|
Sardinian Literature
The literature of Sardinia is the literary production of Sardinian authors, as well as the literary production generally referring to Sardinia as argument, written in various languages. The beginnings The existence and understanding of direct statements of the proto-Sardinian (pre-punic and pre-Latin) language or languages being hotly debated, the first written artifact from the island dates back to the Phoenician period with documents such as the Nora Stele or the trilingual inscription (Punic-Latin-Greek) from San Nicolò Gerrei. This last artifact symbolizes the passage of the island from a Punic cultural and linguistic influence to a Roman one. The Carthaginians took control of Sardinia around the year 500 BC, and lost it in 238 BC after the First Punic War. After that the new Roman province of Sardinia et Corsica established an almost exclusive use of written and spoken Latin for more than eight centuries, as a result of the linguistic Romanization of the entire island. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the 20 regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia and immediately south of the French island of Corsica. It is one of the five Italian regions with some degree of domestic autonomy being granted by a special statute. Its official name, Autonomous Region of Sardinia, is bilingual in Italian and Sardinian: / . It is divided into four provinces and a metropolitan city. The capital of the region of Sardinia — and its largest city — is Cagliari. Sardinia's indigenous language and Algherese Catalan are referred to by both the regional and national law as two of Italy's twelve officially recognized linguistic minorities, albeit gravely endangered, while the regional law provides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corsican Language
Corsican (''corsu'' , ; full name: ''lingua corsa'' , ) is a Romance language constituted by the continuum of the Italo-Romance dialects spoken on the Mediterranean island of Corsica (France) and on the northern end of the island of Sardinia (Italy). Corsican is related to the Tuscan varieties from the Italian peninsula, and therefore also to the Florentine-based standard Italian. Under the long-standing sway of Tuscany's Pisa and Republic of Genoa over Corsica, Corsican used to play the role of a vernacular in combination with Italian functioning as the island's official language. In 1859, Italian was replaced by French, owing to the French acquisition from the Republic of Genoa in 1768. Over the next two centuries, the use of French in the place of Italian grew to the extent that, by the Liberation in 1945, all the islanders had a working knowledge of French. The 20th century saw a language shift, with the islanders changing their language practices to the extent that there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EL FORASTERO
EL, El or el may refer to: Religion * El (deity), a Semitic word for "God" People * EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer * El DeBarge, music artist * El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American politician * Ephrat Livni (born 1972), American street artist Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * El, short for Eleven, a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in ''Superman'' *E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film ''Road Trip'' Literature * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 2000 Japanese adult visual novel Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él'' (Lucero album), a 1982 album by Lucero * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from ''Caminando'' (album) * "Él" (Luc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cima Del Monte Parnaso Español Con Las Tres Musas Castellanas Caliope, Urania Y Euterpe
Cima may refer to: Acronyms *The Center for International Media Assistance, a media development organization in Washington, DC *Centre International de la Mécanique d'Art (International centre for Art Mechanics), a museum in Switzerland *Channel Industries Mutual Aid, a Houston emergency response organization *Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (formed 1919) *Costruzione Italiana Macchine Attrezzi (Italian Machine Tool Company), the gear and transmission manufacturing subsidiary of * Cyprus Institute of Marketing (established 1978) * Chenille International Manufacturers Association People *Cima da Conegliano (about 1459 – 1517), Italian renaissance painter *Cima (wrestler) (born 1977), ring name of Japanese professional wrestler Nobuhiko Oshima Locations *Estádio Ítalo del Cima (inaugurated 1960), football stadium in Campo Grande neighborhood, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil * Fajã de Cima, parish in the district of Ponta Delgada in the Azores *Ilhéu de Cima, islet in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
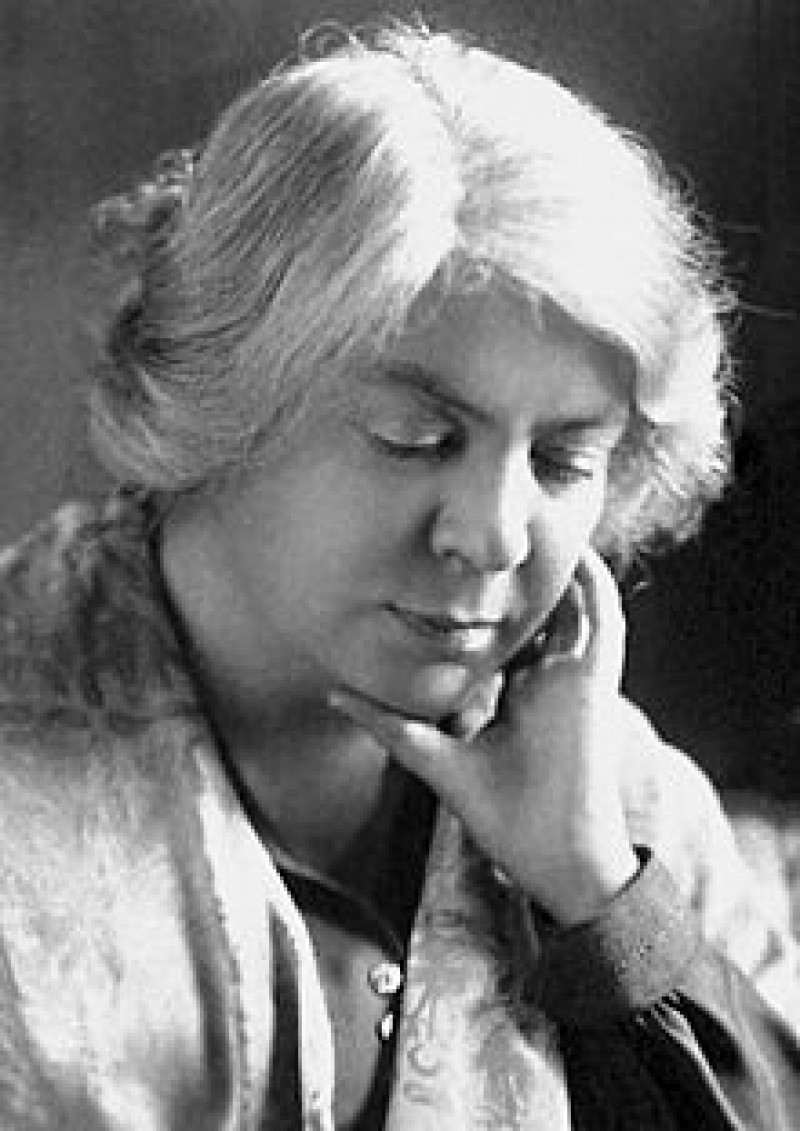
Eleanor Of Arborea
Eleanor of Arborea or Eleanor De Serra Bas ( Sardinian: Elianora de Arbarée / Elianora De Serra Bas, Italian: Eleonora d'Arborea / Eleonora De Serra Bas; 1347— June 1404) was one of the most powerful and important, and one of the last, judges of the Judgedom of Arborea in Sardinia, and Sardinia's most famous heroine. She is also known for updating of the Carta de Logu, promulgated by her father Marianus IV and revisited by her brother Hugh III. First Years Eleanor was born in Molins de Rei (Catalonia, Crown of Aragon), around 1347, from Marianus IV De Serra Bas, judge of Arborea, and Timbora of Roccaberti, a catalan noble. Sibling to Hugh and Beatrix of Arborea, she lived her first years in Oristano, at the castle of Goceano. At the heirless death of Peter III of Arborea, the Corona de Logu of the Judgedom (an assembly of notables, prelates, city and village officials), elected Eleanor's father Marianus IV, Peter's brother, who ruled the Judgedom between 1347 and 1376. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marianus IV Of Arborea
Marianus IV (in Sardinian: Marianu IV de Arbarèe, in Catalan: Marià IV d'Arborea, 1319–1376), called the Great, was the Judge (king) of Arborea, kingdom in the island of Sardinia, from 1347 to his death. He was, as his nickname indicates, the greatest sovereign of Arborea. He was a legislator and a warrior whose reign saw the commencement of massive codification of the laws of his realm and incessant warfare with the Crown of Aragon. He was also a religious man, who had connections to Catherine of Siena. He was, in short, an "wise legislator, able politician, and valiant warrior."Nowé, 174. Early life in Catalonia Born at Oristano, he was the son of Hugh II and successor of his brother Peter III. At the behest of his father he spent most of his youth in Barcelona, where he was educated at the court of Alfonso IV of Aragon. He participated actively in the coronation of Peter IV in 1336. In 1336 in Barcelona, he married Timbora, daughter of Dalmatius IV of Rocabertí ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iglesias, Sardinia
Iglesias (, ; from ; sc, Igrèsias) is a ''comune'' and city in the province of South Sardinia, Italy. It was co-capital of the province of Carbonia-Iglesias with Carbonia, and the province's second-largest community. Under Spanish control Iglesias was one of the most important royal cities on Sardinia, and it is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Iglesias. At an elevation of in the hills of southwestern Sardinia, it was the centre of a mining district from which lead, zinc, and silver were extracted. Iglesias was also a centre for the distillation of sulfuric acid. History Prehistory and ancient history The area around present-day Iglesias was inhabited in prehistory, with the oldest traces of human settlement dating to the Neolithic. The fourth-millennium-BC domus de Janas, attributed to the Ozieri culture, were discovered in the mountainous region of San Benedetto. Other pre-Nuragic finds attributed to the Monte Claro, Bell Beaker and Bonnanaro cultures were discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardinian Medieval Kingdoms
The Judicates (, or in Sardinian, in Latin, or in Italian), in English also referred to as Sardinian Kingdoms, Sardinian Judgedoms or Judicatures, were independent states that took power in Sardinia in the Middle Ages, between the ninth and fifteenth centuries. They were sovereign states with '' summa potestas'', each with a ruler called judge ( in Sardinian), with the powers of a king. Historical causes of the advent of the kingdoms After a relatively brief Vandal occupation (456–534), Sardinia was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 535 until the eighth century. After 705, with the rapid Arab expansion, Saracen pirates from North Africa began to raid the island and encountered no effective opposition by the Byzantine army. In 815, Sardinian ambassadors requested military assistance from the Carolingian Emperor Louis the Pious. In 807, 810–812, and 821–822 the Arabs of Spain and North Africa tried to invade the island but the Sardinians resisted several att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Justinianus
The Code of Justinian ( la, Codex Justinianus, or ) is one part of the ''Corpus Juris Civilis'', the codification of Roman law ordered early in the 6th century AD by Justinian I, who was Eastern Roman emperor in Constantinople. Two other units, the Digest and the Institutes, were created during his reign. The fourth part, the ''Novellae Constitutiones'' (New Constitutions, or Novels), was compiled unofficially after his death but is now also thought of as part of the ''Corpus Juris Civilis''. Creation Shortly after Justinian became emperor in 527, he decided the empire's legal system needed repair. There existed three codices of imperial laws and other individual laws, many of which conflicted or were out of date. The Codex Gregorianus and the Codex Hermogenianus were unofficial compilations. (The term "Codex" refers to the physical aspect of the works, being in book form, rather than on papyrus rolls. The transition to the codex occurred around AD 300.)Jolowicz, 1972, p. 463 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
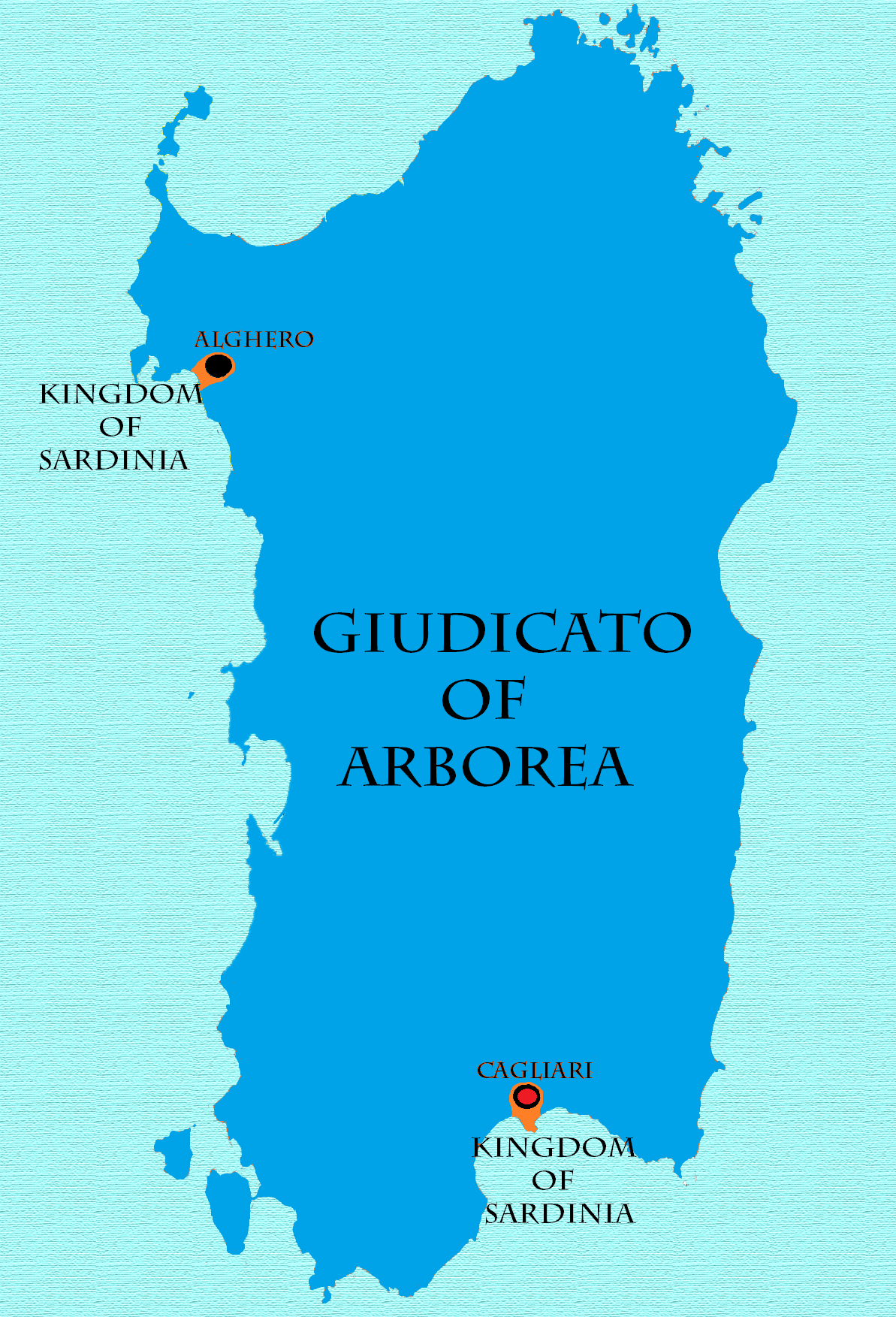
Judicate Of Arborea
The Judicate of Arborea ( sc, Judicadu de Arbaree, it, Giudicato di Arborea, ) or the Kingdom of Arborea (, , ) was one of the four independent judicates into which the island of Sardinia was divided in the Middle Ages. It occupied the central-west portion of the island, wedged between Logudoro to the north and east, Cagliari to the south and east, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. To the north east and beyond Logudoro was located Gallura, with which Arborea had far less interaction. Arborea outlasted her neighbours, surviving well into the 15th century. The earliest known judicial seat was Tharros. The Judicate of Arborea at the times of its maximum expansion occupied the whole island's territory, except the cities of Alghero and Cagliari. Origins In the early 9th century, when the Arabs and Berbers of North Africa became aggressive in expansion and piracy, the central authorities of the Byzantine Empire were unable to effectively defend or consistently govern the imperia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carta De Logu
The Carta de Logu was a legal code of the Judicate of Arborea, written in the Sardinian language and promulgated by the ("Lady Judge") Eleanor of Arborea in 1392. It was in force in Sardinia until it was superseded by the Savoyard code of Charles Felix in April 1827. The Carta was a work of great importance in Sardinian history and in European Juridic history as a whole. It was an organic, coherent, and systematic work of legislation encompassing the civil and penal law. The history of the drafting of the Carta is unknown, but the Carta itself provides an excellent glimpse into the ethnological and linguistic situation of late medieval Sardinia. In the Carta there is the modernizing of certain norms and the juridical wisdom that contains elements of the Roman-canonical tradition, the Byzantine one, the Bolognese jurisprudence and the thought of the glossators of the Catalan court culture, but above all the local juridical elaboration of the Sardinian customs made by Sardinian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carta De Logu
The Carta de Logu was a legal code of the Judicate of Arborea, written in the Sardinian language and promulgated by the ("Lady Judge") Eleanor of Arborea in 1392. It was in force in Sardinia until it was superseded by the Savoyard code of Charles Felix in April 1827. The Carta was a work of great importance in Sardinian history and in European Juridic history as a whole. It was an organic, coherent, and systematic work of legislation encompassing the civil and penal law. The history of the drafting of the Carta is unknown, but the Carta itself provides an excellent glimpse into the ethnological and linguistic situation of late medieval Sardinia. In the Carta there is the modernizing of certain norms and the juridical wisdom that contains elements of the Roman-canonical tradition, the Byzantine one, the Bolognese jurisprudence and the thought of the glossators of the Catalan court culture, but above all the local juridical elaboration of the Sardinian customs made by Sardinian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |