|
Sarariman
In Japan, a is a salaried worker. In Japanese popular culture, this is embodied by a white-collar worker who shows overriding loyalty and commitment to the corporation where he works. Salarymen are expected to work long hours, to put in additional overtime, to participate in after-work leisure activities such as drinking, singing karaoke and visiting hostess bars with colleagues, and to value work over all else. The salaryman typically enters a company after graduating from college and stays with that corporation for the duration of his career. Other popular notions surrounding salarymen include karōshi, or death from overwork. In conservative Japanese culture, becoming a salaryman is the expected career choice for young men and those who do not take this career path are regarded as living with a stigma and less prestige. On the other hand, the word ''salaryman'' is sometimes used with derogatory connotation for his total dependence on his employer and lack of individuali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rush Hour Tokyo
Rush(es) may refer to: Places United States * Rush, Colorado * Rush, Kentucky * Rush, New York * Rush City, Minnesota * Rush Creek (Kishwaukee River tributary), Illinois * Rush Creek (Marin County, California), a stream * Rush Creek (Mono County, California), on the eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada, running into Mono Lake * Rush County, Indiana * Rush County, Kansas * Rush Historic District, a zinc mining region in the Ozark Mountains of Arkansas * Rush Lake (other), various lakes * Rush Street (Chicago), Illinois * Rush Township (other), various places * Rush Valley, Utah Elsewhere * Rush, Dublin, a small seaside town in Fingal, Ireland * Rush Glacier in Brabant Island, Antarctica * Rush Peak in the Karakoram range, Pakistan People * Rush (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name * Rush (''League of Legends'' player) (born 1993), from South Korea * Rush (wrestler) (born 1988), ring name of Mexican professional wrestler William Muñ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Mahjong Tiles 1
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies ( Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japan ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Work Environment
Many both in and outside Japan share an image of the Japanese work environment that is based on a and model used by large companies as well as a reputation of long work-hours and strong devotion to one's company. This environment is said to reflect economic conditions beginning in the 1920s, when major corporations competing in the international marketplace began to accrue the same prestige that had traditionally been ascribed to the ''daimyō''–retainer relationship of feudal Japan or government service in the Meiji Restoration. Large companies At the very top, the most prestigious companies would recruit and retain the best workers by offering better benefits and truly lifetime job security. By the 1960s, employment at a large prestigious company had become the goal of children of the new middle class, the pursuit of which required mobilization of family resources and great individual perseverance in order to achieve success in the fiercely competitive education system. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Management Culture
Japanese management culture refers to working philosophies or methods in Japan. It included concepts and philosophies such as just in time, kaizen and total quality management. Managerial style The Japanese term "hourensou" (also rendered as " Ho-Ren-So") refers to frequent reporting, touching base and discussing – important attributes that are said to characterize collaboration and information flow within effective Japanese corporate culture. Hou' stands for 'Houkoku', the Japanese word for 'reporting'. 'Ren' comes from 'Renraku', the word for 'informing'. 'Sou' is derived from 'Soudan', the word for 'consulting'. refers to "getting your hands dirty", to identify or solve immediate problems and leaders are not exempt from this. Aspects of these principles are often mistaken by western managers as "micromanagement". In contrast, these principles are used as tools to shepherd processes. Mohammed Ala and William Cordeiro (1999) described the Japanese decision-making process of " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Blue Collar Workers
Blue collar workers (Nikutai-rōdō-sha (肉体労働者)) in Japan encompass many different types of manual labor jobs, including factory work, construction, and agriculture. Blue-collar workers make up a very large portion of the labor force in Japan, with 30.1% of employed people ages 15 and over working as "craftsman, mining, manufacturing and construction workers and laborers" as of 1995 census data. The blue-collar class includes regular, non-regular, and part-time workers, as well as a large number of foreign laborers, all with varying work schedules and employment benefits. Factory workers in Japan History of industrialization Most Japanese people prior to the Meiji Restoration worked in the agriculture industry (approximately 70-80 percent), and although some examples of organized production were present in Japanese communities, the lack of modern technology and capital prevented industrial factory work from emerging on a large scale. Blue-collar workers grew into a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hansei
is a central idea in Japanese culture, meaning to acknowledge one's own mistake and to pledge improvement. This is similar to the German proverb ''Selbsterkenntnis ist der erste Schritt zur Besserung,'' where the closest translation to English would be "Insight into oneself is the first step to improvement". Cultural meaning In the ''hansei'' process, the emphasis is on what went wrong and on creating clear plans for ensuring that it does not reoccur; this is done constantly and consistently. At Toyota, even if one completes a project successfully, there is still a ''hansei-kai'' (reflection meeting) to review what went wrong. If a manager or engineer claims that there were not any problems with the project, they will be reminded that “no problem is a problem” – meaning that one has not objectively and critically evaluated the project to find opportunities for improvement. No problems indicate that one did not stretch to meet (or exceed) their expected capacity. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 million vehicles per year. The company was originally founded as a spinoff of Toyota Industries, a machine maker started by Sakichi Toyoda, Kiichiro's father. Both companies are now part of the Toyota Group, one of the largest conglomerates in the world. While still a department of Toyota Industries, the company developed its first product, the Type A engine in 1934 and its first passenger car in 1936, the Toyota AA. After World War II, Toyota benefited from Japan's alliance with the United States to learn from American automakers and other companies, which would give rise to The Toyota Way (a management philosophy) and the Toyota Production System (a lean manufacturing practice) that would transform the small company into a leader in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
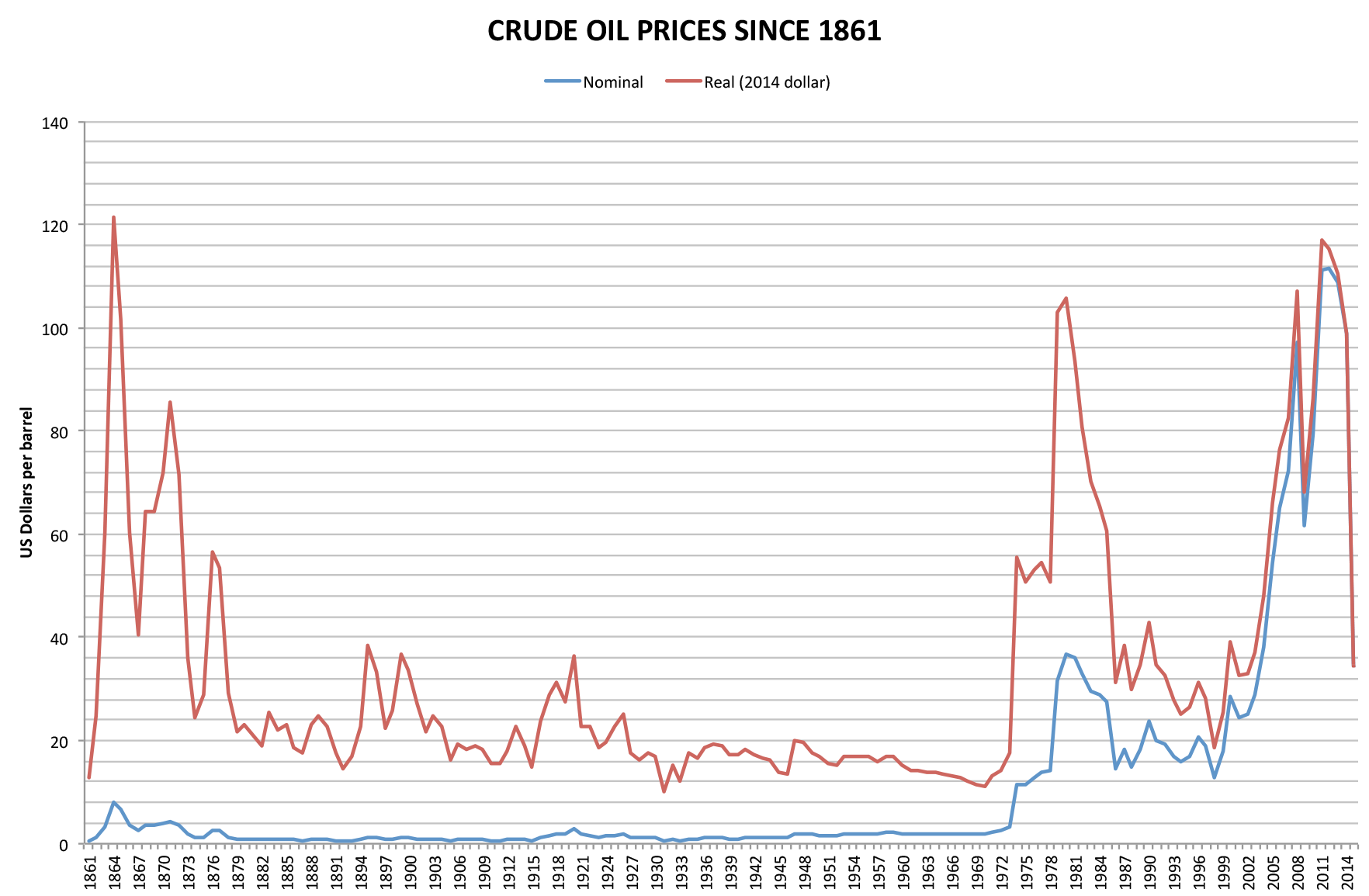
1973 Oil Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli conflict in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Diet
The is the national legislature of Japan. It is composed of a lower house, called the House of Representatives (, ''Shūgiin''), and an upper house, the House of Councillors (, '' Sangiin''). Both houses are directly elected under a parallel voting system. In addition to passing laws, the Diet is formally responsible for nominating the Prime Minister. The Diet was first established as the Imperial Diet in 1890 under the Meiji Constitution, and took its current form in 1947 upon the adoption of the post-war constitution. Both houses meet in the in Nagatachō, Chiyoda, Tokyo. Composition The houses of the National Diet are both elected under parallel voting systems. This means that the seats to be filled in any given election are divided into two groups, each elected by a different method; the main difference between the houses is in the sizes of the two groups and how they are elected. Voters are also asked to cast two votes: one for an individual candidate in a const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large national audience. Daily broadsheet editions are printed for D.C., Maryland, and Virginia. The ''Post'' was founded in 1877. In its early years, it went through several owners and struggled both financially and editorially. Financier Eugene Meyer purchased it out of bankruptcy in 1933 and revived its health and reputation, work continued by his successors Katharine and Phil Graham (Meyer's daughter and son-in-law), who bought out several rival publications. The ''Post'' 1971 printing of the Pentagon Papers helped spur opposition to the Vietnam War. Subsequently, in the best-known episode in the newspaper's history, reporters Bob Woodward and Carl Bernstein led the American press's investigation into what became known as the Watergate scandal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salaryman Asleep On The Tokyo Subway
In Japan, a is a salaried worker. In Japanese popular culture, this is embodied by a white-collar worker who shows overriding loyalty and commitment to the corporation where he works. Salarymen are expected to work long hours, to put in additional overtime, to participate in after-work leisure activities such as drinking, singing karaoke and visiting hostess bars with colleagues, and to value work over all else. The salaryman typically enters a company after graduating from college and stays with that corporation for the duration of his career. Other popular notions surrounding salarymen include karōshi, or death from overwork. In conservative Japanese culture, becoming a salaryman is the expected career choice for young men and those who do not take this career path are regarded as living with a stigma and less prestige. On the other hand, the word ''salaryman'' is sometimes used with derogatory connotation for his total dependence on his employer and lack of individualit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible. Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping with the varied terrains encountered on different courses is a key part of the game. Courses typically have either 18 or 9 ''holes'', regions of terrain that each contain a ''cup'', the hole that receives the ball. Each hole on a course contains a teeing ground to start from, and a putting green containing the cup. There are several standard forms of terrain between the tee and the green, such as the fairway, rough (tall grass), and various ''hazards'' such as water, rocks, or sand-filled ''bunkers''. Each hole on a course is unique in its specific layout. Golf is played for the lowest number of strokes by an individual, known as stroke play, or the lowest score on the most individual holes in a complete round by an individual or team, k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |