|
Salton Sea Test Base
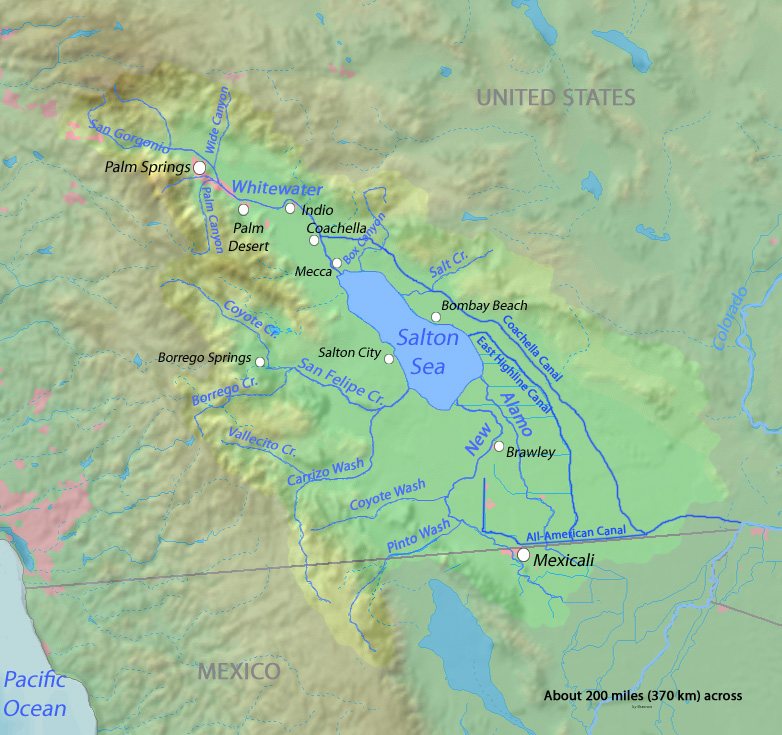
The Salton Sea is a shallow, landlocked, highly saline body of water in Riverside and Imperial counties at the southern end of the U.S. state of California. It lies on the San Andreas Fault within the Salton Trough that stretches to the Gulf of California in Mexico. Over millions of years, the Colorado River has flowed into the Imperial Valley and deposited alluvium (soil), creating fertile farmland, building up the terrain, and constantly moving its main course and river delta. For thousands of years, the river has alternately flowed into the valley, or diverted around it, creating either a saline lake called Lake Cahuilla, or a dry desert basin, respectively. When the Colorado River flows into the valley, the lake level depends on river flows and the balance between inflow and evaporative loss. When the river diverts around the valley, the lake dries completely, as it did around 1580. Hundreds of archaeological sites have been found in this region, indicating possibly long-ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado Desert
California's Colorado Desert is a part of the larger Sonoran Desert. It encompasses approximately , including the heavily irrigated Coachella and Imperial valleys. It is home to many unique flora and fauna. Geography and geology The Colorado Desert is a subdivision of the larger Sonoran Desert encompassing approximately . The desert encompasses Imperial County and includes parts of San Diego County, Riverside County, and a small part of San Bernardino County, California, United States. Most of the Colorado Desert lies at a relatively low elevation, below , with the lowest point of the desert floor at below sea level, at the Salton Sea. Although the highest peaks of the Peninsular Ranges reach elevations of nearly , most of the region's mountains do not exceed . In this region, the geology is dominated by the transition of the tectonic plate boundary from rift to fault. The southernmost strands of the San Andreas Fault connect to the northernmost extensions of the East Pacif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salton Trough
The Salton Trough is an active tectonic pull-apart basin, or graben. It lies within the Imperial, Riverside, and San Diego counties of southeastern California, United States and extends south of the Mexico–United States border into the state of Baja California, Mexico. The northwestern end of the trough starts at the San Gorgonio Pass in Riverside County, and extends southeast to the Gulf of California. Major geographical features located in the trough include the Coachella Valley, the Salton Sea, and the Imperial Valley, in the United States, and the western side of the Mexicali Valley, and the Colorado River Delta in Mexico. The Salton Trough is a result of crustal stretching and sinking caused by the combined actions of the San Andreas Fault and the East Pacific Rise, particularly the Gulf of California Rift Zone (GCRZ), the northernmost portion of the East Pacific Rise. The GCRZ and the San Andreas Fault both terminate near the south end of the Salton Sea, in an area cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
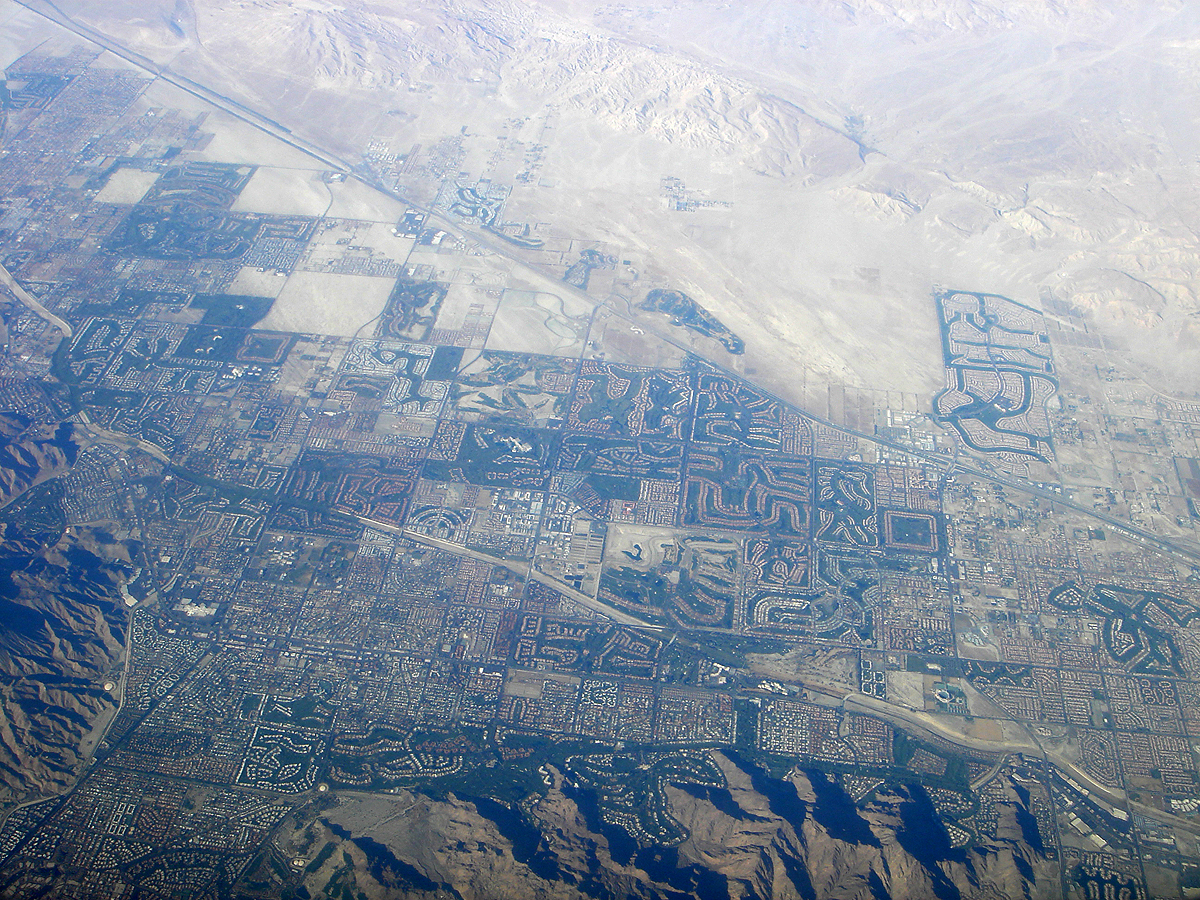
Indio, California
Indio (Spanish language, Spanish for "Indian") is a city in Riverside County, California, Riverside County, California, United States, in the Coachella Valley of Southern California's Colorado Desert region. It lies east of Palm Springs, California, Palm Springs, east of Riverside, California, Riverside, east of Los Angeles, 148 miles (238 km) northeast of San Diego, and 250 miles (402 km) west of Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix. The population was 89,137 in the 2020 United States Census, up from 76,036 at the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, an increase of 17%. Indio is the most populous city in the Coachella Valley, and was formerly referred to as the Hub of the Valley after a Chamber of Commerce slogan used in the 1970s. It was later nicknamed the City of Festivals, a reference to the numerous cultural events held in the city, most notably the Coachella Valley Music and Arts Festival. History Indio was originally inhabited by the Torres Martinez Desert Cahuilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New River (Mexico-United States)
New River may refer to: Waterways Caribbean * Nuevo River (Puerto Rico) * Rio Nuevo (Jamaica) Europe * New River (Fens), a man-made watercourse in the English Fenlands * New River (London), a man-made watercourse in Hertfordshire and London North America * New River (Mexico–United States) (''Rio Nuevo'' in Spanish), which flows from the Mexicali Valley in Baja California into the Salton Sea in California * New River (Trinity River tributary), a tributary of the Trinity River in northern California * New River (Broward County, Florida), a channel which drains the Everglades through Fort Lauderdale in South Florida * New River (Carrabelle River tributary), a tributary of the Carrabelle River in Florida * New River (Santa Fe River tributary), a tributary of the Santa Fe River in northern Florida * New River (Hillsborough River tributary), a tributary of the Hillsborough River (Florida) in Hillsborough and Pasco Counties in Florida * New River (Chattahoochee River trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particulate Pollution
Particulate pollution is pollution of an environment that consists of particles suspended in some medium. There are three primary forms: atmospheric particulate matter, marine debris, and space debris. Some particles are released directly from a specific source, while others form in chemical reactions in the atmosphere. Particulate pollution can be derived from either natural sources or anthropogenic processes. Atmospheric particulate matter Atmospheric particulate matter, also known as particulate matter, or PM, describes solids and/or liquid particles suspended in a gas, most commonly the Earth's atmosphere. Particles in the atmosphere can be divided into two types, depending on the way they are emitted. Primary particles, such as mineral dust, are emitted into the atmosphere. Secondary particles, such as ammonium nitrate, are formed in the atmosphere through gas-to-particle conversion. Sources Some particulates occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Kill
The term fish kill, known also as fish die-off, refers to a localized die-off of fish populations which may also be associated with more generalized mortality of aquatic life.University of Florida. Gainesville, FL (2005) ''Plant Management in Florida's Waters.'' The most common cause is reduced oxygen in the water, which in turn may be due to factors such as drought, algae bloom, overpopulation, or a sustained increase in water temperature. Infectious diseases and parasites can also lead to fish kill. Toxicity is a real but far less common cause of fish kill. Fish kills are often the first visible signs of environmental stress and are usually investigated as a matter of urgency by environmental agencies to determine the cause of the kill. Many fish species have a relatively low tolerance of variations in environmental conditions and their death is often a potent indicator of problems in their environment that may be affecting other animals and plants and may have a direct impact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Flyway
The Pacific Flyway is a major north-south flyway for migratory birds in the Americas, extending from Alaska to Patagonia. Every year, migratory birds travel some or all of this distance both in spring and in fall, following food sources, heading to breeding grounds, or travelling to overwintering sites. Any given bird species travels roughly the same route every year, at almost the same time. Ornithologists and birdwatchers can often predict to the day when a particular species will show up in their area. Notable locations Along the Pacific Flyway, there are many key rest stops where birds of many species gather, sometimes in the millions, to feed and regain their strength before continuing. Some species may remain in these rest stops for the entire season, but most stay a few days before moving on. :''Notable locations include:'' * Boundary Bay, British Columbia, has been listed as an Important Bird Area by the Canadian government in recognition of its value to migratory bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resort Destination
A resort town, often called a resort city or resort destination, is an urban area where tourism or vacationing is the primary component of the local culture and economy. A typical resort town has one or more actual resorts in the surrounding area. Sometimes the term ''resort town'' is used simply for a locale popular among tourists. One task force in British Columbia used the definition of an incorporated or unincorporated contiguous area where the ratio of transient rooms, measured in bed units, is greater than 60% of the permanent population. Generally, tourism is the main export in a resort town economy, with most residents of the area working in the tourism or resort industry. Shops and luxury boutiques selling locally themed souvenirs, motels, and unique restaurants often proliferate the downtown areas of a resort town. In the case of the United States, resort towns were created around the late 1800s and early 1900s with the development of early town-making.Crewe, Kathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert Basin
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the land surface of the Earth is arid or semi-arid. This includes much of the polar regions, where little precipitation occurs, and which are sometimes called polar deserts or "cold deserts". Deserts can be classified by the amount of precipitation that falls, by the temperature that prevails, by the causes of desertification or by their geographical location. Deserts are formed by weathering processes as large variations in temperature between day and night put strains on the rocks, which consequently break in pieces. Although rain seldom occurs in deserts, there are occasional downpours that can result in flash floods. Rain falling on hot rocks can cause them to shatter, and the resulting fragments and rubble strewn over the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Cahuilla
Lake Cahuilla ( ; also known as Lake LeConte and Blake Sea) was a prehistoric lake in California and northern Mexico. Located in the Coachella and Imperial valleys, it covered surface areas of to a height of above sea level during the Holocene. During earlier stages of the Pleistocene, the lake reached even higher elevations, up to above sea level. During the Holocene most of the water came from the Colorado River with little contribution from local runoff; in the Pleistocene local runoff was higher and it is possible that Lake Cahuilla was supported solely from local water sources during the Wisconsin glaciation. The lake overflowed close to Cerro Prieto into the Rio Hardy, eventually draining into the Gulf of California. The lake formed several times during the Holocene, when water from the Colorado River was diverted into the Salton Trough. This tectonic depression forms the northern basin of the Gulf of California, but it was separated from the sea proper by the growth o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saline Lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). In some cases, salt lakes have a higher concentration of salt than sea water; such lakes can also be termed hypersaline lakes, and may also be pink lakes on account of their colour. An alkalic salt lake that has a high content of carbonate is sometimes termed a soda lake. One saline lake classification differentiates between: *subsaline: 0.5–3‰ (0.05-0.3%) *hyposaline: 3–20‰ (0.3-2%) *mesosaline: 20–50‰ (2-5%) *hypersaline: greater than 50‰ (5%) Properties Salt lakes form when the water flowing into the lake, containing salt or minerals, cannot leave because the lake is endorheic (terminal). The water then evaporates, leaving behind any dissolved salts and thus increasing its salinity, making a salt lake an excellent place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |