|
Salicyl Alcohol
Salicyl alcohol (saligenin) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OH)(CH2OH). It is a white solid that is used as a precursor in organic synthesis. Chemical synthesis Salicyl alcohol can be prepared through the reduction of salicylaldehyde via lithium aluminium hydride (LAH) in THF. Applications Chemical sweeteners were formed by acetal formation with ''e.g.'' isovanillin (Cmp4). Salicyl alcohol appears as a pharmacophore in several notable β2-adrenoceptor agonists (e.g. salbutamol), as well as in synthetic estrone analogs, e.gCID:22940780oCID:154236944 Biosynthesis Salicyl alcohol is the precursor of salicylic acid. It is formed from salicin by enzymatic hydrolysis by Salicyl-alcohol beta-D-glucosyltransferase or by acid hydrolysis. See also * Gastrodigenin (4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol) *Discovery and development of beta2 agonists β2-adrenoceptor agonists is a group of drugs that act selectively on β2-receptors in the lungs causing bronchodilation. β2-agonists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrone
Estrone (E1), also spelled oestrone, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estriol. Estrone, as well as the other estrogens, are synthesized from cholesterol and secreted mainly from the gonads, though they can also be formed from adrenal androgens in adipose tissue. Relative to estradiol, both estrone and estriol have far weaker activity as estrogens. Estrone can be converted into estradiol, and serves mainly as a precursor or metabolic intermediate of estradiol. It is both a precursor and metabolite of estradiol. In addition to its role as a natural hormone, estrone has been used as a medication, for instance in menopausal hormone therapy; for information on estrone as a medication, see the estrone (medication) article. Biological activity Estrone is an estrogen, specifically an agonist of the estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ. It is a far less potent estrogen than is estrad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
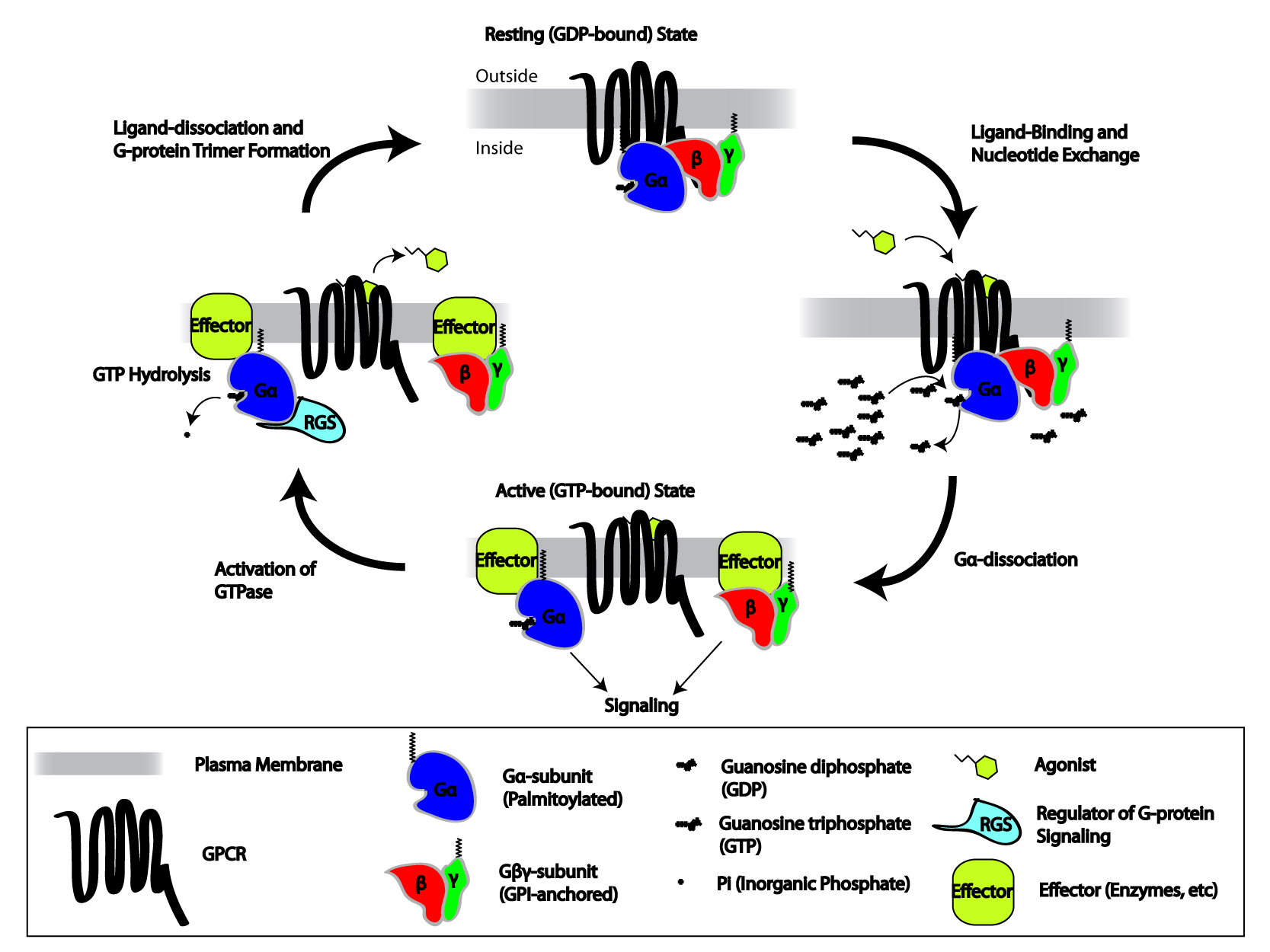
Discovery And Development Of Beta2 Agonists
β2-adrenoceptor agonists is a group of drugs that act selectively on β2-receptors in the lungs causing bronchodilation. β2-agonists are used to treat asthma and COPD, diseases that cause obstruction in the airways. Prior to their discovery, the non-selective beta-agonist isoprenaline was used. The aim of the drug development through the years has been to minimise side effects, achieve selectivity and longer duration of action. The mechanism of action is well understood and has facilitated the development. The structure of the binding site and the nature of the binding is also well known, as is the structure activity relationship. History The β2-selective agonists were developed in the 20th century and are a very valuable class of drugs. In 1901 Jōkichi Takamine isolated the hormone adrenalin, also known as epinephrine. In 1890 adrenalin was first given to asthma patients orally. It had little or no effect because it is metabolized in the digestive tract and is deactivate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrodigenin
Gastrodigenin is a phenolic compound found in the rhizome of ''Gastrodia elata''. Gastrodin is the glucoside of gastrodigenin. See also * Habenariol Habenariol is a phenolic compound found in the semi-aquatic orchid '' Habenaria repens''. It acts as a feeding deterrent against the freshwater crayfish ''Procambarus clarkii ''Procambarus clarkii'', known variously as the red swamp crayfish, ..., a phenolic compound found in the semi aquatic orchid Habenaria repens References Natural phenols diols Gastrodia Perfume ingredients {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Hydrolysis
In organic chemistry, acid hydrolysis is a hydrolysis process in which a protic acid is used to catalyze the cleavage of a chemical bond via a nucleophilic substitution reaction, with the addition of the elements of water (H2O). For example, in the conversion of cellulose or starch to glucose. For the case of esters and amides, it can be defined as an acid catalyzed nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. The term is also applied to certain nucleophilic addition reactions, such as in the acid catalyzed hydrolysis of nitriles to amides. Acid hydrolysis ''does not'' usually refer to the acid catalyzed addition of the elements of water to double or triple bonds by electrophilic addition as may originate from a hydration reaction. Acid hydrolysis is used to prepare monosaccharide with the help of acids, such as: * Hydrochloric acid * Sulfuric acid * Trifluoroacetic acid * Formic acid * Nitric acid Acid hydrolysis can be utilized in the pretreatment of cellulosic material, so as to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicyl-alcohol Beta-D-glucosyltransferase
In enzymology, a salicyl-alcohol beta-D-glucosyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :UDP-glucose + salicyl alcohol \rightleftharpoons UDP + salicin Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are UDP-glucose and salicyl alcohol, whereas its two products are UDP and salicin. This enzyme belongs to the family of glycosyltransferases, specifically the hexosyltransferases. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... of this enzyme class is UDP-glucose:salicyl-alcohol beta-D-glucosyltransferase. Other names in common use include uridine diphosphoglucose-salicyl alcohol 2-glucosyltransferase, and UDPglucose:salicyl alcohol phenyl-glucosyltransferase. References * EC 2.4.1 Enzymes of unknown structure {{2.4-enzyme- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymatic
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicin
Salicin is an alcoholic β-glucoside. Salicin is produced in (and named after) willow (''Salix'') bark. It is a biosynthetic precursor to salicylaldehyde. Medicinal aspects Salicin is found in the bark of and leaves of willows, poplars and various other plants. Derivates are found in castoreum. Salicin from meadowsweet was used in the synthesis of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), in 1899 by scientists at Bayer. Salicin tastes bitter like quinine Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to '' Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal le .... Salicin may cause an allergic skin reaction (skin sensitization; category 1). Mild side effects are standard, with rare occurrences of nausea, vomiting, rash, dizziness and breathing problems. Overdose from high quantities of salicin can be toxic, damaging kidneys, causing stomach ul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CO2H. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin ''salix'' for willow tree. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates. Uses Medicine Salicylic acid as a medication is commonly used to remove the outer layer of the skin. As such, it is used to treat warts, psoriasis, acne vulgaris, ringworm, dandruff, and ichthyosis. Similar to other hydroxy acids, salicylic acid is an ingredient in many skincare products for the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis, acne, psoriasis, calluses, corns, keratosis pilaris, acanthosis nigricans, ichthyosis, and warts. Uses in manufacturing Salicylic acid is used as a food preservative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precursor (chemistry)
In chemistry, a precursor is a compound that participates in a chemical reaction that produces another compound. In biochemistry, the term "precursor" often refers more specifically to a chemical compound preceding another in a metabolic pathway, such as a protein precursor. Illicit drug precursors In 1988, the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances introduced detailed provisions and requirements relating the control of precursors used to produce drugs of abuse. In Europe the Regulation (EC) No. 273/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council on drug precursors was adopted on 11 February 2004. ( European law on drug precursors) Illicit explosives precursors On January 15, 2013, the Regulation (EU) No. 98/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the marketing and use of explosives precursors was adopted. The Regulation harmonises rules across Europe on the making available, introduction, possession and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salbutamol
Salbutamol, also known as albuterol and sold under the brand name Ventolin among others, is a medication that opens up the medium and large airways in the lungs. It is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist which works by causing relaxation of airway smooth muscle. It is used to treat asthma, including asthma attacks, exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It may also be used to treat high blood potassium levels. Salbutamol is usually used with an inhaler or nebulizer, but it is also available in a pill, liquid, and intravenous solution. Onset of action of the inhaled version is typically within 15 minutes and lasts for two to six hours. Common side effects include shakiness, headache, fast heart rate, dizziness, and feeling anxious. Serious side effects may include worsening bronchospasm, irregular heartbeat, and low blood potassium levels. It can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but safety is not entirel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: ''total synthesis'', ''semisynthesis'', and ''methodology''. Total synthesis A total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simple, commercially available petrochemical or natural precursors. Total synthesis may be accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed one after another until the molecule is complete; the chemical compounds made in each step are called synthetic intermediates. Most often, each step in a synthesis refers to a separate rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |