|
Salisbury Cathedral Noah
Salisbury ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers River Avon, Hampshire, Avon, River Nadder, Nadder and River Bourne, Wiltshire, Bourne. The city is approximately from Southampton and from Bath, Somerset, Bath. Salisbury is in the southeast of Wiltshire, near the edge of Salisbury Plain. Salisbury Cathedral was formerly north of the city at Old Sarum Cathedral, Old Sarum. The cathedral was relocated and a settlement grew up around it, which received a city charter in 1227 as . This continued to be its official name until 2009 structural changes to local government in England, 2009, when Salisbury City Council was established. Salisbury railway station is an interchange between the West of England Main Line and the Wessex Main Line. Stonehenge is a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site and is northwest of Salisbury. Name The name ''Salisbury'', which is first rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In The United Kingdom
This is a list of cities in the United Kingdom that are officially designated such . It lists those places that have been granted city status by letters patent or royal charter. There are currently a total of 76 such cities in the United Kingdom: 55 in England, eight in Scotland, seven in Wales, and six in Northern Ireland.Department for Culture, Media and Sport.Civic Honours Competition: UK Cities. The National Archives (United Kingdom), 18 January 2011. Accessed 17 December 2018. Of these, 23 in England, two in Wales, and two in Northern Ireland have Lord Mayors; four in Scotland have Lord Provosts. In some cases, the area holding city status does not coincide with the built up area or conurbation of which it forms part. In Greater London, for example, the City of London and that of Westminster each hold city status separately but no other local authority has been granted city status, nor has Greater London as a whole. In other cases, such as the Cities of Canterbury and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
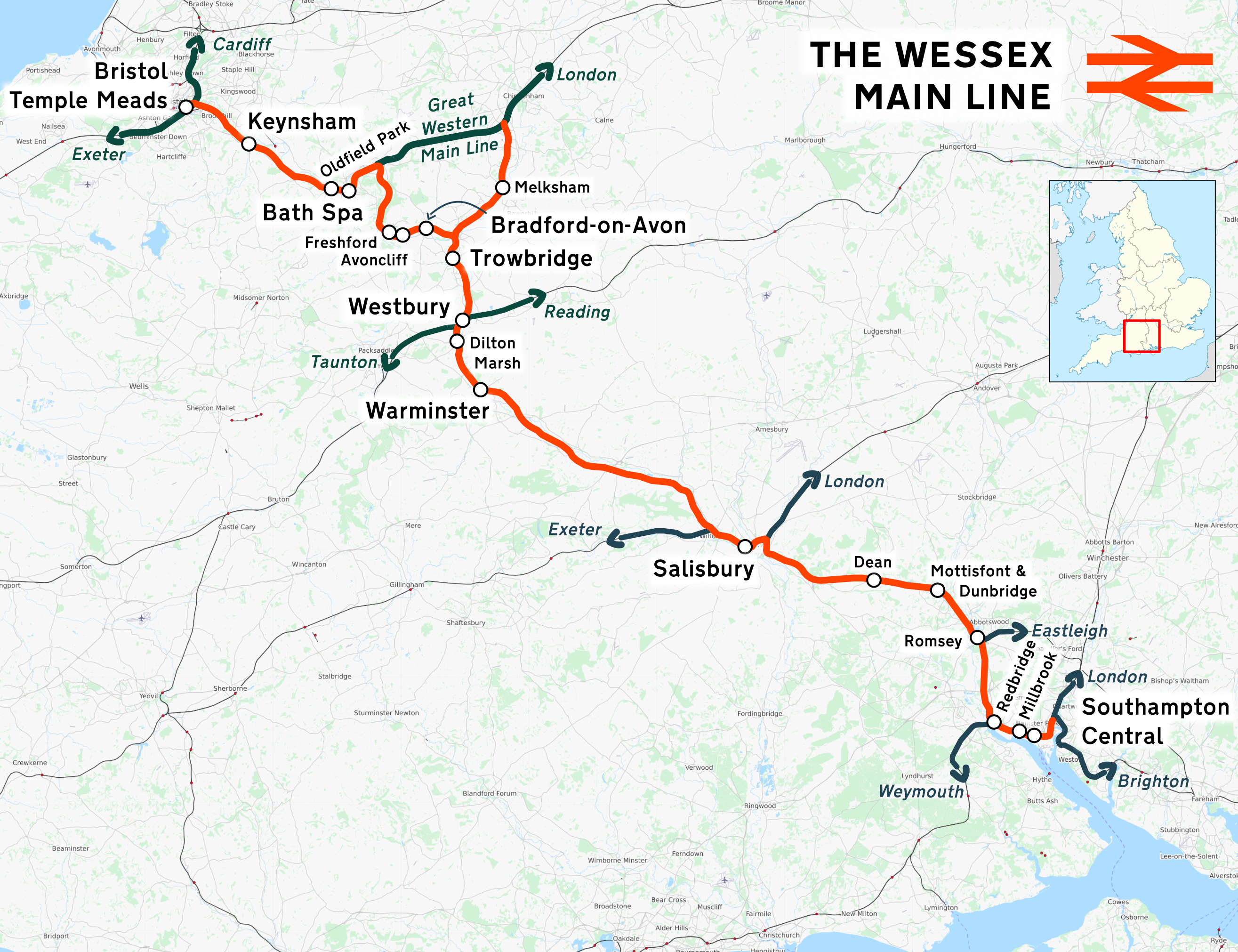
Wessex Main Line
The Wessex Main Line is the railway line from Bristol Temple Meads to Southampton Central. Diverging from this route is the Heart of Wessex Line from Westbury to Weymouth. The Wessex Main Line intersects the Reading to Taunton Line at and the West of England Main Line at . Places served The places served are listed below. *Bristol Temple Meads * Keynsham * Oldfield Park * Bath Spa ** Great Western Main Line diverges to Chippenham, Swindon and London Paddington * Freshford *Avoncliff *Bradford-on-Avon *Trowbridge * Westbury **Heart of Wessex Line diverges to Weymouth *Dilton Marsh *Warminster *Salisbury *Dean * Mottisfont & Dunbridge * Romsey ** Eastleigh to Romsey Line diverges to Chandler's Ford and Eastleigh *Southampton Passenger services are currently operated by Great Western Railway Portsmouth - Cardiff services, supplemented by South Western Railway between Salisbury and Southampton, and by Great Western high-speed express services between Bristol and Bath. Some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
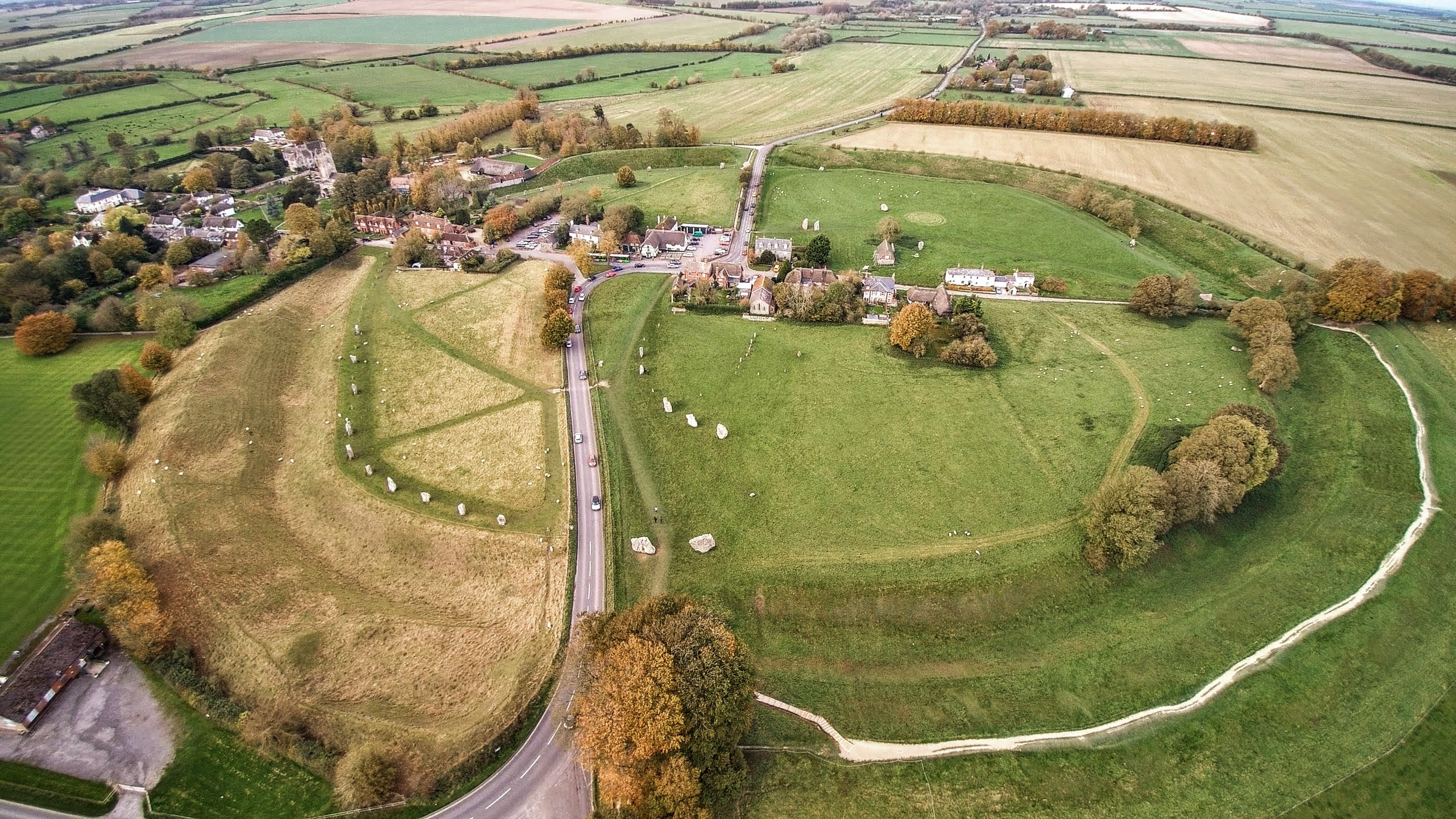
Avebury
Avebury () is a Neolithic henge monument containing three stone circles, around the village of Avebury in Wiltshire, in southwest England. One of the best known prehistoric sites in Britain, it contains the largest megalithic stone circle in the world. It is both a tourist attraction and a place of religious importance to contemporary pagans. Constructed over several hundred years in the third millennium BC, during the Neolithic, or New Stone Age, the monument comprises a large henge (a bank and a ditch) with a large outer stone circle and two separate smaller stone circles situated inside the centre of the monument. Its original purpose is unknown, although archaeologists believe that it was most likely used for some form of ritual or ceremony. The Avebury monument is a part of a larger prehistoric landscape containing several older monuments nearby, including West Kennet Long Barrow, Windmill Hill and Silbury Hill. By the Iron Age, the site had been effectively abandoned, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Europe
The European Neolithic is the period when Neolithic (New Stone Age) technology was present in Europe, roughly between 7000 BCE (the approximate time of the first farming societies in Greece) and c.2000–1700 BCE (the beginning of the Bronze Age in Scandinavia). The Neolithic overlaps the Mesolithic and Bronze Age periods in Europe as cultural changes moved from the southeast to northwest at about 1 km/year – this is called the Neolithic Expansion. The duration of the Neolithic varies from place to place, its end marked by the introduction of bronze tools: in southeast Europe it is approximately 4,000 years (i.e. 7000 BCE–3000 BCE) while in parts of Northwest Europe it is just under 3,000 years (c. 4500 BCE–1700 BCE). In parts of Europe, notably the Balkans, the period after c. 5000 BC is known as the Chalcolithic (Copper Age), due to the invention of copper smelting and the prevalence of copper tools, weapons and other artefacts. The spread of the Neolithic from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
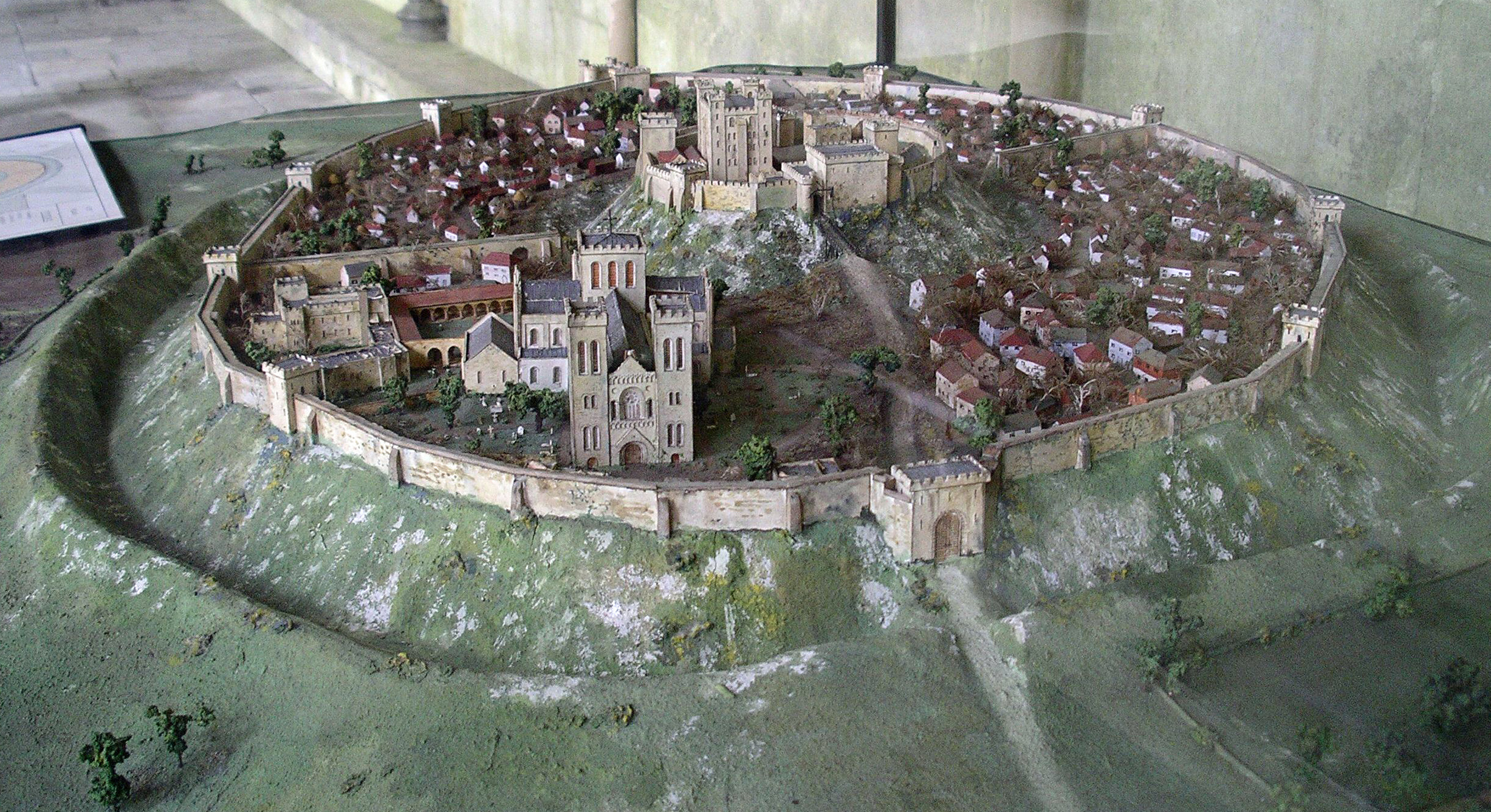
Old Sarum
Old Sarum, in Wiltshire, South West England, is the now ruined and deserted site of the earliest settlement of Salisbury. Situated on a hill about north of modern Salisbury near the A345 road, the settlement appears in some of the earliest records in the country. It is an English Heritage property and is open to the public. The great stone circles of Stonehenge and Avebury were erected nearby and indications of prehistoric settlement have been discovered from as early as 3000 BC. An Iron Age hillfort was erected around 400 BC, controlling the intersection of two trade paths and the Hampshire Avon. The site continued to be occupied during the Roman period, when the paths were made into roads. The Saxons took the British fort in the 6th century and later used it as a stronghold against marauding Vikings. The Normans constructed a motte and bailey castle, a stone curtain wall, and a great cathedral. A royal palace was built within Old Sarum Castle for and was subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salisbury From Old Sarum
Salisbury ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Wiltshire, England with a population of 41,820, at the confluence of the rivers River Avon, Hampshire, Avon, River Nadder, Nadder and River Bourne, Wiltshire, Bourne. The city is approximately from Southampton and from Bath, Somerset, Bath. Salisbury is in the southeast of Wiltshire, near the edge of Salisbury Plain. Salisbury Cathedral was formerly north of the city at Old Sarum Cathedral, Old Sarum. The cathedral was relocated and a settlement grew up around it, which received a city charter in 1227 as . This continued to be its official name until 2009 structural changes to local government in England, 2009, when Salisbury City Council was established. Salisbury railway station is an interchange between the West of England Main Line and the Wessex Main Line. Stonehenge is a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site and is northwest of Salisbury. Name The name ''Salisbury'', which is first rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Sarum Model From West
Old or OLD may refer to: Places *Old, Baranya, Hungary *Old, Northamptonshire, England *Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD) *OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Maine, United States People *Old (surname) Music *OLD (band), a grindcore/industrial metal group * ''Old'' (Danny Brown album), a 2013 album by Danny Brown * ''Old'' (Starflyer 59 album), a 2003 album by Starflyer 59 * "Old" (song), a 1995 song by Machine Head *''Old LP'', a 2019 album by That Dog Other uses * ''Old'' (film), a 2021 American thriller film *''Oxford Latin Dictionary'' *Online dating *Over-Locknut Distance (or Dimension), a measurement of a bicycle wheel and frame *Old age See also *List of people known as the Old * * *Olde, a list of people with the surname *Olds (other) Olds may refer to: People * The olds, a jocular and irreverent online nickname for older adults * Bert Olds (1891–1953), Australian rules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Britons
''The History of the Britons'' ( la, Historia Brittonum) is a purported history of the indigenous British (Brittonic) people that was written around 828 and survives in numerous recensions that date from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Brittonum'' is commonly attributed to Nennius, as some recensions have a preface written in his name. Some experts have dismissed the Nennian preface as a late forgery, arguing that the work was actually an anonymous compilation. Overview The ''Historia Brittonum'' describes the supposed settlement of Britain by Trojan expatriates and states that Britain took its name after Brutus, a descendant of Aeneas. The work was the "single most important source used by Geoffrey of Monmouth in creating his ''Historia Regum Britanniae''" and via the enormous popularity of the latter work, this version of the earlier history of Britain, including the Trojan origin tradition, would be incorporated into subsequent chronicles for the long-running history o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brut Y Brenhinedd
''Brut y Brenhinedd'' ("Chronicle of the Kings") is a collection of variant Middle Welsh versions of Geoffrey of Monmouth's Latin ''Historia Regum Britanniae''. About 60 versions survive, with the earliest dating to the mid-13th century. Adaptations of Geoffrey's ''Historia'' were extremely popular throughout Western Europe during the Middle Ages, but the ''Brut'' proved especially influential in medieval Wales, where it was largely regarded as an accurate account of the early history of the Celtic Britons. Geoffrey's ''Historia'' and the ''Brut y Brenhinedd'' Geoffrey's ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' (completed by ) purports to narrate the history of the Kings of Britain from its eponymous founder Brutus of Troy to Cadwaladr, the last in the line. Geoffrey professed to have based his history on "a certain very ancient book" written in ''britannicus sermo'' (the "British tongue", i.e. Common Brittonic, Welsh, Cornish or Breton) which he had received from Walter of Oxford. It bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English language became fragmented, localized, and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470) and aided by the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany. It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a theorized parent tongue that, by the first half of the first millennium BC, was diverging into separate dialects or languages. Pictish is linked, likely as a sister language or a descendant branch. Evidence from early and modern Welsh shows that Common Brittonic took a significant amount of influence from Latin during the Roman period, especially in terms related to the church and Christianity. By the sixth century AD, the tongues of the Celtic Britons were more rapidly splitting into Neo-Brittonic: Welsh, Cumbric, Cornish, Breton, and possibly the Pictish language. Over the next three centuries it was replaced in most of Scotland by Scottish Gaelic and by Old English (from which descend Modern English and Scots) throughout most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_Enwau_ac_Anrhyfeddodau_Ynys_Prydain.jpg)
_Severus.jpg)


