|
Schizopoda
Schizopoda is a former Taxonomy (biology), taxonomical classification of a division of the Class (biology), class Malacostraca. Although it was split in 1883 by Johan Erik Vesti Boas into the two distinct order (biology), orders Mysidacea and Euphausiacea, the order Schizopoda continued to be in use until the 1930s. References Malacostraca Obsolete arthropod taxa {{Malacostraca-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
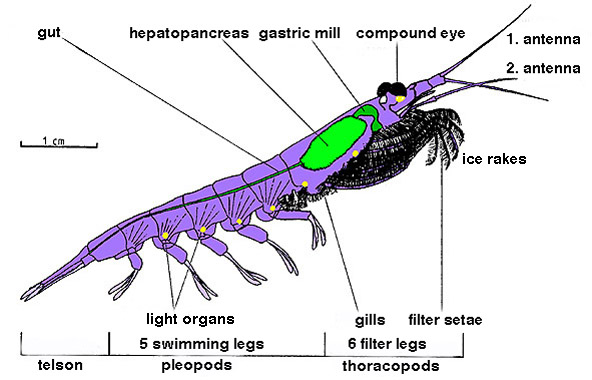
Euphausiacea
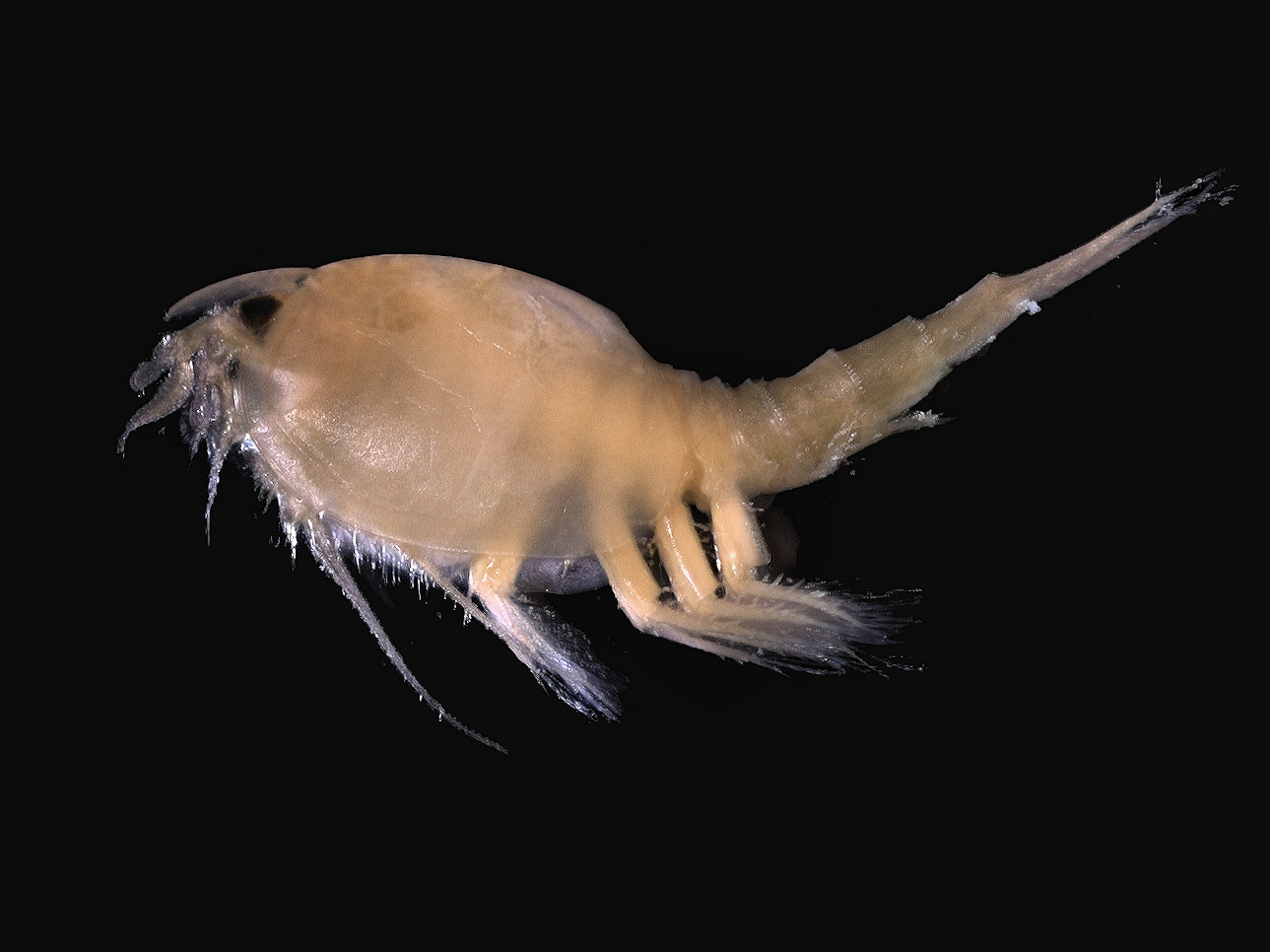
Krill are small crustaceans of the order (biology), order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian language, Norwegian word ', meaning "small Fry (biology), fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish. Krill are considered an important trophic level connection – near the bottom of the food chain. They feed on phytoplankton and (to a lesser extent) zooplankton, yet also are the main source of food for many larger animals. In the Southern Ocean, one species, the Antarctic krill, ''Euphausia superba'', makes up an estimated biomass (ecology), biomass of around 379,000,000 tonnes, making it among the species with the largest total biomass. Over half of this biomass is eaten by whales, Pinniped, seals, penguins, seabirds, squid, and fish each year. Most krill species display large diel vertical migration, daily vertical migrations, thus providing food for predators near the surface at night and in deeper w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the evolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class ( la, classis) is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class fitting between phylum and order. History The class as a distinct rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name (and not just called a ''top-level genus'' ''(genus summum)'') was first introduced by the French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in his classification of plants that appeared in his ''Eléments de botanique'', 1694. Insofar as a general definition of a class is available, it has historically been conceived as embracing taxa that combine a distinct ''grade'' of organization—i.e. a 'level of complexity', measured in terms of how differentiated their organ systems are into distinct regions or sub-organs—with a distinct ''type'' of construction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malacostraca
Malacostraca (from New Latin; ) is the largest of the six classes of crustaceans, containing about 40,000 living species, divided among 16 orders. Its members, the malacostracans, display a great diversity of body forms and include crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, woodlice, amphipods, mantis shrimp, tongue-eating lice and many other less familiar animals. They are abundant in all marine environments and have colonised freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are segmented animals, united by a common body plan comprising 20 body segments (rarely 21), and divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen. Etymology The name Malacostraca was coined by a French zoologist Pierre André Latreille in 1802. He was curator of the arthropod collection at the National Museum of Natural History in Paris. The name comes from the Greek roots (', meaning "soft") and (', meaning "shell"). The name is misleading, since the shell is soft only immediately after moulting, and is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Erik Vesti Boas
Johan Erik Vesti Boas (2 July 1855 – 25 January 1935), "Biographical Etymology of Marine Organism Names. B" (biographies of scientists with names beginning "B"), Hans G. Hansson, TJärnö Marine Biological Laboratory, Göteborg University and Stockholm University, ''tmbl.gu.se'' webpageTMBL-P-Etymol-B also J.E.V. Boas, was a Danish zoologist and a disciple of Carl Gegenbaur and Steenstrup. During the beginning and end of his career, Johan Erik Vesti Boas worked at the Zoological Museum of Copenhagen. However, during an intervening period of 35 years, Boas worked with the Veterinary and Agricultural University of Copenhagen Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan ar ..., because Boas had felt ignored at the appointment of the museum curator post, which went, instead, to G.M. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, wikt:ordo#Latin, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between Family_(biology), family and Class_(biology), class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysidacea
The Mysidacea is a group of shrimp-like crustaceans in the superorder Peracarida, comprising the two extant orders Mysida and Lophogastrida and the prehistoric Pygocephalomorpha The order Pygocephalomorpha is an extinct group of peracarid crustaceans. Pygocephalomorpha were abundant from the Carboniferous until their extinction in the Permian. Families The order contains extinct five families, and seven genera ''incert .... Current data indicate that despite their external similarities, the three orders are not closely related, and the taxon Mysidacea is not used in modern taxonomy. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1208947 Malacostraca Obsolete arthropod taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceana
''Crustaceana'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal specialising in carcinology. It was established in 1960 and is published monthly by Brill Publishers. The journal is abstracted and indexed by BIOSIS Previews, the Science Citation Index, The Zoological Record, and GeoRef. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2011 impact factor of 0.464. The journal is edited by J.C. von Vaupel Klein. It charges an unspecified publication fee from authors of all regular papers, and an optional open access fee of USD 1830.CrustaceanaInstructions for Authors Brill Publishers Brill Academic Publishers (known as E. J. Brill, Koninklijke Brill, Brill ()) is a Dutch international academic publisher founded in 1683 in Leiden, Netherlands. With offices in Leiden, Boston, Paderborn and Singapore, Brill today publishes 27 ... References External links * *{{Official website, http://www.brill.nl/crustaceana Carcinology journals Publications established in 1960 Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |