|
Sally–Anne Test
The Sally–Anne test is a psychological test, used in developmental psychology to measure a person's social cognitive ability to attribute false beliefs to others. The flagship implementation of the Sally–Anne test was by Simon Baron-Cohen, Alan M. Leslie, and Uta Frith (1985); in 1988, Leslie and Frith repeated the experiment with human actors (rather than dolls) and found similar results. Test description To develop an efficacious test, Baron-Cohen ''et al.'' modified the puppet play paradigm of Wimmer and Perner (1983), in which puppets represent tangible characters in a story, rather than hypothetical characters of pure storytelling. In the Baron-Cohen, Leslie, and Frith study of theory of mind in autism, 61 children—20 of whom were diagnosed autistic under established criteria, 14 with Down syndrome and 27 of whom were determined as clinically unimpaired—were tested with "Sally" and "Anne". In the test process, after introducing the dolls, the child is asked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
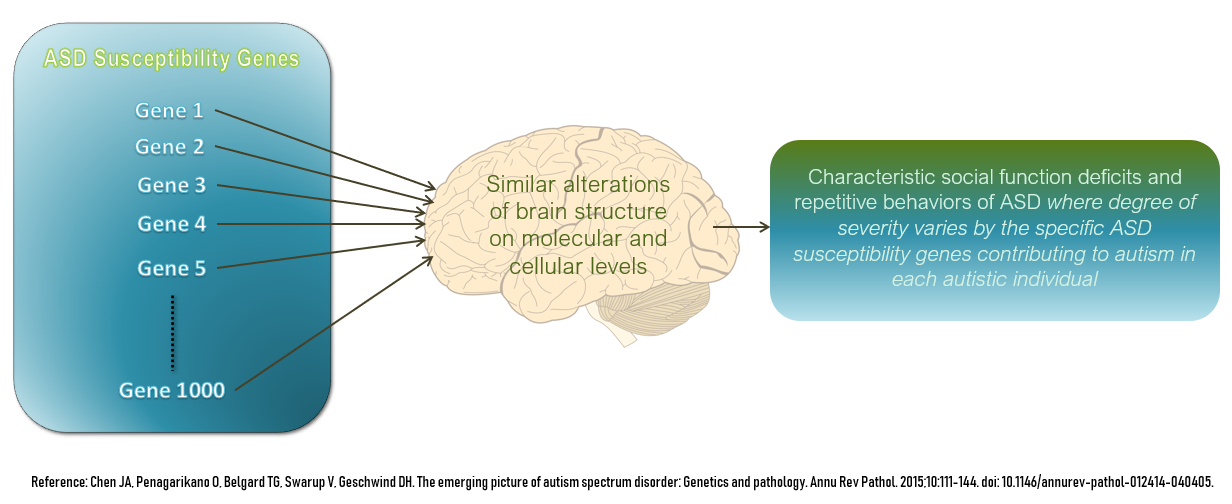
Autism
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPT-4
Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4 (GPT-4) is a multimodal large language model created by OpenAI and the fourth in its GPT series. It was released on March 14, 2023, and has been made publicly available in a limited form via ChatGPT Plus, with access to its commercial API being provided via a waitlist. As a transformer, GPT-4 was pretrained to predict the next token (using both public data and "data licensed from third-party providers"), and was then fine-tuned with reinforcement learning from human and AI feedback for human alignment and policy compliance. Observers reported the GPT-4 based version of ChatGPT to be an improvement on the previous (GPT-3.5 based) ChatGPT, with the caveat that GPT-4 retains some of the same problems. Unlike the predecessors, GPT-4 can take images as well as text as input. OpenAI has declined to reveal technical information such as the size of the GPT-4 model. Background OpenAI published their first paper on GPT in 2018, called "Improv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washington, United States. Its best-known software products are the Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft Office suite, and the Internet Explorer and Edge web browsers. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 21 in the 2020 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; it was the world's largest software maker by revenue as of 2019. It is one of the Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, and Meta. Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen on April 4, 1975, to develop and sell BASIC interpreters for the Altair 8800. It rose to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Directions In Psychological Science
''Current Directions in Psychological Science '' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal from the Association for Psychological Science (APS) that is published by SAGE Publications. Publication Scope ''Current Directions in Psychological Science'' publishes concise reviews by leading experts spanning all of scientific psychology and its applications. The reviews published in this journal cover diverse topics such as language, memory and cognition, development, the neural basis of behavior and emotions, various aspects of psychopathology, and theory of mind. These articles allow readers to stay apprised of important developments across subfields beyond their areas of expertise and bodies of research they might not otherwise be aware of. The articles in ''Current Directions'' are also written to be accessible to non-experts, making them suitable for use in the classroom as teaching supplements. The current editor of the journal is Robert Goldstone at Indiana University Bloo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Tager-Flusberg
Helen Tager-Flusberg, Ph.D., is a professor in the Department of Psychological and Brain Science at Boston University and the Departments of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Pediatrics at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM). She is the Director of the Center for Autism Research Excellence at Boston University. Personal life and education Tager-Flusberg was born in England. She received her bachelor's degree from the University College London in psychology. She moved to the US in the 1970s and obtained her PhD in Experimental Psychology from Harvard University in 1978. Her dissertation compared children with autism to children with severe developmental language disorders in studies on syntax, semantics and object play. She was a professor in the psychology department at the University of Massachusetts (UMass) until 2001, and between 1996 and 2001, she was a Senior Scientist at the UMass Medical Center. She has been at Boston University since 2001. initially at the School of Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Child Psychology And Psychiatry
scope The ''Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering both child and adolescent psychology and psychiatry providing an interdisciplinary perspective to the multidisciplinary field of child and adolescent mental health, though publication of high-quality empirical research, clinically-relevant studies and highly cited research reviews and practitioner review articles. It is one of two journals of the Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health. Publication history The ''Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry'' was first published in 1960 by the then Association for Child Psychology and Psychiatry (now the ''Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health'' following a name change on 18 March 2005). It dropped the "''Allied Disciplines''" component from its title in 2004. The primary founding aim of the journal was to "bring together original papers concerned with the child, from such diverse disciplines as psych ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autistic
The autism spectrum, often referred to as just autism or in the context of a professional diagnosis autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental condition (or conditions) characterized by difficulties in social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and the presence of repetitive behavior and restricted interests. Other common signs include unusual responses to sensory stimuli. Autism is generally understood as a ''spectrum disorder'', which means that it can manifest differently in each person: any given autistic individual is likely to show some, but not all, of the characteristics associated with it, and the person may exhibit them to varying degrees. Some autistic people remain nonspeaking over the course of their lifespan, while others have relatively unimpaired spoken language. There is large variation in the level of support people require, and the same person may present differently at varying times. Historically, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotypical
Neurotypical (NT, an abbreviation of neurologically typical) is a neologism widely used in the neurodiversity movement as a label for non-neurodivergent people. That is, anyone who has a typical neurotype, so excluding autistic people, those with ADHD, dyslexia, and so on. The term has been adopted by both the neurodiversity movement and the scientific community. It is not to be confused with the term ''allistic'', which refers specifically to non-autistic people, who may or may not have a divergent neurotype. Term Early definitions described neurotypicals as "people who do not have autistic-type brains", clarifying that this would exclude "autistic cousins" who are recognizably “autistic-like” but not necessarily autistic. Early uses of "NT" were often satirical, as in the Institute for the Study of the Neurologically Typical, but with time it came to be widely used unironically. People with any form of neurocognitive or mental disorder, whether congenital or acquired, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Down Syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic facial features. The average IQ of a young adult with Down syndrome is 50, equivalent to the mental ability of an eight- or nine-year-old child, but this can vary widely. The parents of the affected individual are usually genetically normal. The probability increases from less than 0.1% in 20-year-old mothers to 3% in those of age 45. The extra chromosome is believed to occur by chance, with no known behavioral activity or environmental factor that changes the probability. Down syndrome can be identified during pregnancy by prenatal screening followed by diagnostic testing or after birth by direct observation and genetic testing. Since the introduction of screening, Down syndrome pregnancies are often abor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory Of Mind
In psychology, theory of mind refers to the capacity to understand other people by ascribing mental states to them (that is, surmising what is happening in their mind). This includes the knowledge that others' mental states may be different from one's own states and include beliefs, desires, intentions, emotions, and thoughts. Possessing a functional theory of mind is considered crucial for success in everyday human social interactions. People use such a theory when analyzing, judging, and inferring others' behaviors. The discovery and development of theory of mind primarily came from studies done with animals and infants. Factors including drug and alcohol consumption, language development, cognitive delays, age, and culture can affect a person's capacity to display theory of mind. It has been proposed that deficits in theory of mind can occur in people with autism (although this is contentious), anorexia nervosa, schizophrenia, dysphoria, attention deficit hyperactivity diso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Test
Psychological testing is the administration of psychological tests. Psychological tests are administered by trained evaluators. A person's responses are evaluated according to carefully prescribed guidelines. Scores are thought to reflect individual or group differences in the construct the test purports to measure. The science behind psychological testing is psychometrics. Psychological tests According to Anastasi and Urbina, psychological tests involve observations made on a "carefully chosen ''sample'' mphasis authorsof an individual's behavior." A psychological test is often designed to measure unobserved constructs, also known as latent variables. Psychological tests can include a series of tasks or problems that the respondent has to solve. Psychological tests can include questionnaires and interviews, which are also designed to measure unobserved constructs. Questionnaire- and interview-based scales typically differ from psychoeducational tests, which ask for a responden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |