|
Scamander, Tasmania
Scamander is a small town at the mouth of the Scamander River between St Helens and St Marys on the north-east coast of Tasmania in Australia. The town is a popular holiday destination because of its wide, sandy beaches and views of the ocean. Recreational activities include surfing, swimming and fishing for bream in the river. History The first European to travel through the area was surveyor John Helder Wedge in 1825. He named the river "Borthwick" and the position itself he named "Yarmouth" after the English port Great Yarmouth but both the river and town were both later renamed "Scamander". The wide river mouth has been a challenge to bridge builders for many years. Richard Terry constructed a timber bridge in 1865, but it collapsed around May in 1875 while a large herd of cattle was being driven across it. A second and third bridge were successively washed away in floods in 1889 and 1911. Further bridges succumbed to flood and shipworms, the last timber bridge collapsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Lyons (state)
The electoral division of Lyons is one of the five electorates in the Tasmanian House of Assembly, it is the largest electorate covering most of central and eastern Tasmania. Lyons is named jointly in honor of Joseph Lyons, Prime Minister of Australia (1932–1939); Premier of Tasmania (1923–1928), and Joseph's wife, Dame Enid Lyons, the first woman elected to the Australian House of Representatives in 1943. The electorate shares its name and boundaries with the federal division of Lyons. Lyons and the other House of Assembly electoral divisions are each represented by five members elected under the Hare-Clark electoral system. History and electoral profile Before 1984, it was known as the Division of Wilmot. In 1984, it was renamed to jointly honour Joseph Lyons, and his wife, Dame Enid Lyons, the first woman elected to the Australian House of Representatives in 1943 and subsequently the first female member of Cabinet (1949–1951). Joseph Lyons represented the area fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Helder Wedge
John Helder Wedge (1793 – 22 November 1872) was a surveyor, explorer and politician in Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania, Australia).G. H. Stancombe'Wedge, John Helder (1793 - 1872), Australian Dictionary of Biography, Online Edition Wedge was the second son of Charles Wedge of Shudy Camps, of Cambridgeshire, England. John Wedge learned the basics of surveying from his father. Due to financial losses during the post-war depression in agriculture, Wedge and his brother Edward decided to migrate to Van Diemen's Land; before leaving London Wedge had obtained an appointment in the colony as assistant surveyor. Van Diemens Land The brothers arrived in Van Diemen's Land aboard the ''Heroine'' on the morning of 15 April 1824. Wedge led several expeditions through heavily timbered and mountainous country in the north-east and central highlands of the island. On one of these journeys Wedge found a camp of the bushrangers led by Matthew Brady. For Wedge's efforts in their capture he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Meteorology (Australia)
The Bureau of Meteorology (BOM or BoM) is an executive agency of the Australian Government responsible for providing weather services to Australia and surrounding areas. It was established in 1906 under the Meteorology Act, and brought together the state meteorological services that existed before then. The states officially transferred their weather recording responsibilities to the Bureau of Meteorology on 1 January 1908. History The Bureau of Meteorology was established on 1 January 1908 following the passage of the ''Meteorology Act 1906''. Prior to Federation in 1901, each colony had had its own meteorological service, with all but two colonies also having a subsection devoted to astronomy. In August 1905, federal home affairs minister Littleton Groom surveyed state governments for their willingness to cede control, finding South Australia and Victoria unwilling. However, at a ministerial conference in April 1906 the state governments agreed to transfer responsibility for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasman Highway
The Tasman Highway (or A3) is a highway in Tasmania, Australia. Like the Midland Highway, it connects the major cities of Hobart and Launceston – however it takes a different route, via the north-eastern and eastern coasts of the state. The Highway also acts as a major commuter road to Hobart residents living on the eastern side of the Derwent River. The designation "Tasman Highway" arises from its location facing the Tasman Sea – named, like the state itself, after Abel Tasman. The highway is one of the longest in Tasmania - , with an average traveling time of 4 hours. Eastern Outlet The Eastern Outlet is a section of the Tasman Highway between Hobart and Sorell. As one of the city's 3 major radial highways, the outlet connects traffic from the Hobart city centre with Hobart Airport and commuters on the eastern shore of the River Derwent as well as intrastate traffic on the east coast and Tasman Peninsula. With recorded Annual average daily traffic of 67,000, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truss Bridge
A truss bridge is a bridge whose load-bearing superstructure is composed of a truss, a structure of connected elements, usually forming triangular units. The connected elements (typically straight) may be stressed from tension, compression, or sometimes both in response to dynamic loads. The basic types of truss bridges shown in this article have simple designs which could be easily analyzed by 19th and early 20th-century engineers. A truss bridge is economical to construct because it uses materials efficiently. Design The nature of a truss allows the analysis of its structure using a few assumptions and the application of Newton's laws of motion according to the branch of physics known as statics. For purposes of analysis, trusses are assumed to be pin jointed where the straight components meet, meaning that taken alone, every joint on the structure is functionally considered to be a flexible joint as opposed to a rigid joint with strength to maintain its own shape, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
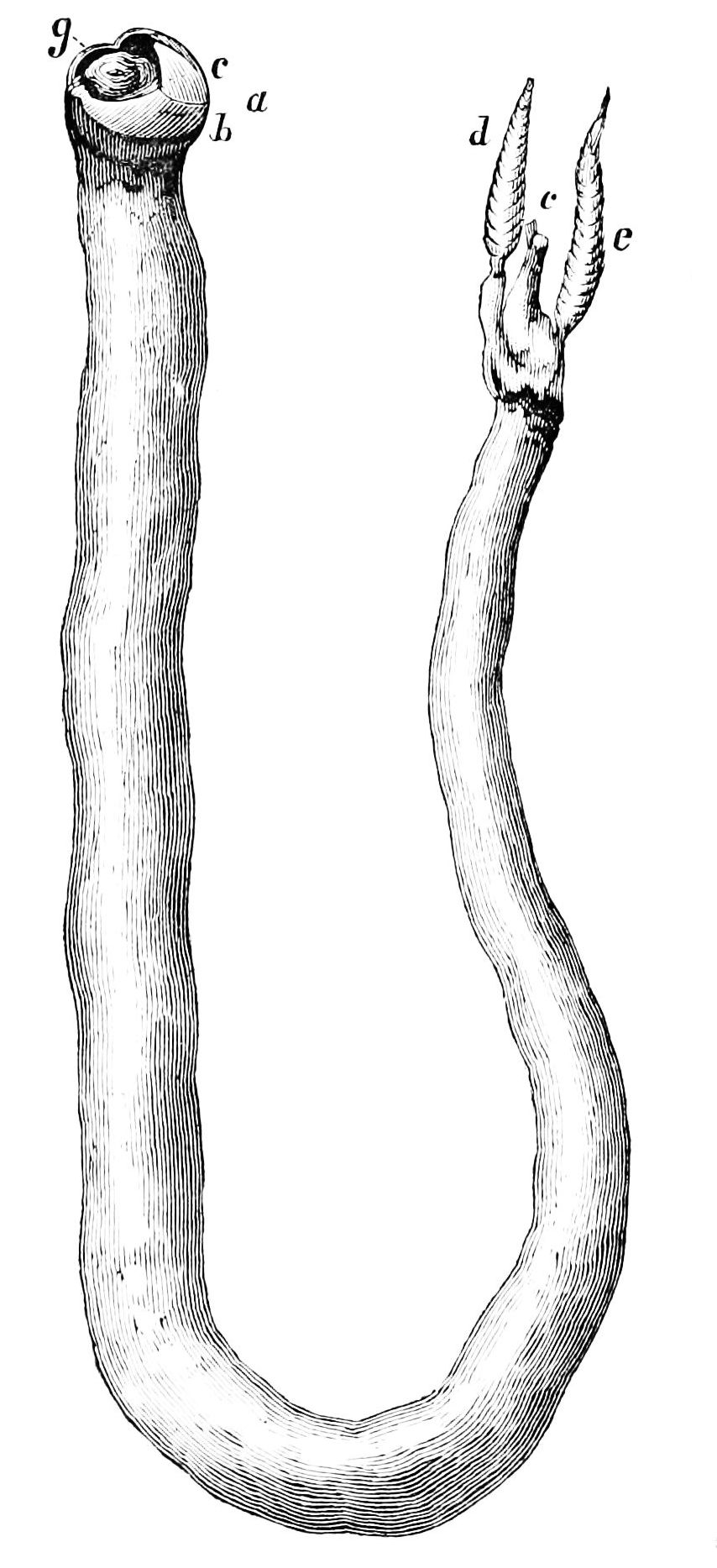
Shipworm
The shipworms are marine bivalve molluscs in the family Teredinidae: a group of saltwater clams with long, soft, naked bodies. They are notorious for boring into (and commonly eventually destroying) wood that is immersed in sea water, including such structures as wooden piers, docks and ships; they drill passages by means of a pair of very small shells (“ valves”) borne at one end, with which they rasp their way through. Sometimes called "termites of the sea", they also are known as " Teredo worms" or simply Teredo (from grc, τερηδών, , translit=terēdṓn, lit=wood-worm via ). Carl Linnaeus assigned the common name '' Teredo'' to the best-known genus of shipworms in the 10th edition of his taxonomic '' magnum opus'', ''Systema Naturæ'' (1758). Description Removed from its burrow, the fully grown teredo ranges from several centimetres to about a metre in length, depending on the species. The body is cylindrical, slender, naked and superficially vermiform, meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Terry (bridge Builder) (born 1974), American football player
{{hndis, Terry, Richard ...
Richard Terry may refer to: *Ben Terry (Richard Benjamin Terry, fl. 1877–1881), Test cricket umpire *Sir Richard Terry (musicologist) (1864–1938), English organist, choir director and musicologist *Richard Terry, chef de cuisine of the Oriental Club, author of ''Indian Cookery'' (1861) *Rick Terry Richard Ross Terry, Jr. (born April 5, 1974) is a former American football defensive tackle in the National Football League (NFL). He played from 1997 to 1999 for the New York Jets and the Carolina Panthers. He played college football at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Yarmouth
Great Yarmouth (), often called Yarmouth, is a seaside resort, seaside town and unparished area in, and the main administrative centre of, the Borough of Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, England; it straddles the River Yare and is located east of Norwich. A population of 38,693 in the 2011 Census made it Norfolk's third most populous. Its fishing industry, mainly for herring, shrank after the mid-20th century and has all but ended. North Sea oil from the 1960s supplied an oil-rig industry that services offshore natural gas rigs; more recently, offshore wind power and other renewable energy industries have ensued. Yarmouth has been a resort since 1760 and a gateway from the Norfolk Broads to the North Sea. Holiday-making rose when a railway opened in 1844, bringing easier, cheaper access and some new settlement. Wellington Pier opened in 1854 and Britannia Pier in 1858. Through the 20th century, Yarmouth boomed as a resort, with a promenade, pubs, trams, fish-and-chip shops, theatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bream
Bream ( ) are species of freshwater and marine fish belonging to a variety of genera including '' Abramis'' (e.g., ''A. brama'', the common bream), '' Acanthopagrus'', '' Argyrops'', '' Blicca'', '' Brama'', '' Chilotilapia'', ''Etelis'', '' Lepomis'', '' Gymnocranius'', ''Lethrinus'', '' Nemipterus'', '' Pharyngochromis'', '' Rhabdosargus'', '' Scolopsis'', or ''Serranochromis''. Although species from all of these genera are called "bream", the term does not imply a degree of relatedness between them. Fish termed "bream" tend to be narrow, deep-bodied species. The name is a derivation of the Middle English word ''breme'', of Old French origin. The term sea bream is sometimes used for gilt-head bream (''Sparus aurata''), (''orata'' in Italy, ''dorada'' in Spain) or porgies (both family Sparidae) or pomfrets (family Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Lyons
The Division of Lyons is an Australian electoral division in Tasmania. Geography Since 1984, federal electoral division boundaries in Australia have been determined at redistributions by a redistribution committee appointed by the Australian Electoral Commission. Redistributions occur for the boundaries of divisions in a particular state, and they occur every seven years, or sooner if a state's representation entitlement changes or when divisions of a state are malapportioned. History The division was created at the Federal redistribution of 12 September 1984 as a reconfigured version of the abolished Division of Wilmot. The name jointly honours Joseph Lyons, Prime Minister of Australia 1932–39, Member for Wilmot from 1929–39, and his wife Dame Enid Lyons, the first woman elected to the Australian House of Representatives (1943) and subsequently the first female member of Cabinet (1949–51). Joseph Lyons had previously represented Wilmot at the state level from 1909 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign ''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'. The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ... country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |