|
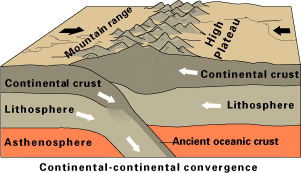
San Rafael Orogeny
The San Rafael orogeny was an orogeny that affected parts of western Argentina and Chile during the Late Paleozoic. The resulting orogenic belt has a NW-NNW curved form. The San Rafael orogeny might have been linked with the roughly contemporary Gondwanide orogeny of eastern Argentina. Parts of the Choiyoi Group sediments were deformed by the San Rafael orogeny. During the Neogene ancient faults related to the San Rafael orogeny conditioned the geometry of the blocks affected by the Andean orogeny. Some of the plutons of the Elqui-Limarí Batholith were emplaced a context of crustal thickening Thrust tectonics or contractional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the tectonic processes associated with, the shortening and thickening of the crust or lithosphere. It is one of the three main types of tectonic regime, ... derivative of the San Rafael orogeny. References Orogenies of South America Geology of Mendoza Province Geology of Chile Paleozoic oro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwanide Orogeny
The Gondwanide orogeny was an orogeny active in the Permian that affected parts of Gondwana that are by current geography now located in southern South America, South Africa, Antarctica, Australia and New Guinea. The zone of deformation in Argentina extends as a belt south and west of the cratonic nucleus of Río de la Plata–Pampia. The deformation of the orogeny is visible in the Sierra de la Ventana mountains in Argentina and the Cape Fold Belt in South Africa. The Gondwanide orogeny might have been linked with the roughly contemporary San Rafael orogeny of western Argentina. The Gondwanide orogeny is the successor to the Neoproterozoic-Paleozoic Terra Australis orogeny in Gondwana. The Gondwanide orogeny was widespread across the southern hemisphere during the Late Permian-Early Triassic. Alexander du Toit described Gondwanide deformation as consisting of asymmetric folding, thrusting and cleavage formation. The uplift and erosion which followed is evidenced by an unc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choiyoi Group
Choiyoi Group ( es, Grupo Choiyoi) is a Permian and Triassic-aged group of volcano-sedimentary formations in Argentina and Chile. The group bears evidence of bimodal-style volcanism related to an ancient subduction zone that existed along the western margin of the supercontinent Gondwana. The Choiyoi Group has a large areal extent through western Argentina and parts of Chile, covering at least , but probably around . While the subsurface extent of the group is large, exposures in Argentina are most common in the Frontal Cordillera, the San Rafael Massif and the Principal Cordillera of southern Mendoza and northern Neuquén. In parts the group reaches thicknesses of 2 to 4 km. The plutonic equivalent of the Choiyoi Group volcanic material are mostly granitoids. The remnants of the magmatic arc that produced much of volcanic material is now preserved as a series of batholiths, including the Coastal Batholith of central Chile in the Chilean Coast Range. During the Permian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonophysics (journal)
''Tectonophysics, The International Journal of Geotectonics and the Geology and Physics of the Interior of the Earth'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier. It was established in 1964 and covers the field of tectonophysics, including kinematics, structure, composition, and dynamics of the solid Earth at all scales. Organization The editors-in-chief are Philippe Agard (Pierre and Marie Curie University), Jean-Philippe Avouac (California Institute of Technology), Ramon Carbonell (Spanish National Research Council), Rob Govers (Utrecht University), Zheng Xiang Li (Curtin University), and Kelin Wang (Geological Survey of Canada). Abstracting and indexing This journal is abstracted and indexed in over fifty databases, including Current Contents, GeoRef, Inspec, Scopus and Web of Science. Notable articles According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Tectonophysics'' has a 2011 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first humans (''Homo habilis'') appeared in Africa near the end of the period. Some continental movements took place, the most significant event being the connection of North and South America at the Isthmus of Panama, late in the Pliocene. This cut off the warm ocean currents from the Pacific to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andean Orogeny
The Andean orogeny ( es, Orogenia andina) is an ongoing process of orogeny that began in the Early Jurassic and is responsible for the rise of the Andes mountains. The orogeny is driven by a reactivation of a long-lived subduction system along the western margin of South America. On a continental scale the Cretaceous (90 Ma) and Oligocene (30 Ma) were periods of re-arrangements in the orogeny. Locally the details of the nature of the orogeny varies depending on the segment and the geological period considered. Overview Subduction orogeny has been occurring in what is now western South America since the break-up of the supercontinent Rodinia in the Neoproterozoic. The Paleozoic Pampean, Famatinian and Gondwanan orogenies are the immediate precursors to the later Andean orogeny.Charrier ''et al''. 2006, pp. 113–114. The first phases of Andean orogeny in the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous were characterized by extensional tectonics, rifting, the development of back-arc basins a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluton
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and compositions, illustrated by examples like the Palisades Sill of New York and New Jersey; the Henry Mountains of Utah; the Bushveld Igneous Complex of South Africa; Shiprock in New Mexico; the Ardnamurchan intrusion in Scotland; and the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California. Because the solid country rock into which magma intrudes is an excellent insulator, cooling of the magma is extremely slow, and intrusive igneous rock is coarse-grained (phaneritic). Intrusive igneous rocks are classified separately from extrusive igneous rocks, generally on the basis of their mineral content. The relative amounts of quartz, alkali feldspar, plagioclase, and feldspathoid is particularly important in classifying intrusive igneous rocks. Intrusions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elqui-Limarí Batholith
The Elqui-Limarí Batholith is a group of plutons in the Andes of Chile and Argentina between the latitudes of 28 and 30° S. The plutons of the batholith were Methods of pluton emplacement, emplaced and cooled in the Paleozoic, Late Paleozoic and the Triassic, earliest Mesozoic. Some of the plutons were emplaced in a context of crustal thickening related to the San Rafael orogeny. Together with the Coastal Batholith of central Chile, Chilean Coastal Batholith and the Colangüil Batholith the Elqui-Limarí Batholith is a remnant of the volcanic arcs that erupted the volcanic material of the Choiyoi Group. As Pangaea broke up at the end of the Paleozoic, ocean crust material was Subduction, subducted under the eastern and western continental plates. Volcanic melts from this oceanic crustal material rose through the mantle and embedded themselves in the overlying continental crust. This process was the ultimate cause of these igneous intrusive bodies. References Carboniferous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustal Thickening
Thrust tectonics or contractional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the tectonic processes associated with, the shortening and thickening of the crust or lithosphere. It is one of the three main types of tectonic regime, the others being extensional tectonics and strike-slip tectonics. These match the three types of plate boundary, convergent (thrust), divergent (extensional) and transform (strike-slip). There are two main types of thrust tectonics, thin-skinned and thick-skinned, depending on whether or not basement rocks are involved in the deformation. The principle geological environments where thrust tectonics is observed are zones of continental collision, restraining bends on strike-slip faults and as part of detached fault systems on some passive margins. Deformation styles In areas of thrust tectonics, two main processes are recognized: thin-skinned deformation and thick-skinned deformation. The distinction is important as attempts to structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogenies Of South America
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |