|
Schanze
A ''schanze'' () is, according to the specialist terminology of German fortification construction, an independent fieldwork, that is frequently used in the construction of temporary (not permanent) field fortifications.Rüstow: ''Militärisches Handwörterbuch.'' 1859, s.v. Schanze The word is German and has no direct English equivalent, although the word sconce is derived from Dutch ''schans'', which is cognate to the German word. In everyday German speech, however, it is commonplace to refer to permanent fortifications as ''schanzen'', because in many places in times of war, fieldworks that were only temporarily thrown up were later turned into permanent fortifications. Derivation The word ''Schanze'' derives originally from the fact that, during sieges in the Late Middle Ages, temporary defensive positions had frequently been built out of gabions, known in German as ''Schanzkörbe''.Duden: ''Herkunftswörterbuch.'' under ''Schanze'' Later such ''schanzen'' very often consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
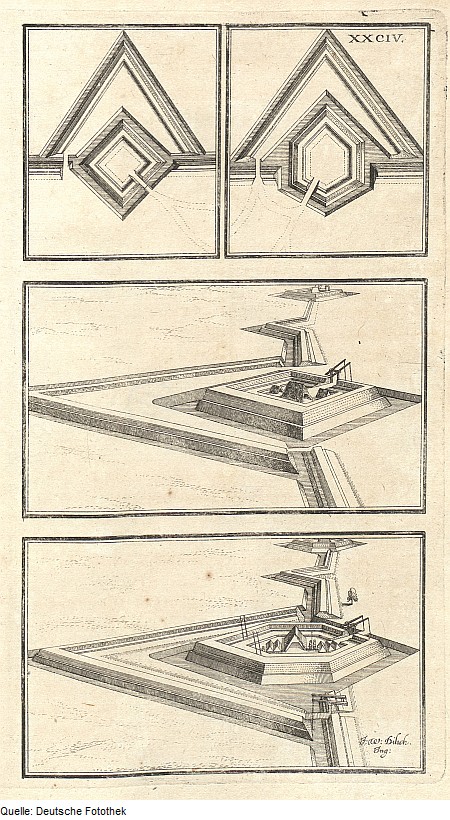
Baroque Schanzen
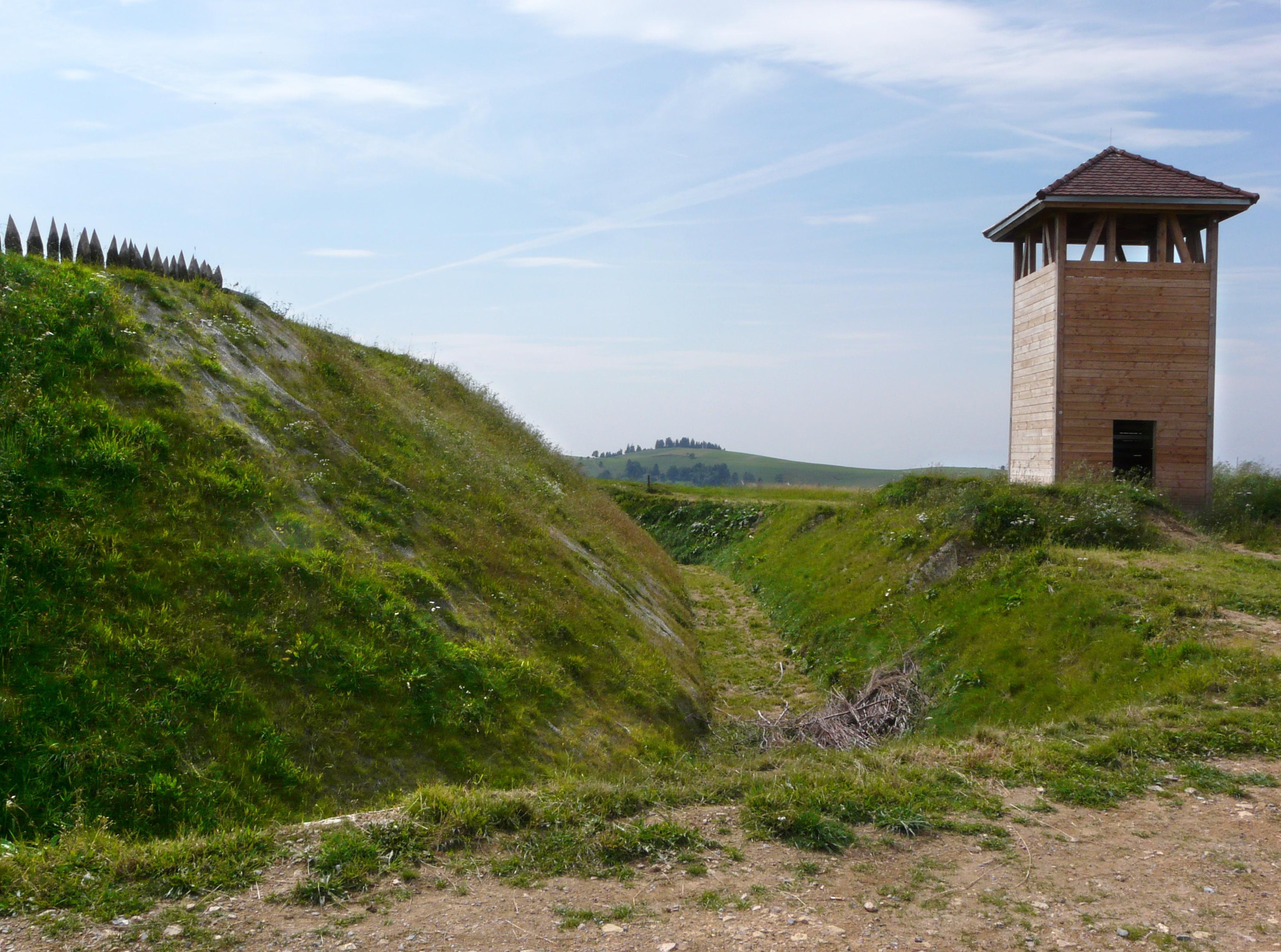
The Baroque fortifications in the Black Forest (german: link=no, Barocke Verteidigungsanlagen im Schwarzwald), also called Baroque Schanzen (''Barockschanzen'') or Black Forest lines (''Schwarzwaldlinien''), are historical, military earthworks, known as ''schanzen'', that were built in the Black Forest in what is now Germany. They were built in the 17th century to defend the Margraviate of Baden from French invasion. Together with their adjoining defensive lines, the Black Forest fortifications formed a defensive system over long that ran from north to south. Construction These defensive positions were built during the time of the conflicts between the House of Habsburg and the Kingdom of France in the 17th and 18th centuries, mainly during the War of the Palatine Succession and the War of the Spanish Succession. After the events of 1689 (including the destruction of Heidelberg Castle), Margrave Louis William of Baden-Baden (1655–1707), who was also known as "Turkish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barockschanze Gersbach
The Baroque fortifications in the Black Forest (german: link=no, Barocke Verteidigungsanlagen im Schwarzwald), also called Baroque Schanzen (''Barockschanzen'') or Black Forest lines (''Schwarzwaldlinien''), are historical, military earthworks, known as ''schanzen'', that were built in the Black Forest in what is now Germany. They were built in the 17th century to defend the Margraviate of Baden from French invasion. Together with their adjoining defensive lines, the Black Forest fortifications formed a defensive system over long that ran from north to south. Construction These defensive positions were built during the time of the conflicts between the House of Habsburg and the Kingdom of France in the 17th and 18th centuries, mainly during the War of the Palatine Succession and the War of the Spanish Succession. After the events of 1689 (including the destruction of Heidelberg Castle), Margrave Louis William of Baden-Baden (1655–1707), who was also known as "Turkish Louis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barockschanze
The Baroque fortifications in the Black Forest (german: link=no, Barocke Verteidigungsanlagen im Schwarzwald), also called Baroque Schanzen (''Barockschanzen'') or Black Forest lines (''Schwarzwaldlinien''), are historical, military earthworks, known as ''schanzen'', that were built in the Black Forest in what is now Germany. They were built in the 17th century to defend the Margraviate of Baden from French invasion. Together with their adjoining defensive lines, the Black Forest fortifications formed a defensive system over long that ran from north to south. Construction These defensive positions were built during the time of the conflicts between the House of Habsburg and the Kingdom of France in the 17th and 18th centuries, mainly during the War of the Palatine Succession and the War of the Spanish Succession. After the events of 1689 (including the destruction of Heidelberg Castle), Margrave Louis William of Baden-Baden (1655–1707), who was also known as "Turkish Louis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Fortifications In The Black Forest
The Baroque fortifications in the Black Forest (german: link=no, Barocke Verteidigungsanlagen im Schwarzwald), also called Baroque Schanzen (''Barockschanzen'') or Black Forest lines (''Schwarzwaldlinien''), are historical, military earthworks, known as '' schanzen'', that were built in the Black Forest in what is now Germany. They were built in the 17th century to defend the Margraviate of Baden from French invasion. Together with their adjoining defensive lines, the Black Forest fortifications formed a defensive system over long that ran from north to south. Construction These defensive positions were built during the time of the conflicts between the House of Habsburg and the Kingdom of France in the 17th and 18th centuries, mainly during the War of the Palatine Succession and the War of the Spanish Succession. After the events of 1689 (including the destruction of Heidelberg Castle), Margrave Louis William of Baden-Baden (1655–1707), who was also known as "Turkish Loui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sconce (fortification)
A sconce is a small protective fortification, such as an earthwork, often placed on a mound as a defensive work for artillery. It was used primarily in Northern Europe from the late Middle Ages until the 19th century. This type of fortification was common during the English Civil War, and the remains of one such structure can be seen on Fort Royal Hill in Worcester, England. During the Eighty Years' War for Dutch independence, the sconces (''schans'' in Dutch) were often used to defend strategic places, but were used also during sieges and in circumvallations. Several more or less intact sconces remain in the Netherlands. The Zaanse Schans, one of the top tourist locations in the Netherlands, derived its name from its original function as a sconce. Sconces played a major part in the Serbian Revolution, countering the numerical superiority of the Turkish army. Etymology The etymology of sconce is from the Latin ''absconsus'', via the French ''esconce'': a word of many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sconce (fortification)
A sconce is a small protective fortification, such as an earthwork, often placed on a mound as a defensive work for artillery. It was used primarily in Northern Europe from the late Middle Ages until the 19th century. This type of fortification was common during the English Civil War, and the remains of one such structure can be seen on Fort Royal Hill in Worcester, England. During the Eighty Years' War for Dutch independence, the sconces (''schans'' in Dutch) were often used to defend strategic places, but were used also during sieges and in circumvallations. Several more or less intact sconces remain in the Netherlands. The Zaanse Schans, one of the top tourist locations in the Netherlands, derived its name from its original function as a sconce. Sconces played a major part in the Serbian Revolution, countering the numerical superiority of the Turkish army. Etymology The etymology of sconce is from the Latin ''absconsus'', via the French ''esconce'': a word of many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf's Lair
The ''Wolf's Lair'' (german: Wolfsschanze; pl, Wilczy Szaniec) served as Adolf Hitler's first Eastern Front military headquarters in World War II. The headquarters was located in the Masurian woods, near the small village of Görlitz in Ostpreußen (now Gierłoż), about 8 kilometres (5 miles) east of the small East Prussian town of Rastenburg (now Kętrzyn), in present-day Poland. Being one of the most heavily guarded places in the world, the central complex and the ''Führer'''s bunker was surrounded by three security zones guarded by two SS units: the '' SS-Begleitkommando des Führers'', and the '' Reichssicherheitsdienst''. The ''Wehrmacht''s armoured '' Führerbegleitbrigade'' was held in readiness nearby but, as a part of the ''Heer'''s elite ''Großdeutschland'' Division, was used to counter-attack Red Army break-throughs in Army Group Centre's front and rescue cut-off ''Heer'', ''Luftwaffe'' '' Fallschirmjager'' and SS panzer troops. The most notable event that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Forest
The Black Forest (german: Schwarzwald ) is a large forested mountain range in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwest Germany, bounded by the Rhine Valley to the west and south and close to the borders with France and Switzerland. It is the source of the Danube and Neckar rivers. Its highest peak is the Feldberg with an elevation of above sea level. Roughly oblong in shape, with a length of and breadth of up to , it has an area of about 6,009 km2 (2,320 sq mi). Historically, the area was known for forestry and the mining of ore deposits, but tourism has now become the primary industry, accounting for around 300,000 jobs. There are several ruined military fortifications dating back to the 17th century. History In ancient times, the Black Forest was known as , after the Celtic deity, Abnoba. In Roman times ( Late antiquity), it was given the name ("Marcynian Forest", from the Germanic word ''marka'' = "border"). The Black Forest probably represented the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunette (fortification)
In fortification, a ''lunette'' was originally an outwork of half-moon shape; later it became a redan with short flanks, in trace somewhat resembling a bastion standing by itself without curtains on either side. The gorge was generally open. One noted historical example of a lunette was the one used at the Battle of the Alamo in San Antonio, Texas, in March 1836. Another were the Bagration flèches, at the Battle of Borodino, in 1812. See also * List of established military terms This is a list of established military terms which have been in use for at least 50 years. Since technology and doctrine have changed over time, not all of them are in current use, or they may have been superseded by more modern terms. However, the ... References {{fortifications Fortification (architectural elements) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meyers Konversations-Lexikon
' or ' was a major encyclopedia in the German language that existed in various editions, and by several titles, from 1839 to 1984, when it merged with the '. Joseph Meyer (1796–1856), who had founded the publishing house in 1826, intended to issue a universal encyclopaedia meant for a broad public: people having a general knowledge as well as businessmen, technicians and scholars, considering contemporary works like those of and to be superficial or obsolete. First edition The first part of ' ("Great encyclopaedia for the educated classes") appeared in October 1839. In contrast to its contemporaries, it contained maps and illustrations with the text. There is no indication of the planned number of volumes or a time limit for this project, but little headway had been made by the otherwise dynamic . After six years, 14 volumes had appeared, covering only one fifth of the alphabet. Another six years passed before the last (46th) volume was published. Six supplementary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after Frederick Barbarossa ("red beard"), a 12th-century Holy Roman emperor and German king, put into action Nazi Germany's ideological goal of conquering the western Soviet Union to repopulate it with Germans. The German aimed to use some of the conquered people as forced labour for the Axis war effort while acquiring the oil reserves of the Caucasus as well as the agricultural resources of various Soviet territories. Their ultimate goal was to create more (living space) for Germany, and the eventual extermination of the indigenous Slavic peoples by mass deportation to Siberia, Germanisation, enslavement, and genocide. In the two years leading up to the invasion, Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union signed political and economic pacts fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)