|
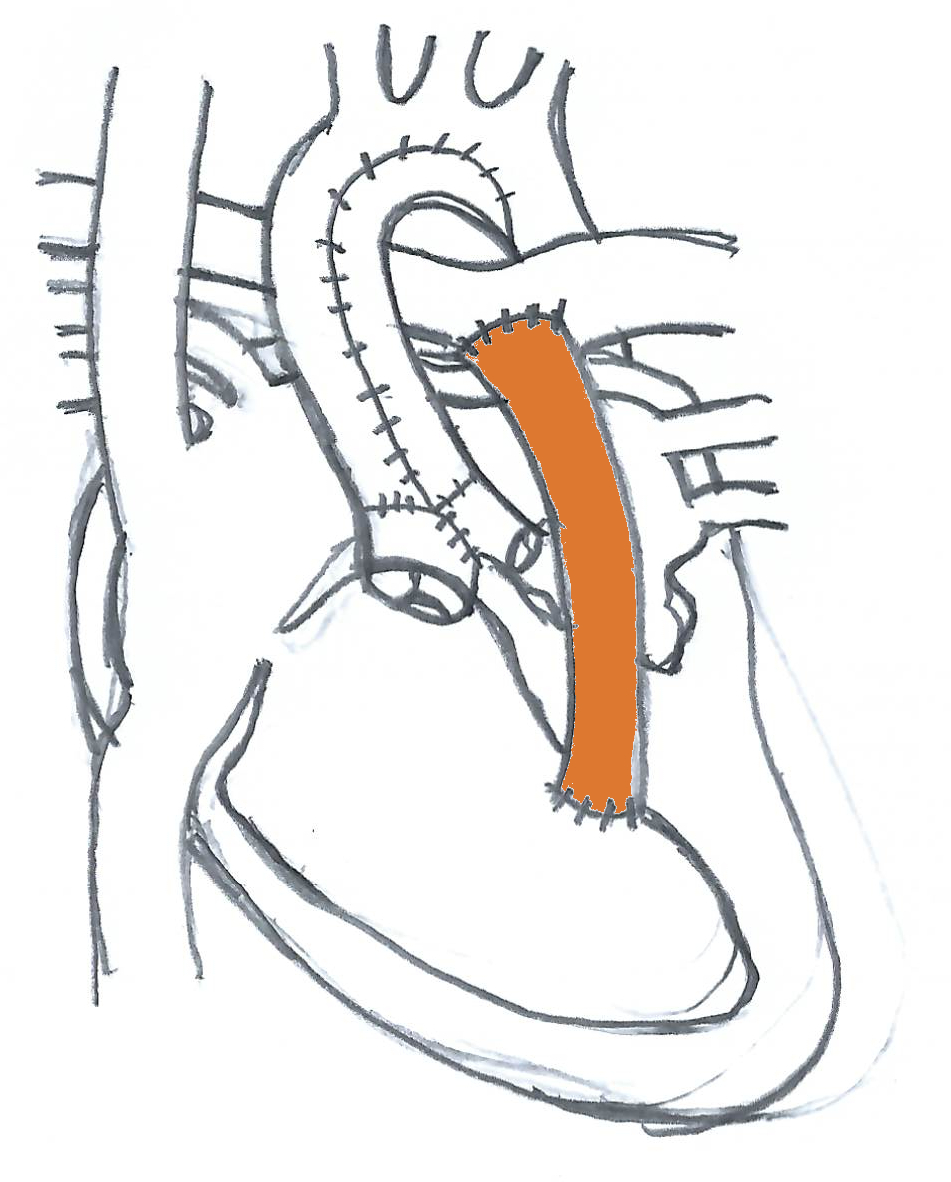
Sano Shunt
A Sano shunt is a shunt from the right ventricle to the pulmonary circulation. In contrast to a Blalock–Taussig shunt, circulation is primarily in systole. It is sometimes used as the first step in a Norwood procedure The Norwood procedure is the first of three surgeries intended to create a new functional systemic circuit in patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome and other complex heart defects with single ventricle physiology. The first successful Norw .... This procedure was pioneered by the Japanese Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Shunji Sano (b.1953) in 2003. References Cardiac surgery {{surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the atria t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
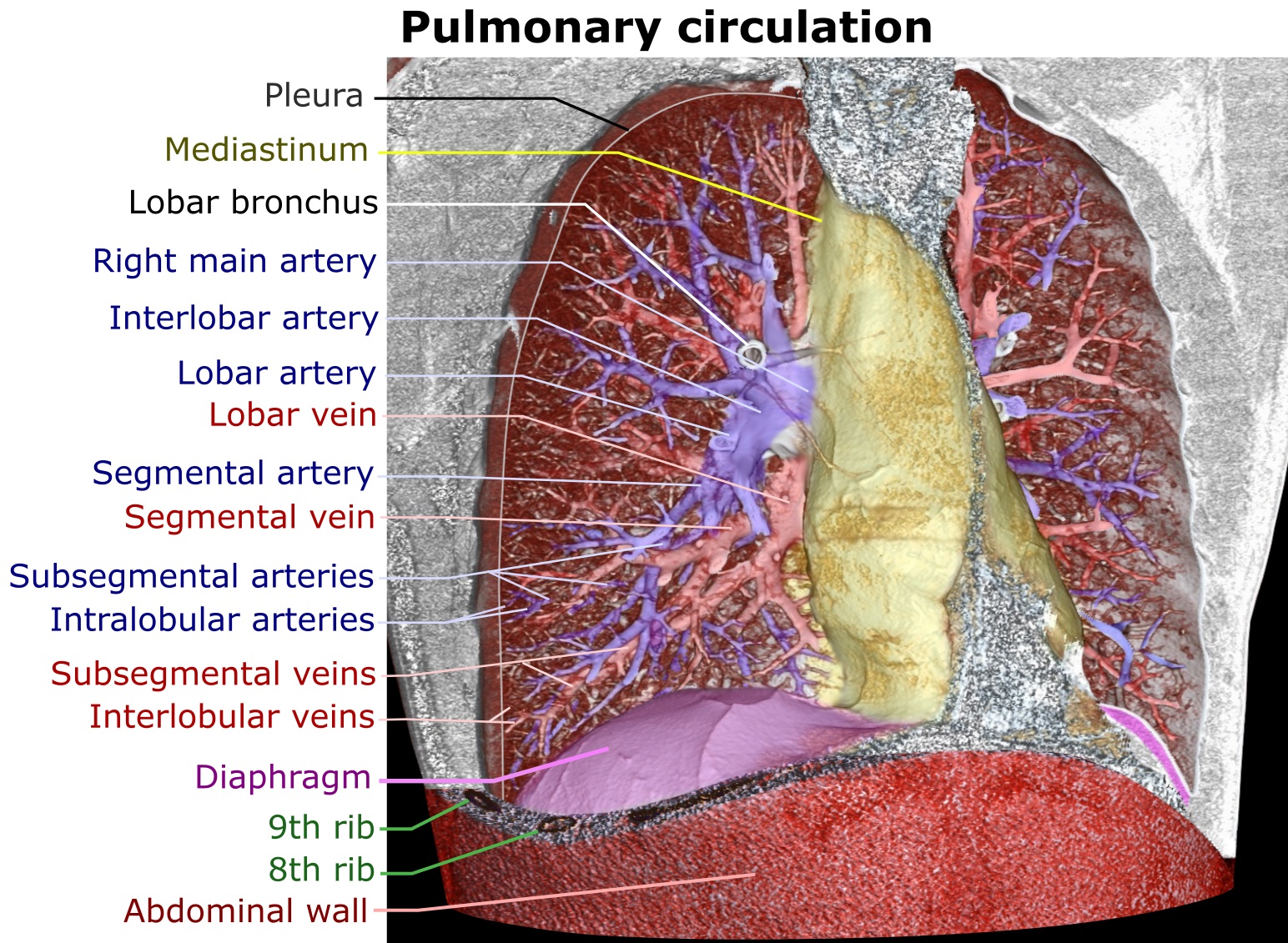
Pulmonary Circulation
The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungs. In the lungs the blood is oxygenated and returned to the left atrium to complete the circuit. The other division of the circulatory system is the systemic circulation that begins with receiving the oxygenated blood from the pulmonary circulation into the left atrium. From the atrium the oxygenated blood enters the left ventricle where it is pumped out to the rest of the body, returning as deoxygenated blood back to the pulmonary circulation. The blood vessels of the pulmonary circulation are the pulmonary arteries and the pulmonary veins. A separate circulatory circuit known as the bronchial circulation supplies oxygenated blood to the tissue of the larger airways of the lung. Structure De-oxygenated blood leaves the heart, goe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systole (medicine)
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and send blood to the larger, lower ventricle chambers. This flow fills the ventricles with blood, and the resulting pressure closes the valves to the atria. The ventricles now perform i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwood Procedure
The Norwood procedure is the first of three surgeries intended to create a new functional systemic circuit in patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome and other complex heart defects with single ventricle physiology. The first successful Norwood procedure involving the use of a cardiopulmonary bypass was reported by Dr. William Imon Norwood, Jr. and colleagues in 1981. Variations of Norwood procedure, or Stage 1 palliation, have been proposed and adopted over the last 30 years, however the key steps have remain unchanged. In order to utilize the right ventricle as the main blood pumping mechanism into the systemic and pulmonary circulation, a connection between left and right atria is established via atrial septectomy. Next a connection between the right ventricle and aorta is forged with the reconstruction of the narrowed outflow track using a tissue graft from the distal main pulmonary artery. Lastly, an aortopulmonary shunt is created connecting the aorta to the main pulm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |