|
Sakti, Chhattisgarh
Sakti is a city and a district in the state of Chhattisgarh. The assembly constituency number of District Sakti is 33, Earlier it was the only Education District of Chhattisgarh. There are 245 panchayats and 458 villages under Sakti district. Sakti district was formed on 15 August 2021 And came into complete district existence on 9 September 2022 by Chief Minister Bhupesh Baghel. The current 2018 - 2023 MLA here is Shri Charan Das Mahant , who is the Speaker of the Chhattisgarh Legislative assembly. The First Collector and District Magistrate of Sakti is Nupur Rashi Panna I.A.S, First Superintendent of Police is M.R. Ahire I.P.S and First District Education Officer is B.L. Khare, who was also the last District Education Officer of Education District Sakti. Geography Sakti is located at . It has an average elevation of 237 metres (777 feet). Sakti is a hill station situated on the banks of Borai river and foothills of Udaigiri Mountain range of Chhattisgarh. It ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Indian Cities
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janjgir–Champa District
Janjgir–Champa district is a district in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. The district headquarters of the district Janjgir–Champa, Janjgir, is the city of Maharaja Jajawalya Dev of the Kalachuri dynasty. Earlier a part of the Bilaspur district, Jangir was carved out in 1998 to a separate district of its own, and ran to a political controversy about the name of the freshly minted district, which it carries to date as the name "Janjgir–Champa". Inhabitants are generally migrants from nearby villages. The present collector of Janjgir-Champa is Shri Jitendra Kumar Shukla. History The Janjgir–Champa district, which is best known as the heart of Chhattisgarh because of its central location in state, was established on 25 May 1998. The Vishnu Mandir of the district reflects its golden past. Janjgir- Champa is also a place where one can find a number of temples having very versatile history. Geography The district is located in the central area of Chhattisgarh. It is borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatanagar–Bilaspur Section
The Tatanagar–Bilaspur section is part of the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line and connects in the Indian state of Jharkhand and in Chhattisgarh. Part of one of the major trunk lines in the country, it passes through an industrial-mining area and handles high volumes of freight, particularly coal and iron ore. Geography The Tatanagar–Bilaspur section of Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line passes through the Saranda forest on the Chota Nagpur Plateau in southern Jharkhand. The area through which it passes includes portions of northern Odisha and northern Chhattisgarh, with topography similar to that of the Chota Nagpur Plateau. It is generally forested area amidst hills alternating with valleys. The major rivers flowing through the area are: Subarnarekha, Kharkai, South Karo, South Koel, Sankh, Brahmani, Ib, Mand and Hasdeo. While the eastern portion of this line connects to iron ore mines spread on both sides of the Jharkhand–Odisha border, the western portion caters to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakti Railway Station , King of Buleleng, in present-day Indonesia
{{disambiguation, geo, surname ...
Sakti may refer to: * Shakti, the primordial cosmic energy in Hinduism * Sakti, Chhattisgarh, a town in India ** Sakti State, a former princely state in India * Sakti, Leh, a village in India * ST ''Sakti'', a tugboat * Sakti Burman, Indian artist * Bima Sakti, Indonesian footballer * Gusti Panji Sakti Gusti Panji Sakti was King of the Kingdom of Buleleng, in northern Bali, Indonesia, from around 1660 to 1700. He is commemorated as an heroic ancestral figure who expanded the power of Buleleng to Blambangan on East Java East Java ( id, Jawa T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
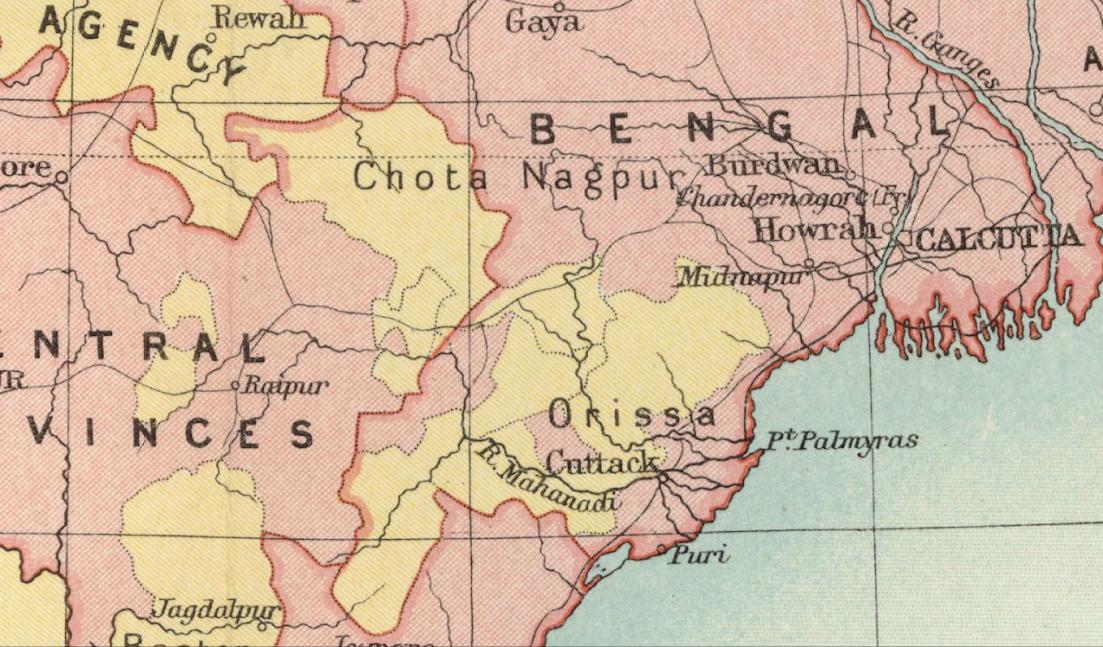
Eastern States Agency
The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the Indian Empire. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agency; the agencies remained intact within the grouping. In 1936, the Bengal States Agency was added. History Since the 19th century the princely states and the tributary states of Orissa and Chhota Nagpur were not part of Bengal, but British relations with them were managed by its government through the Bengal Presidency. The Eastern States Agency was created on 1 April 1933. This agency dealt with forty-two princely states in eastern India, located in the present-day Indian states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal and Tripura. Before the creation of the Eastern States Agency in 1933, twenty-three native states of the former Orissa Tributary States and Chhota Nagpur States were under the suzerainty of the British provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely States
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large (Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from thousands of zamindari estates and jagirs. In 1947, princely states covered 40% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
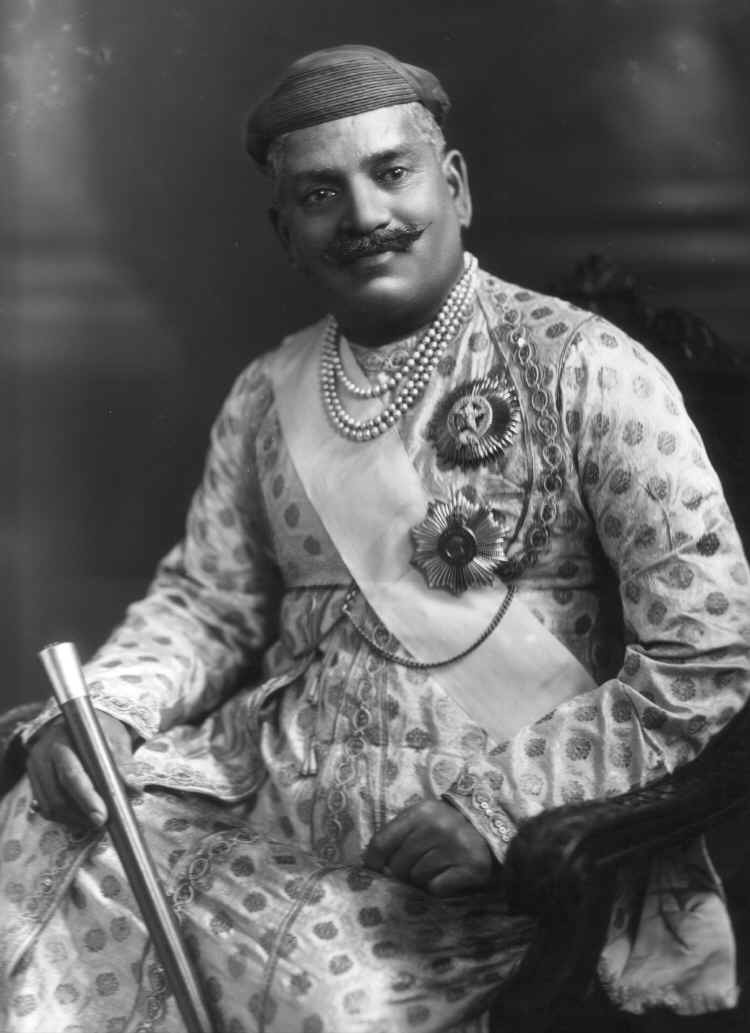
Sakti State
Sakti State was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. It belonged to the Chhattisgarh States Agency, which later became the Eastern States Agency. The capital was Sakti town, which had 1,791 inhabitants, according to the 1901 Census of India. Today, it is located in the state of Chhattisgarh. It had an area of 357 km2 and, Its rulers were Gond and had a privy purse of 29,000 rupees. The princely state acceded to the Indian Union on 1 January 1948, thus ceasing to exist. History Sakti State's rulers were Raj Gonds. The year when the state was founded is not known. Legend says that it was founded by two twin brothers, who were soldiers of the Raja of Sambalpur. The capital was in Sakti, Janjgir-Champa district, Chhattisgarh. Sakti's last ruler was Rana Bahadur Leeladhar Singh, born on 3 February 1892, who succeeded as new rana on 4 July 1914. The princely family still exists and is headed by Raja Surender Bahadur Singh, who represented India in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarangarh
Sarangarh is a New District in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. History During the British Raj era, Sarangarh State was one of several princely states governed by the Raj Gond dynasty of Rajputs. It was originally a dependency of the Ratanpur Kingdom and later became one of the eighteen Garhjat states under Sambalpur State. According to legend Sarangarh state was founded in the first century AD by Gond ancestors that had migrated from Bhandara. It was originally a dependency of the Ratanpur Kingdom and later became one of the eighteen Garhjat states under Sambalpur State The Sambalpur kings favoured Sarangarh owing to its readiness to help their kingdom during military campaigns. In 1818 Sarangarh became a British protectorate. Between 1878 and 1889 Sarangarh state was placed under the direct administration of British India owing to economic mismanagement and the infancy of the ruler Bhawani Pratap Singh. Sarangarh was a small feudatory state, part of the Chhattisgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raigarh
Raigarh is a city in Eastern Chhattisgarh. History The tradition preserved by the ruling family of the erstwhile state of Raigarh maintains that the Raj Gond family migrated to this region from Bairagarh/Wariagarh of Chanda district of Maharashtra state about the beginning of the eighteenth century and first stayed at Phuljhar in Raipur district. From there Madan Singh, head of the family migrated to Banda of the present-day Raigarh. The successor kings of Raigarh state after Maharaja Madan Singh were Maharaja Takhat Singh, Maharaha Beth Singh, Maharaja Dilip Singh, Maharaja Jujhar Singh, Maharaja Devnath Singh, Maharaja Ghansyam Singh, Maharaja Bhupdev Singh, Maharaja Natwar Singh, and Maharaja Chakradhar Singh. Truly speaking music, dance, and literature got fillip during the reign of Maharaja Bhupdev Singh and developed further during the rule of Maharaja Chakradhar Singh. Prior to Indian Independence, Raigarh was capital of Princely State of Raigarh. Geography and climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korba, Chhattisgarh
Korba is a city and an industrial area in Korba District in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. Korba was erstwhile part of Bilaspur District before 25 May 1998 later that Korba was made a separate District for ease of administration but it is still under Bilaspur Division. Korba is called power capital of Chhattisgarh due to its Coal reserves and Industrial base for multiple thermal based power plants from Public sector like NTPC Limited, CSEB from State of Chhattisgarh as well as from private sector apart from Power plants Korba has the Asia's second largest and India's largest open cast coal mine in Gevra area of Korba Coalfield. Korba produces 140 Million tons of coal every year which accounts for 17% of Country's total coal production and 85% of Chhattisgarh Coal production. BALCO Private owned Aluminium producer has its smelter Aluminium Plant in Korba. Here mainly the protected tribal tribe Korwa (Pahadi Korwa) resides. Korba district is blessed by lush green forests fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |