|
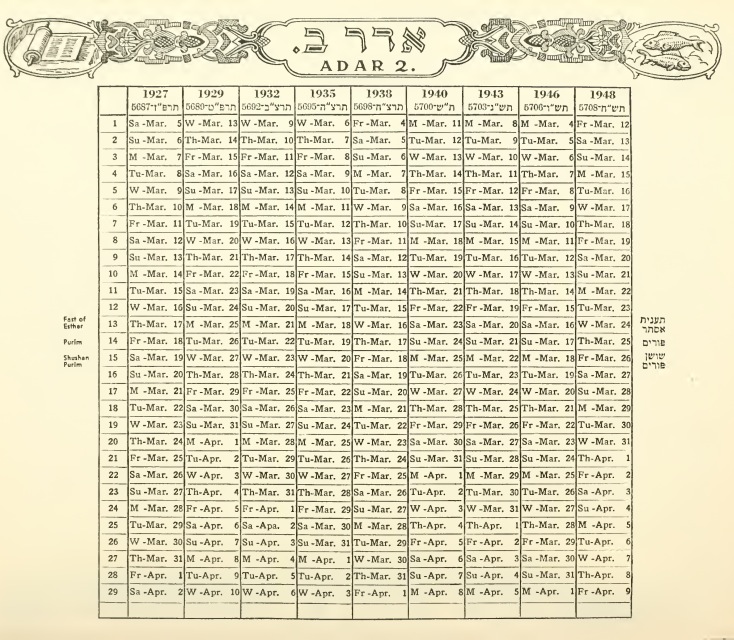
Sardica Paschal Table
The Sardica paschal table or Sardica document is a document from a Latin manuscript of the 7th/8th century AD. It is a copy in Latin translation of the creed of the Eastern Christian bishops attending the Council of Sardica who, fearing that their deliberations would be dominated by Western bishops, met separately at Philippopolis. Appended to the creed and anathemas is a table of Paschal full moon dates, given as dates in the Julian calendar, for the years 328 to 357, together with a list of dates of 14 Nisan in the Jewish calendar, also referred to the Julian calendar, for the years 328 to 343, the year of the Council. The calendrical information contained in the document has been used by scholars in tracing the history of the computus and of the Hebrew calendar. The manuscript and the contents of the document The Sardica paschal table is a part of Codex Verona LX(58), or, more fully, MS Verona, Biblioteca Capitolare LX(58). It was first published by Eduard Schwartz in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Language
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italy (geographical region), Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a fusional language, highly inflected language, with three distinct grammatical gender, genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunction (astronomy And Astrology)
In astronomy, a conjunction occurs when two astronomical objects or spacecraft have either the same right ascension or the same ecliptic longitude, usually as observed from Earth. When two objects always appear close to the ecliptic—such as two planets, the Moon and a planet, or the Sun and a planet—this fact implies an apparent close approach between the objects as seen in the sky. A related word, ''appulse'', is the minimum apparent separation in the sky of two astronomical objects. Conjunctions involve either two objects in the Solar System or one object in the Solar System and a more distant object, such as a star. A conjunction is an apparent phenomenon caused by the observer's perspective: the two objects involved are not actually close to one another in space. Conjunctions between two bright objects close to the ecliptic, such as two bright planets, can be seen with the naked eye. The astronomical symbol for conjunction is (Unicode U+260C ☌). The conjunction sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiction
An indiction ( la, indictio, impost) was a periodic reassessment of taxation in the Roman Empire which took place every fifteen years. In Late Antiquity, this 15-year cycle began to be used to date documents and it continued to be used for this purpose in Medieval Europe, and can also refer to an individual year in the cycle; for example, "the fourth indiction" came to mean the fourth year of the current indiction. Since the cycles themselves were not numbered, other information is needed to identify the specific year. History Indictions originally referred to the periodic reassessment for an agricultural or land tax in the Roman Empire. There were three different cycles: a 15-year cycle used throughout the empire; a 14-year cycle used in Roman Egypt; and a five year cycle called the ''lustrum'', derived from the Roman Republican census. Changes to the tax system usually took place at the beginning of one of these cycles and at the end of the indiction Emperors often chose to forg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardica Doc 2a
Serdika or Serdica (Bulgarian: ) is the historical Roman name of Sofia, now the capital of Bulgaria. Currently, Serdika is the name of a district located in the city. It includes four neighbourhoods: "Fondovi zhilishta"; "Banishora", "Orlandovtsi" and "Malashevtsi" as well as the central parts of "Draz mahala". It has an area of 17.53 km² that counts for 1.3% of the total Capital Municipality area and 8.8% of the city proper. Serdica has a population of 52,918. There are 6 kindergartens, 13 schools and 6 chitalishta in the territory of the district. Healthcare infrastructure includes II and V City Hospitals; Institute of Transport Medicine and two polyclinics. The Sofia Central Railway Station; Central Bus Station Sofia and the Lavov Most are also located in Serdica. See also *Edict of Serdica (AD 311), through which Emperor Galerius decreed a policy of tolerance towards Christianity *History of Sofia The history of Sofia, Bulgaria's capital and largest city, spans th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardica Doc 1a
Serdika or Serdica (Bulgarian: ) is the historical Roman name of Sofia, now the capital of Bulgaria. Currently, Serdika is the name of a district located in the city. It includes four neighbourhoods: "Fondovi zhilishta"; "Banishora", "Orlandovtsi" and "Malashevtsi" as well as the central parts of "Draz mahala". It has an area of 17.53 km² that counts for 1.3% of the total Capital Municipality area and 8.8% of the city proper. Serdica has a population of 52,918. There are 6 kindergartens, 13 schools and 6 chitalishta in the territory of the district. Healthcare infrastructure includes II and V City Hospitals; Institute of Transport Medicine and two polyclinics. The Sofia Central Railway Station; Central Bus Station Sofia and the Lavov Most are also located in Serdica. See also *Edict of Serdica (AD 311), through which Emperor Galerius decreed a policy of tolerance towards Christianity *History of Sofia The history of Sofia, Bulgaria's capital and largest city, spans th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward , established = , type = Public research university , endowment = £143 million (2020) , budget = £1.544 billion (2019/20) , chancellor = Anne, Princess Royal(as Chancellor of the University of London) , provost = Michael Spence , head_label = Chair of the council , head = Victor L. L. Chu , free_label = Visitor , free = Sir Geoffrey Vos , academic_staff = 9,100 (2020/21) , administrative_staff = 5,855 (2020/21) , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , coordinates = , campus = Urban , city = London, England , affiliations = , colours = Purple and blue celeste , nickname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Δάφνῃ "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; la, Antiochia ad Orontem; hy, Անտիոք ''Antiokʽ''; syr, ܐܢܛܝܘܟܝܐ ''Anṭiokya''; he, אנטיוכיה, ''Anṭiyokhya''; ar, أنطاكية, ''Anṭākiya''; fa, انطاکیه; tr, Antakya. was a Hellenistic, and later, a Biblical Christian city, founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. This city served as the capital of the Seleucid Empire and later as regional capital to both the Roman and Byzantine Empire. During the Crusades, Antioch served as the capital of the Principality of Antioch, one of four Crusader states that were founded in the Levant. Its inhabitants were known as ''Antiochenes''; the city's ruin lies on the Orontes River, near Antakya, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleography
Palaeography ( UK) or paleography ( US; ultimately from grc-gre, , ''palaiós'', "old", and , ''gráphein'', "to write") is the study of historic writing systems and the deciphering and dating of historical manuscripts, including the analysis of historic handwriting. It is concerned with the forms and processes of writing; not the textual content of documents. Included in the discipline is the practice of deciphering, reading, and dating manuscripts, and the cultural context of writing, including the methods with which writing and books were produced, and the history of scriptoria. The discipline is one of the auxiliary sciences of history. It is important for understanding, authenticating, and dating historic texts. However, it generally cannot be used to pinpoint dates with high precision. Application Palaeography can be an essential skill for historians and philologists, as it tackles two main difficulties. First, since the style of a single alphabet in each given langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Sardica
The Council of Serdica, or Synod of Serdica (also Sardica located in modern day Sofia, Bulgaria), was a synod convened in 343 at Serdica in the civil diocese of Dacia, by Emperors Constans I, augustus in the West, and Constantius II, augustus in the East. It attempted to resolve the Arian controversy, and was attended by about 170 bishops. It was convened by the two augusti at the request of Pope Julius I. Background The first ecumenical council (Nicaea I) canon 5 decreed that bishops should convene in biannual synods within every province to act as a court of second instance and review cases with excommunication sentences pronounced by individual bishops. But, there was no appeal to a court of final instance "if an unjust sentence was imposed" by a provincial synod acting as a court of second instance. Nicaea I canon 5 "implied that" provincial synods "had an acknowledged authority to" judge the acts of individual bishops of their province. Provincial synods' authority "was becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Schwartz
Eduard Schwartz (22 August 1858 – 13 February 1940) was a German classical philologist. Born in Kiel, he studied under Hermann Sauppe in Göttingen, under Hermann Usener and Franz Bücheler in Bonn, under Theodor Mommsen in Berlin and under Ulrich von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff in Greifswald. In 1880 he obtained his doctorate from the University of Bonn.Saint Cyril of Alexandria">Saint Cyril, Patriarch of Alexandria. With Introduction and Notes by E. Schwartz, 1927 publications References External links Deutsche Wikisource extensive bibliography. {{DEFAULTSORT:Schwartz, Eduard [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Calendar
The Hebrew calendar ( he, הַלּוּחַ הָעִבְרִי, translit=HaLuah HaIvri), also called the Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today for Jewish religious observance, and as an official calendar of the state of Israel. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate Torah reading, public reading of Weekly Torah portion, Torah portions, ''yahrzeits'' (dates to commemorate the death of a relative), and daily Psalm readings, among many ceremonial uses. In Israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official calendar for civil holidays, alongside the Gregorian calendar. The present Hebrew calendar is the result of a process of development, including a Babylonian calendar, Babylonian influence. Until the Tannaitic period (approximately 10–220 Common Era, CE), the calendar employed a new lunar phase, crescent moon, with an Intercalation (timekeeping), additional month normally added every two or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |