|
Samsung Galaxy Trend Plus
Samsung Galaxy Ace 2 (GT-I8160) is a smartphone manufactured by Samsung that runs the Android operating system. Announced and released by Samsung in February 2012, the Galaxy Ace 2 is the successor to the Galaxy Ace Plus. Being a mid-range smartphone, Galaxy Ace 2 contains hardware between that of the Galaxy Ace Plus and Galaxy S Advance; it features a dual-core 800 MHz processor on the NovaThor U8500 chipset with the Mali-400 GPU. In May 2012, the device went on sale in the UK. Hardware Galaxy Ace 2 is a 3.5G mobile device that offers quad-band GSM, and was announced with dual-band 900/2100 MHz HSDPA at 14.4 Mbit/s downlink and 5.76 Mbit/s uplink speeds. The display is a 3.8-inch capacitive PLS TFT LCD touchscreen with 16M colours in a WVGA (480x800) resolution. There is also a 5-megapixel camera with LED flash and auto-focus, capable of recording videos at QVGA (320x240), VGA (640x480) and HD (1280x720) resolutions. Galaxy Ace 2 also has a front-facing VGA camera. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samsung Galaxy
Samsung Galaxy (, stylised as SΛMSUNG Galaxy since 2015 (except Japan where it omits the Samsung branding), previously stylised as Samsung GALAXY; abbreviated as SG) is a series of computing and mobile computing devices that are designed, manufactured and marketed by Samsung Electronics. The product line includes the Samsung Galaxy S series of high-end smartphones, the Samsung Galaxy Tab series of tablets, the Samsung Galaxy Note series of tablets and phablets with the added functionality of a stylus, the foldable Samsung Galaxy Z series, and smartwatches including the first version of the Samsung Galaxy Gear, with later versions dropping the Galaxy branding, until the release of the Samsung Galaxy Watch in 2018. Samsung Galaxy devices use the Android operating system produced by Google, with a custom user interface called One UI (with previous versions being known as Samsung Experience and TouchWiz). However, the Galaxy TabPro S is the first Galaxy-branded Windows 10 d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827). Definition One volt is defined as the electric potential between two points of a conducting wire when an electric current of one ampere dissipates one watt of power between those points. Equivalently, it is the potential difference between two points that will impart one joule of energy per coulomb of charge that passes through it. It can be expressed in terms of SI base units ( m, kg, second, s, and ampere, A) as : \text = \frac = \frac = \frac. It can also be expressed as amperes times ohms (current times resistance, Ohm's law), webers per second (magnetic flux per time), watts per ampere (power per current), or joules per coulomb (energy per charge), which is also equivalent to electronvolts per elementary charge: : \text = \tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megapixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as red, green, and blue, or cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although ''sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet other contexts (like MRI) it may refer to a set of component intensities for a spatial position. Etymology The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Display Resolution
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized (e.g. by VESA) and typically given a name and an initialism that is descriptive of its dimensions. A graphics display resolution can be used in tandem with the size of the graphics display to calculate pixel density. An increase in the pixel density often correlates with a decrease in the size of individual pixels on a display. Overview by vertical resolution and aspect ratio Aspect ratio The favored aspect ratio of mass-market display industry products has changed gradually from 4:3, then to 16:10, then to 16:9, and is now changing to 18:9 for smartphones. The 4:3 aspect ratio generally reflects older products, especially the era of the cathode ray tube (CRT). The 16:10 aspect ratio had its largest use in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TFT LCD
A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments. TFT LCDs are used in appliances including television sets, computer monitors, mobile phones, handheld devices, video game systems, personal digital assistants, navigation systems, projectors, and dashboards in automobiles. History In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark's ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitive Sensing
In electrical engineering, capacitive sensing (sometimes capacitance sensing) is a technology, based on capacitive coupling, that can detect and measure anything that is conductive or has a dielectric constant different from air. Many types of sensors use capacitive sensing, including sensors to detect and measure proximity, pressure, position and displacement, force, humidity, fluid level, and acceleration. Human interface devices based on capacitive sensing, such as touchpads, can replace the computer mouse. Digital audio players, mobile phones, and tablet computers will sometimes use capacitive sensing touchscreens as input devices. Capacitive sensors can also replace mechanical buttons. A capacitive touchscreen typically consists of a capacitive touch sensor along with at least two complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuit (IC) chips, an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) controller and a digital signal processor (DSP). Capacitive sensing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push Button
A push-button (also spelled pushbutton) or simply button is a simple switch mechanism to control some aspect of a machine or a process. Buttons are typically made out of hard material, usually plastic or metal. The surface is usually flat or shaped to accommodate the human finger or hand, so as to be easily depressed or pushed. Buttons are most often biased switches, although many un-biased buttons (due to their physical nature) still require a spring to return to their un-pushed state. Terms for the "pushing" of a button include pressing, depressing, mashing, slapping, hitting, and punching. Uses The "push-button" has been utilized in calculators, push-button telephones, kitchen appliances, and various other mechanical and electronic devices, home and commercial. In industrial and commercial applications, push buttons can be connected together by a mechanical linkage so that the act of pushing one button causes the other button to be released. In this way, a stop button ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximity Sensor
A proximity sensor is a sensor able to detect the presence of nearby objects without any physical contact. A proximity sensor often emits an electromagnetic field or a beam of electromagnetic radiation (infrared, for instance), and looks for changes in the field or return signal. The object being sensed is often referred to as the proximity sensor's target. Different proximity sensor targets demand different sensors. For example, a capacitive proximity sensor or photoelectric sensor might be suitable for a plastic target; an inductive proximity sensor always requires a metal target. Proximity sensors can have a high reliability and long functional life because of the absence of mechanical parts and lack of physical contact between the sensor and the sensed object. Proximity sensors are also used in machine vibration monitoring to measure the variation in distance between a shaft and its support bearing. This is common in large steam turbines, compressors, and motors that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with magnetic north. Other methods may be used, including gyroscopes, magnetometers, and GPS receivers. Compasses often show angles in degrees: north corresponds to 0°, and the angles increase clockwise, so east is 90°, south is 180°, and west is 270°. These numbers allow the compass to show azimuths or bearings which are commonly stated in degrees. If local variation between magnetic north and true north is known, then direction of magnetic north also gives direction of true north. Among the Four Great Inventions, the magnetic compass was first invented as a device for divination as early as the Chinese Han Dynasty (since c. 206 BC),Li Shu-hua, p. 176 and later adopted for navigation by the Song Dynasty Chinese during the 11th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLONASS
GLONASS (russian: ГЛОНАСС, label=none, ; rus, links=no, Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, r=Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, t=Global Navigation Satellite System) is a Russian satellite navigation system operating as part of a radionavigation-satellite service. It provides an alternative to Global Positioning System (GPS) and is the second navigational system in operation with global coverage and of comparable precision. Satellite navigation devices supporting both GPS and GLONASS have more satellites available, meaning positions can be fixed more quickly and accurately, especially in built-up areas where buildings may obscure the view to some satellites. GLONASS supplementation of GPS systems also improves positioning in high latitudes (north or south). Development of GLONASS began in the Soviet Union in 1976. Beginning on 12 October 1982, numerous rocket launches added satellites to the system, unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-GPS
Assisted GNSS (A-GNSS) is a GNSS augmentation system that often significantly improves the startup performance—i.e., time-to-first-fix (TTFF)—of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS). A-GNSS works by providing the necessary data to the device via a radio network instead of the slow satellite link, essentially "warming up" the receiver for a fix. When applied to GPS, it is known as assisted GPS or augmented GPS (abbreviated generally as A-GPS and less commonly as aGPS). Other local names include A-GANSS for Galileo and A-Beidou for BeiDou. A-GPS is extensively used with GPS-capable cellular phones, as its development was accelerated by the U.S. FCC's 911 requirement to make cell phone location data available to emergency call dispatchers. Background Every GPS device requires orbital data about the satellites to calculate its position. The data rate of the satellite signal is only 50 bit/s, so downloading orbital information like ephemerides and the almanac directly fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
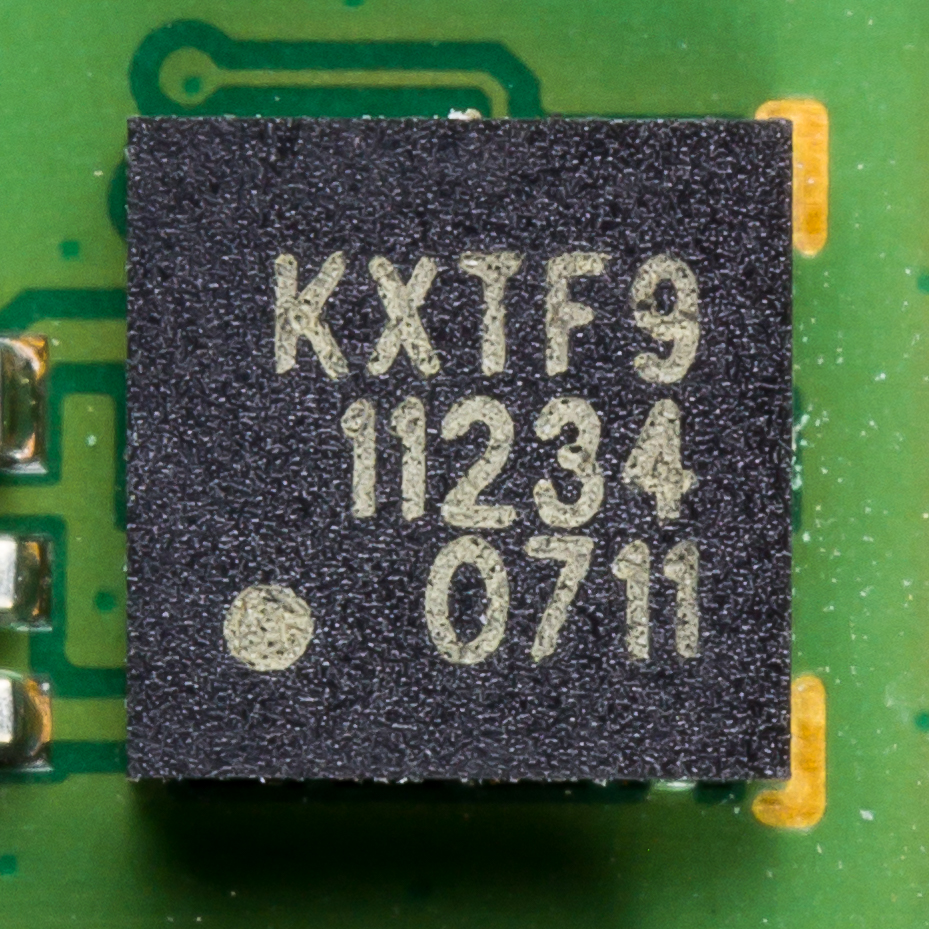
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |