|
Sanhujori
Sanhujori ( ko, 산후조리) is the Korean system of postpartum care, a culturally specific form of postpartum care. ''Sanhujori'' include consuming healthy foods, doing exercise and warming up the body. The ''sanhujori'' period typically lasts approximately from one week to one month. ''Sanhujori'' is a compound word: 'sanhu' ( ko, 산후; after the childbirth) and 'jori' ( ko, 조리; the regaining of the physical condition by doing a variety of recovery activities). In a pre-modern society, ''sanhujori'' services were provided by the family members of mothers. However, the traditional extended family system has been broken up and the services began to be offered by private postpartum centers (''sanhujoriwon'') and postpartum care workers (''sanhujorisa''). People often believe that ''sanhujori'' has a great impact on women's life-long health conditions; mothers who do not properly perform ''sanhujori'' practices may suffer from a range of illnesses, such as joint inflammation, ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Care
Postpartum care or postnatal care is a service provided to individuals in the postpartum period, to help with postpartum recuperation and restoration. Traditional postpartum care Many traditional forms of postpartum confinement exist throughout the world. Chinese '' Zuo Yuezi'' (sitting the month) and European Lying-in are examples. Korea ''Sanhujori'' is Korea's version of postpartum care. It draws on principles that emphasize activities and foods that keep the body warm, rest and relaxation to maximize the body's return to its normal state, maintaining cleanliness, eating nutritious foods, and peace of mind and heart. The confinement period is known as ''samchil-il'' (three seven days). Modern commercial versions Traditionally, women were taken care of by their elders: their mother, mother-in-law, sister, or aunt. The lying-in hospitals provided an institutional variation which gave women weeks of bedrest and a respite from household chores. Increasingly, these older wome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Care
Postpartum care or postnatal care is a service provided to individuals in the postpartum period, to help with postpartum recuperation and restoration. Traditional postpartum care Many traditional forms of postpartum confinement exist throughout the world. Chinese '' Zuo Yuezi'' (sitting the month) and European Lying-in are examples. Korea ''Sanhujori'' is Korea's version of postpartum care. It draws on principles that emphasize activities and foods that keep the body warm, rest and relaxation to maximize the body's return to its normal state, maintaining cleanliness, eating nutritious foods, and peace of mind and heart. The confinement period is known as ''samchil-il'' (three seven days). Modern commercial versions Traditionally, women were taken care of by their elders: their mother, mother-in-law, sister, or aunt. The lying-in hospitals provided an institutional variation which gave women weeks of bedrest and a respite from household chores. Increasingly, these older wome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Nurse
A monthly nurse is a woman who looks after a mother and her baby during the postpartum period, postpartum or postnatal period. The phrase is now largely obsolete, but the job continues under other names and various conditions around the world. Historically, women were expected to bedrest, rest in bed or at home for extended periods of time after childbirth, giving birth; care was provided either by her female relatives (mother or mother-in-law), or by those who could afford a monthly nurse. These weeks were called confinement or lying-in and ended with the re-introduction of the mother to the community in the Christian ceremony of the churching of women. The term "monthly nurse" was most common in the 18th and 19th centuries in England, because such a nurse frequently remained with the patient for four weeks. The term "monthly" is somewhat inaccurate, as there was no reason for the nurse's services to be dispensed with after ten days or retained for much longer, but it is entirel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanny
A nanny is a person who provides child care. Typically, this care is given within the children's family setting. Throughout history, nannies were usually servants in large households and reported directly to the lady of the house. Today, modern nannies, like other domestic workers, may live in or out of the house, depending on their circumstances and those of their employers. Some employment agencies specialize in providing nannies, as there are families that specifically seek them and may make them a part of the household. Nannies differ slightly from other child care providers. A childminder works out of their own home, operating as a small business. In America, childminders are often advertised as a daycare. Depending on the country the childminder or daycare is in, government registration may or may not be required. Within the UK, a childminder must be Ofsted registered, hold a current paediatric first aid qualification, public liability insurance and follow the EYFS. A mothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have been exposed to a communicable disease, yet do not have a confirmed medical diagnosis. It is distinct from medical isolation, in which those confirmed to be infected with a communicable disease are isolated from the healthy population. Quarantine considerations are often one aspect of border control. The concept of quarantine has been known since biblical times, and is known to have been practised through history in various places. Notable quarantines in modern history include the village of Eyam in 1665 during the bubonic plague outbreak in England; East Samoa during the 1918 flu pandemic; the Diphtheria outbreak during the 1925 serum run to Nome, the 1972 Yugoslav smallpox outbreak, the SARS pandemic, the Ebola pandemic and extensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Culture
The traditional culture of Korea is the shared cultural and historical heritage of Korea and southern Manchuria before the division of Korea in 1945. Manchuria refers to the ancient geographical and historical region in Northeast Asia, including countries like China and Russia. Since the mid-20th century, Korea has been split between the North Korean and South Korean states, resulting in a number of cultural differences that can be observed even today. the practice of Confucianism and Korean shamanism is deeply rooted in Korean culture. Clothing The traditional dress known as ''hanbok'' (한복, 韓服) (known as ''joseonot'' ��선옷in the DPRK). The ''hanbok'' consists of a shirt (''jeogori'') and a skirt (''chima''). According to social status, Koreans used to dress differently, making clothing an important mark of social rank. Costumes were worn by the ruling class and the royal family. These upper classes also used jewelry to distance themselves from the ordinar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
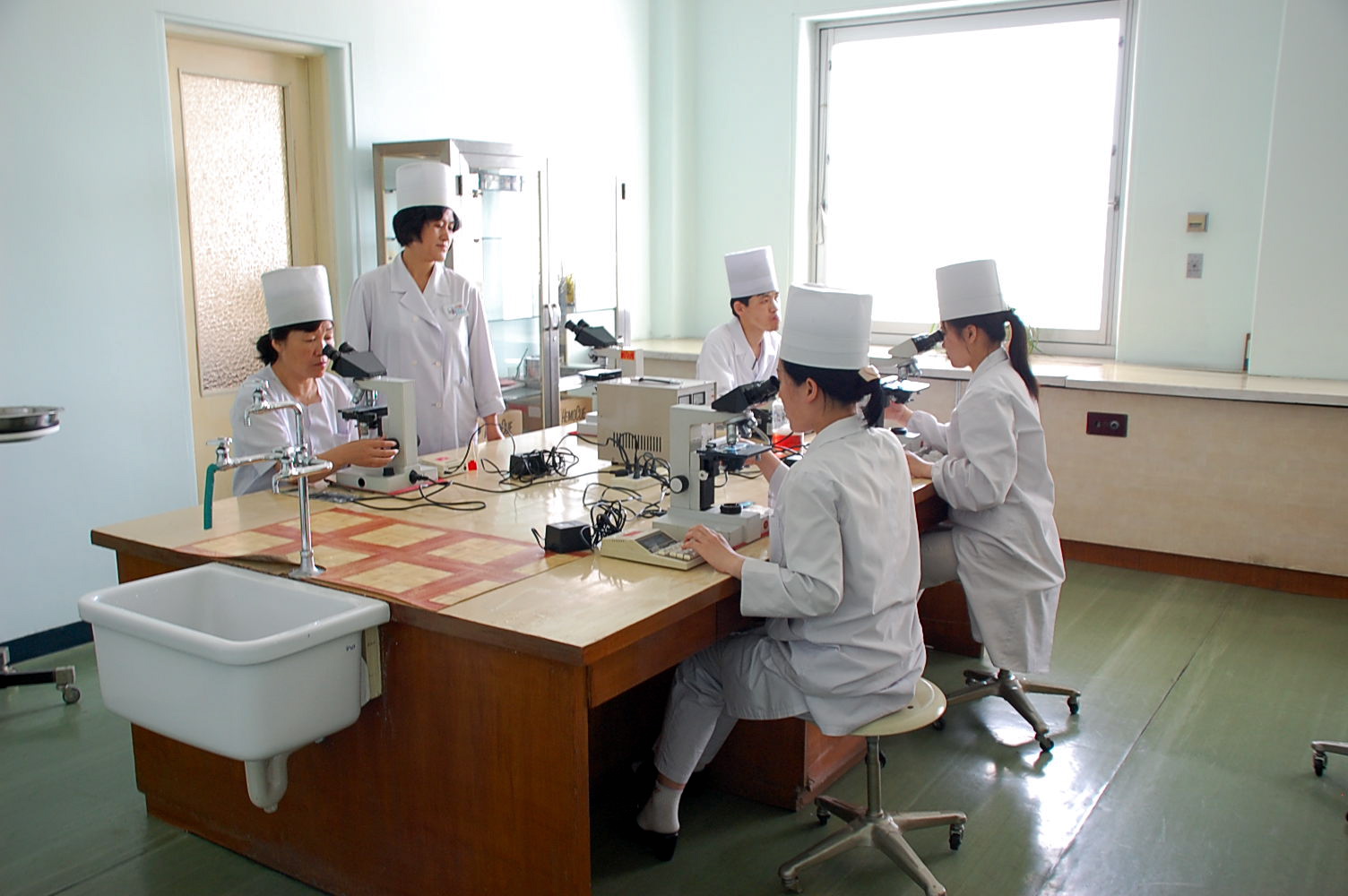
Healthcare In North Korea
North Korea has a life expectancy of 72 years . While North Korea is classified as a low-income country, the structure of North Korea's causes of death (2013) is unlike that of other low-income countries. Instead, it is closer to the worldwide averages, with non-communicable diseases – such as cardiovascular disease – accounting for two-thirds of the total deaths. A 2013 study stated that the largest obstacle for understanding the accurate health status of North Korea is the lack of the validity and reliability of its health data. North Korea claims to provide universal health care with a national medical service and health insurance system. It claims that health services are offered for free. However, this claim has been contested by North Korean defectors, who claim that patients must in fact pay for health services, that the upper classes have access to a higher standard of healthcare than ordinary ones do, and that "how much money a patient has determines whether they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taegyo
Taegyo refers to a set of practices and beliefs related to prenatal development. Taegyo is said to be regulations that a mother should observe in order to have good effects on her unborn child during maternity. Also, it is the education occurring in the period of maternity and considered that when an expectant mother tries to be careful of everything, prudent in speech and action, and keep distance from evil thoughts, it affects the unborn child in good ways. In other words, Taegyo is all the effort for the mother to provide the best environment for the fetal development. This is based on the belief that fetal environment has a huge influence on the fetal development and the whole life of the baby. History Taegyo was introduced into Korea from China at the end of the Goryeo dynasty (918-1392). During the Joseon Dynasty (1392–1910), it grew in popularity. The Korean female scholar Sajudang Lee (사주당 이씨 師朱堂李氏) wrote a book titled ''Taegyosingi'' (태교 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Period
The postpartum (or postnatal) period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to end within 6 weeks as the mother's body, including hormone levels and uterus size, returns to a non-pregnant state. The terms puerperium, puerperal period, or immediate postpartum period are commonly used to refer to the first six weeks following childbirth. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes the postnatal period as the most critical and yet the most neglected phase in the lives of mothers and babies; most maternal and infant mortality, newborn deaths occur during this period. In scientific literature, the term is commonly abbreviated to P''x'', where ''x'' is a number; for example, "day P5" should be read as "the fifth day after birth". This is not to be confused with the medical nomenclature that uses G P to stand for number and outcomes of pregnancy (gravidity and parity). A female giving birth in a hospital may leave as soon as they are medically stable, which can be as ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Confinement
Postpartum confinement is a traditional practice following childbirth. Those who follow these customs typically begin immediately after the birth, and the seclusion or special treatment lasts for a culturally variable length: typically for one month or 30 days, up to 40 days, two months, or 100 days. This postnatal recuperation can include care practices in regards of "traditional health beliefs, taboos, rituals, and proscriptions." The practice used to be known as "lying-in", which, as the term suggests, centres around bed rest. In some cultures it may be connected to taboos concerning impurity after childbirth. Overview Postpartum confinement refers both to the mother and the baby. Human newborns are so underdeveloped that pediatricians such as Harvey Karp refer to the first three months as the "fourth trimester". The weeks of rest while the mother heals also protect the infant as it adjusts to the world, and both learn the skills of breastfeeding. Almost all countries have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamja-tang
''Gamja-tang'' * () or pork back-bone stew is a spicy Korean soup made from the spine or neck bones of a pig. It often contains potatoes, cellophane noodles, dried radish greens, perilla leaves, green onions, hot peppers and ground sesame seeds. The vertebrae are usually separated with bits of meat clinging to them. The vertebrae are boiled at high temperatures to soften the meat. To remove the meat, one must use an instrument such as a chopstick. The meal is usually served with kimchi and a bowl of rice. This food is served as a lunch or dinner and often as a late-night snack, as well. The soup base is a deep red colour from the red hot peppers. The soup is now common in Korean restaurants outside Korea, including the United States and Canada. History Gamjatang originated in the southern Korean province of Jeolla. The main industry of Jeolla Province was agriculture, and hogs were widely raised and used for food. The origins of gamjatang can be traced back to the Three Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Family
An extended family is a family that extends beyond the nuclear family of parents and their children to include aunts, uncles, grandparents, cousins or other relatives, all living nearby or in the same household. Particular forms include the stem and joint families. Description In some circumstances, the extended family comes to live either with or in place of a member of the immediate family. These families include, in one household or close proximity, relatives in addition to an immediate family. An example would be an elderly parent who moves in with his or her children due to old age. In modern Western cultures dominated by immediate family constructs, the term has come to be used generically to refer to grandparents, uncles, aunts, and cousins, whether they live together within the same household or not. However, it may also refer to a family unit in which several generations live together within a single household. In some cultures, the term is used synonymously with consang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |