|
Samuel Untermyer II
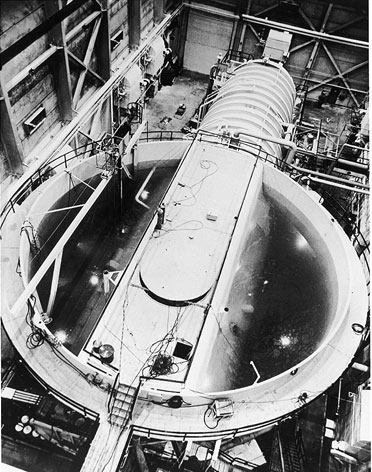
Samuel Untermyer II, (25 November 1912 – 26 January 2001) was an American nuclear scientist. He was the son of notable New York City jurist Irwin Untermyer and grandson of attorney Samuel Untermyer. Samuel Untermyer II theorized that steam bubble formation in a nuclear reactor core would not produce unstable reactions, but would instead result in an inherently stable and self-controlling reactor design. This was eventually proved in the BORAX experiments, which led to the design of the Boiling water reactor. In recognition of his fundamental development work on water-cooled reactors, the American Nuclear Society The American Nuclear Society (ANS) is an international, not-for-profit organization of scientists, engineers, and industry professionals that promote the field of nuclear engineering and related disciplines. ANS is composed of three communities: ... now has an award named after him for work in this field. Untermyer was awarded the Newcomen Medal in 1980. External ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Science
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter. Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the atom as a whole, including its electrons. Discoveries in nuclear physics have led to applications in many fields. This includes nuclear power, nuclear weapons, nuclear medicine and magnetic resonance imaging, industrial and agricultural isotopes, ion implantation in materials engineering, and radiocarbon dating in geology and archaeology. Such applications are studied in the field of nuclear engineering. Particle physics evolved out of nuclear physics and the two fields are typically taught in close association. Nuclear astrophysics, the application of nuclear physics to astrophysics, is crucial in explaining the inner workings of stars and the origin of the chemical elements. History The history of nuclear physics as a discipline d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory is a science and engineering research United States Department of Energy National Labs, national laboratory operated by University of Chicago, UChicago Argonne LLC for the United States Department of Energy. The facility is located in Lemont, Illinois, outside of Chicago, and is the largest national laboratory by size and scope in the Midwest. Argonne had its beginnings in the Metallurgical Laboratory of the University of Chicago, formed in part to carry out Enrico Fermi's work on nuclear reactors for the Manhattan Project during World War II. After the war, it was designated as the first national laboratory in the United States on July 1, 1946. In the post-war era the lab focused primarily on non-weapon related nuclear physics, designing and building the first power-producing nuclear reactors, helping design the reactors used by the United States' nuclear navy, and a wide variety of similar projects. In 1994, the lab's nuclear mission ended, and today ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish American Scientists
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The people of the Kingdom of Israel and the ethnic and religious group known as the Jewish people that descended from them have been subjected to a number of forced migrations in their history" and Hebrews of historical Israel and Judah. Jewish ethnicity, nationhood, and religion are strongly interrelated, "Historically, the religious and ethnic dimensions of Jewish identity have been closely interwoven. In fact, so closely bound are they, that the traditional Jewish lexicon hardly distinguishes between the two concepts. Jewish religious practice, by definition, was observed exclusively by the Jewish people, and notions of Jewish peoplehood, nation, and community were suffused with faith in the Jewish God, the practice of Jewish (religious) la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American People Of German-Jewish Descent
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Nuclear Physicists
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams Soccer * B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2001 Deaths
This is a list of deaths of notable people, organised by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked here. 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 See also * Lists of deaths by day The following pages, corresponding to the Gregorian calendar, list the historical events, births, deaths, and holidays and observances of the specified day of the year: Footnotes See also * Leap year * List of calendars * List of non-standard ... * Deaths by year {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1912 Births
Year 191 ( CXCI) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Apronianus and Bradua (or, less frequently, year 944 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 191 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Parthia * King Vologases IV of Parthia dies after a 44-year reign, and is succeeded by his son Vologases V. China * A coalition of Chinese warlords from the east of Hangu Pass launches a punitive campaign against the warlord Dong Zhuo, who seized control of the central government in 189, and held the figurehead Emperor Xian hostage. After suffering some defeats against the coalition forces, Dong Zhuo forcefully relocates the imperial capital from Luoyang to Chang'an. Before leaving, Dong Zhuo orders his troops to loot the tombs of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idaho National Laboratory
Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is one of the national laboratories of the United States Department of Energy and is managed by the Battelle Energy Alliance. While the laboratory does other research, historically it has been involved with nuclear research. Much of current knowledge about how nuclear reactors behave and misbehave was discovered at what is now Idaho National Laboratory. John Grossenbacher, former INL director, said, "The history of nuclear energy for peaceful application has principally been written in Idaho". Various organizations have built more than 50 reactors at what is commonly called "the Site", including the ones that gave the world its first usable amount of electricity from nuclear power and the power plant for the world's first nuclear submarine. Although many are now decommissioned, these facilities are the largest concentration of reactors in the world. It is on a complex in the high desert of eastern Idaho, between Arco to the west and Idaho Fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin Institute
The Franklin Institute is a science museum and the center of science education and research in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is named after the American scientist and statesman Benjamin Franklin. It houses the Benjamin Franklin National Memorial. Founded in 1824, the Franklin Institute is one of the oldest centers of science education and development in the United States. Its chief astronomer is Derrick Pitts. History On February 5, 1824, Samuel Vaughan Merrick and William H. Keating founded the Franklin Institute of the State of Pennsylvania for the Promotion of the Mechanic Arts. Begun in 1825, the institute was an important force in the professionalization of American science and technology through the nineteenth century, beginning with early investigations into steam engines and water power. In addition to conducting scientific inquiry, it fostered research and education by running schools, publishing the influential ''Journal of The Franklin Institute'', sponsoring e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Nuclear Society
The American Nuclear Society (ANS) is an international, not-for-profit organization of scientists, engineers, and industry professionals that promote the field of nuclear engineering and related disciplines. ANS is composed of three communities: professional divisions, local sections/plant branches, and student sections. Individual members consist of fellows, professional members, and student members. Various organization members are also included in the Society including corporations, governmental agencies, educational institutions, and associations. As of spring 2020, ANS is composed of more than 10,000 members from more than 40 countries. ANS is also a member of the International Nuclear Societies Council (INSC). History The American Nuclear Society was founded in 1954 as a not-for-profit association to promote the growing nuclear field. Shortly thereafter in 1955, ANS held its first annual meeting and elected Walter Zinn as its first president. Originally headquartered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiling Water Reactor
A boiling water reactor (BWR) is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. It is a design different from a Soviet graphite-moderated RBMK. It is the second most common type of electricity-generating nuclear reactor after the pressurized water reactor (PWR), which is also a type of light water nuclear reactor. The main difference between a BWR and PWR is that in a BWR, the reactor core heats water, which turns to steam and then drives a steam turbine. In a PWR, the reactor core heats water, which does not boil. This hot water then exchanges heat with a lower pressure system, which turns water into steam that drives the turbine. The BWR was developed by the Argonne National Laboratory and General Electric (GE) in the mid-1950s. The main present manufacturer is GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, which specializes in the design and construction of this type of reactor. Overview A boiling water reactor uses demineralized water as a coolant and neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |