|
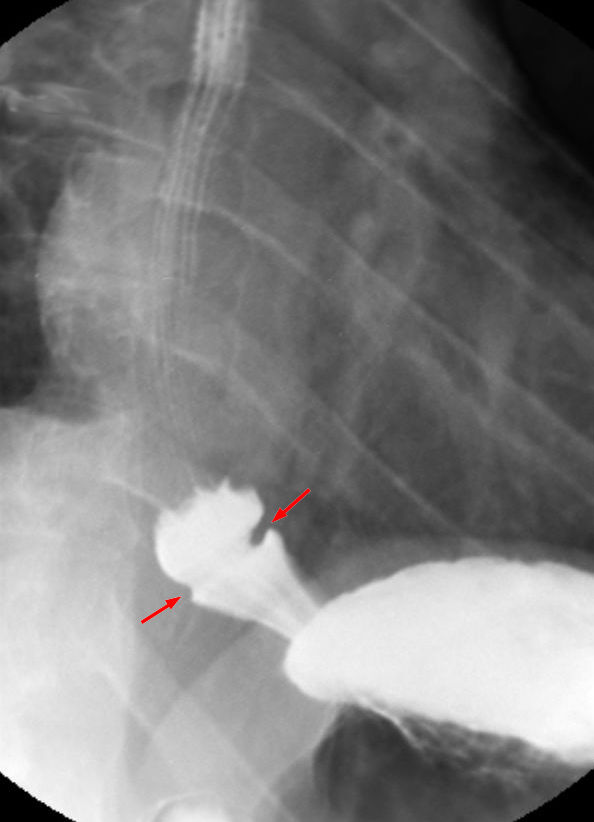
Schatzki Ring
A Schatzki ring or Schatzki–Gary ring is a narrowing of the lower esophagus that can cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). The narrowing is caused by a ring of mucosal tissue (which lines the esophagus) or muscular tissue. A Schatzki ring is a specific type of "esophageal ring", and Schatzki rings are further subdivided into those above the esophagus/stomach junction (A rings), and those found at the squamocolumnar junction in the lower esophagus (B rings). Patients with Schatzki rings can develop intermittent difficulty swallowing or, more seriously, a completely blocked esophagus. The ring is named after the German-American physician Richard Schatzki. Signs and symptoms Not all patients with Schatzki rings have symptoms; barium swallow tests of the esophagus sometimes show Schatzki rings in patients with no swallowing difficulties. When Schatzki rings cause symptoms, they usually result in episodic difficulties with swallowing (dysphagia) solid foods, or a sensation that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD), also called by various other names, is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract down to the duodenum. It is considered a minimally invasive procedure since it does not require an incision into one of the major body cavities and does not require any significant recovery after the procedure (unless sedation or anesthesia has been used). However, a sore throat is common. Alternative names The words ''esophagogastroduodenoscopy'' (EGD; American English) and ''oesophagogastroduodenoscopy'' (OGD; British English; see spelling differences) are both pronounced . It is also called ''panendoscopy'' (PES) and ''upper GI endoscopy''. It is also often called just ''upper endoscopy'', ''upper GI'', or even just ''endoscopy''; because EGD is the most commonly performed type of endoscopy, the ambiguous term ''endoscopy'' is sometimes informally used to refer to EGD b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrett's Esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine and large intestine. This change is considered to be a premalignant condition because it is associated with a high incidence of further transition to esophageal adenocarcinoma, an often-deadly cancer. The main cause of Barrett's esophagus is thought to be an adaptation to chronic acid exposure from reflux esophagitis. Barrett's esophagus is diagnosed by endoscopy: observing the characteristic appearance of this condition by direct inspection of the lower esophagus; followed by microscopic examination of tissue from the affected area obtained from biopsy. The cells of Barrett's esophagus are classified into four categories: nondysplastic, low-grade dysplasia, high-grade dysplasia, and fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Dilatation
Esophageal dilatation is a therapeutic endoscopy, endoscopic procedure that enlarges the lumen (anatomy), lumen of the esophagus. Indications It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions that result in narrowing of the esophageal lumen, or decrease motility in the distal esophagus. These include the following: * Esophageal stricture, Peptic stricture * Eosinophilic esophagitis * Schatzki rings * Achalasia * Scleroderma esophagus * Rarely esophageal cancer Types of dilators There are three major classes of dilators: * Mercury-weighted bougies are blindly inserted Bougie (medical instrument), bougies placed into the esophagus by the treating physician. They are passed in sequentially increasing sizes to dilate the obstructed area. They must be used with precaution in patients with narrow strictures, as they may curl proximal to the obstruction. * Bougie over guidewire dilators are used at the time of esophagogastroduodenoscopy, gastroscopy or fluoroscopy. An endoscopy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Web
Esophageal webs are thin membranes occurring anywhere along the esophagus. Presentation Its main symptoms are pain and difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia). Esophageal webs are thin membranes of normal esophageal tissue consisting of mucosa and submucosa that can partially protrude/obstruct the esophagus. They can be congenital or acquired. Congenital webs commonly appear in the middle and inferior third of the esophagus, and they are more likely to be circumferential with a central or eccentric orifice. Acquired webs are much more common than congenital webs and typically appear in the cervical area (postcricoid). Clinical symptoms of this condition are selective (solid more than liquids) dysphagia, thoracic pain, nasopharyngeal reflux, aspiration, perforation and food impaction (the last two are very rare). file:Zervikales Web.jpg, Esophageal web stenosis in barium swallow examination lateral view. file:Web mit Jet-Phaenomen.jpg, Web with "jet-phenomenon". Arrowhead on inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroesophageal Reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include dental corrosion, dysphagia, heartburn, odynophagia, regurgitation, non-cardiac chest pain, extraesophageal symptoms such as chronic cough, hoarseness, reflux-induced laryngitis, or asthma. On the long term, and when not treated, complications such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus may arise. Risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, and taking certain medications. Medications that may cause or worsen the disease include benzodiazepines, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, NSAIDs, and certain asthma medicines. Acid reflux is due to poor closure of the lower esophageal sphincter, which is at the junction between the stomach and the esoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Pump Inhibitor
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump. They are the most potent inhibitors of acid secretion available. Proton-pump inhibitors have largely superseded the H2-receptor antagonists, a group of medications with similar effects but a different mode of action, and antacids. PPIs are among the most widely sold medications in the world. The class of proton-pump inhibitor medications is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Omeprazole is the specific listed example. Medical uses These medications are used in the treatment of many conditions, such as: * Dyspepsia * Peptic ulcer disease including after endoscopic treatment for bleeding * As part of ''Helicobacter pylori'' eradication therapy * Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD or GORD) including symptomatic endoscopy-negative reflux disea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ether, propofol, etomidate, ketamine, pentobarbital, lorazepam and midazolam. Medical uses Sedation is typically used in minor surgical procedures such as endoscopy, vasectomy, or dentistry and for reconstructive surgery, some cosmetic surgeries, removal of wisdom teeth, or for high-anxiety patients. Sedation methods in dentistry include inhalation sedation (using nitrous oxide), oral sedation, and intravenous (IV) sedation. Inhalation sedation is also sometimes referred to as ''relative analgesia''. Sedation is also used extensively in the intensive care unit so that patients who are being ventilated tolerate having an endotracheal tube in their trachea. It can also be used during a long term brain EEG to help patient relax. Risks There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consumpti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver and was formerly named hydrargyrum ( ) from the Greek words, ''hydor'' (water) and ''argyros'' (silver). A heavy, silvery d-block A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-blo ... element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Mercury is used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Dilatation
Esophageal dilatation is a therapeutic endoscopy, endoscopic procedure that enlarges the lumen (anatomy), lumen of the esophagus. Indications It can be used to treat a number of medical conditions that result in narrowing of the esophageal lumen, or decrease motility in the distal esophagus. These include the following: * Esophageal stricture, Peptic stricture * Eosinophilic esophagitis * Schatzki rings * Achalasia * Scleroderma esophagus * Rarely esophageal cancer Types of dilators There are three major classes of dilators: * Mercury-weighted bougies are blindly inserted Bougie (medical instrument), bougies placed into the esophagus by the treating physician. They are passed in sequentially increasing sizes to dilate the obstructed area. They must be used with precaution in patients with narrow strictures, as they may curl proximal to the obstruction. * Bougie over guidewire dilators are used at the time of esophagogastroduodenoscopy, gastroscopy or fluoroscopy. An endoscopy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Web
Esophageal webs are thin membranes occurring anywhere along the esophagus. Presentation Its main symptoms are pain and difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia). Esophageal webs are thin membranes of normal esophageal tissue consisting of mucosa and submucosa that can partially protrude/obstruct the esophagus. They can be congenital or acquired. Congenital webs commonly appear in the middle and inferior third of the esophagus, and they are more likely to be circumferential with a central or eccentric orifice. Acquired webs are much more common than congenital webs and typically appear in the cervical area (postcricoid). Clinical symptoms of this condition are selective (solid more than liquids) dysphagia, thoracic pain, nasopharyngeal reflux, aspiration, perforation and food impaction (the last two are very rare). file:Zervikales Web.jpg, Esophageal web stenosis in barium swallow examination lateral view. file:Web mit Jet-Phaenomen.jpg, Web with "jet-phenomenon". Arrowhead on inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumen (anatomy)
In biology, a lumen (plural lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine. It comes . It can refer to: *The interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows. *The interior of the gastrointestinal tract *The pathways of the bronchi in the lungs *The interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ducts *The pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vagina, splitting up in two lumina in the uterus, both of which continue through the Fallopian tubes In cell biology, a lumen is a membrane-defined space that is found inside several organelles, cellular components, or structures: *thylakoid, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondrion, or microtubule Transluminal procedures ''Transluminal procedures'' are procedures occurring through lumina, including: *Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in the lumina of, for example, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |