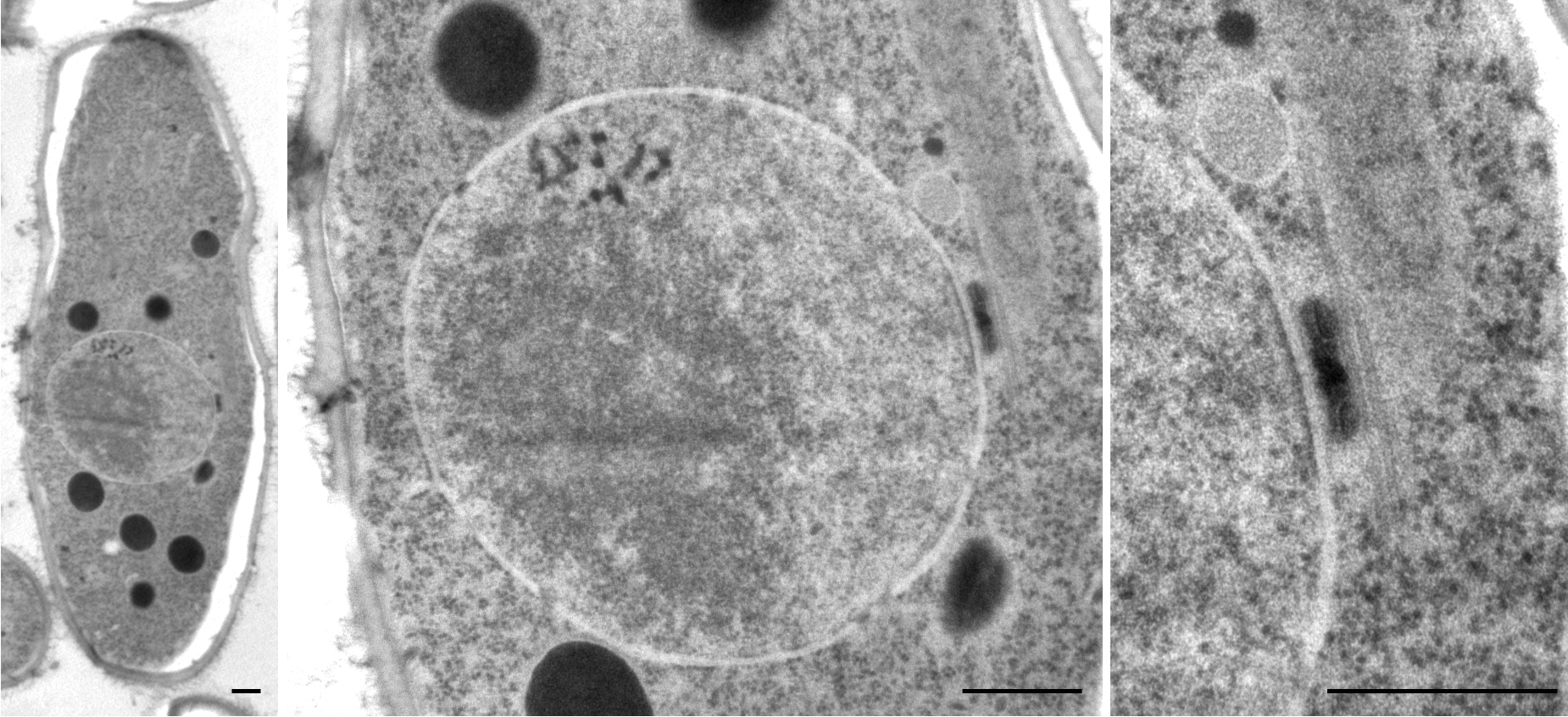
''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs. These cells maintain their shape by growing exclusively through the cell tips and divide by medial fission to produce two daughter cells of equal size, which makes them a powerful tool in cell cycle research. Fission yeast was isolated in 1893 by Paul Lindner from East African millet beer. The species name ''pombe'' is the Swahili word for beer. It was first developed as an experimental model in the 1950s: by Urs Leupold for studying genetics, and by Murdoch Mitchison for studying the cell cycle. Paul Nurse, a fission yeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomyces Japonicus
''Schizosaccharomyces'' is a genus of fission yeasts. The most well-studied species is ''S. pombe''. At present five Schizosaccharomyces species have been described (''S. pombe'', ''S. japonicus'', ''S. octosporus'', ''S. cryophilus'' and ''S. osmophilus''). Like the distantly related ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', ''S. pombe'' is a significant model organism in the study of eukaryotic cell biology. It is particularly useful in evolutionary studies because it is thought to have diverged from the ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' lineage between 300 million and 1 billion years ago, and thus provides an evolutionarily distant comparison. See also *Yeast in winemaking The role of yeast in winemaking is the most important element that distinguishes wine from fruit juice. In the absence of oxygen, yeast converts the sugars of the fruit into alcohol and carbon dioxide through the process of fermentation.Jeff Co ... References External linksdiArk - Schizosaccharomyces {{Taxonbar, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomyces Osmophilus
''Schizosaccharomyces'' is a genus of fission yeasts. The most well-studied species is ''S. pombe''. At present five Schizosaccharomyces species have been described (''S. pombe'', ''S. japonicus'', ''S. octosporus'', ''S. cryophilus'' and ''S. osmophilus''). Like the distantly related ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', ''S. pombe'' is a significant model organism in the study of eukaryotic cell biology. It is particularly useful in evolutionary studies because it is thought to have diverged from the ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' lineage between 300 million and 1 billion years ago, and thus provides an evolutionarily distant comparison. See also *Yeast in winemaking The role of yeast in winemaking is the most important element that distinguishes wine from fruit juice. In the absence of oxygen, yeast converts the sugars of the fruit into alcohol and carbon dioxide through the process of fermentation.Jeff Co ... References External linksdiArk - Schizosaccharomyces {{Taxonbar, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomyces Octosporus
''Schizosaccharomyces'' is a genus of fission yeasts. The most well-studied species is ''S. pombe''. At present five Schizosaccharomyces species have been described (''S. pombe'', ''S. japonicus'', ''S. octosporus'', ''S. cryophilus'' and ''S. osmophilus''). Like the distantly related ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', ''S. pombe'' is a significant model organism in the study of eukaryotic cell biology. It is particularly useful in evolutionary studies because it is thought to have diverged from the ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' lineage between 300 million and 1 billion years ago, and thus provides an evolutionarily distant comparison. See also *Yeast in winemaking The role of yeast in winemaking is the most important element that distinguishes wine from fruit juice. In the absence of oxygen, yeast converts the sugars of the fruit into alcohol and carbon dioxide through the process of fermentation.Jeff Co ... References External linksdiArk - Schizosaccharomyces {{Taxonbar, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomyces Cryophilus
''Schizosaccharomyces'' is a genus of fission yeasts. The most well-studied species is ''S. pombe''. At present five Schizosaccharomyces species have been described (''S. pombe'', ''S. japonicus'', ''S. octosporus'', ''S. cryophilus'' and ''S. osmophilus''). Like the distantly related ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', ''S. pombe'' is a significant model organism in the study of eukaryotic cell biology. It is particularly useful in evolutionary studies because it is thought to have diverged from the ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' lineage between 300 million and 1 billion years ago, and thus provides an evolutionarily distant comparison. See also *Yeast in winemaking The role of yeast in winemaking is the most important element that distinguishes wine from fruit juice. In the absence of oxygen, yeast converts the sugars of the fruit into alcohol and carbon dioxide through the process of fermentation.Jeff Co ... References External linksdiArk - Schizosaccharomyces {{Taxonbar, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditions) are ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeasts
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditions) are calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomycetes
Schizosaccharomycetes is a class in the kingdom of fungi. It contains the order Schizosaccharomycetales, the fission yeasts. The genus Schizosaccharomycetes is a broad and ancient clade within Ascomycota including five known fission yeast: ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically meas ...'', ''Schizosaccharomyces japonicius'', ''Schizosaccharomyces octosporus'', and ''Schizosaccharomyces cryophilus'', and ''Schizosaccharomyces osmophilus''. References Yeasts Fungus classes Taxa described in 1997 {{yeast-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomycetaceae
The Schizosaccharomycetaceae are a family of yeasts in the order Schizosaccharomycetales Schizosaccharomycetales is an order in the kingdom of fungi A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms .... References Yeasts Ascomycota Ascomycota families {{Yeast-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizosaccharomycetales
Schizosaccharomycetales is an order in the kingdom of fungi A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ... that contains the family Schizosaccharomycetaceae. References Yeasts Ascomycota Ascomycota orders {{yeast-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycota
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomyce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |