|
Sakhalin I
The Sakhalin-I (russian: Сахалин-1) project, a sister project to Sakhalin-II, is a consortium for production of oil and gas on Sakhalin Island and immediately offshore. It operates three fields in the Okhotsk Sea: Chayvo, Odoptu and Arkutun-Dagi."Sakhalin-1: A New Frontier" - PennWell Custom Publishing (c/o of ExxonMobil) In 1996, the consortium completed a production-sharing agreement between the Sakhalin-I consortium, the Russian Federation and the Sakhalin government. The consortium was managed and operated by Exxon Neftegas Limited (ENL), a unit of , until Exxon's withdrawal in March 2022 following the |
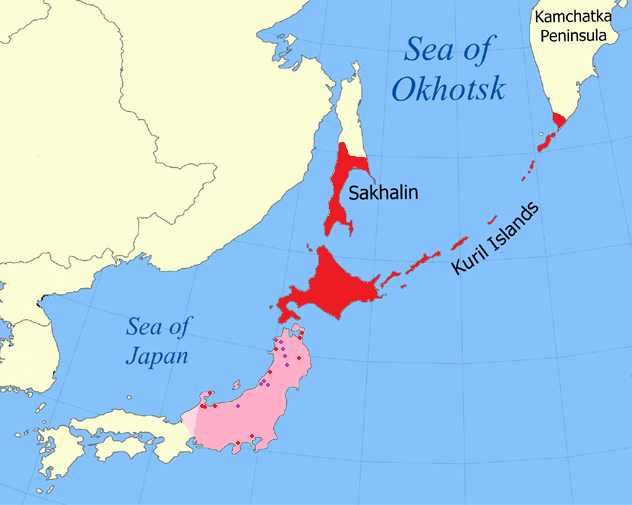
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exxon Neftegas Ltd
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November 30, 1999, by the merger of Exxon and Mobil, both of which are used as retail brands, alongside Esso, for fueling stations and downstream products today. The company is vertically integrated across the entire oil and gas industry, and within it is also a chemicals division which produces plastic, synthetic rubber, and other chemical products. ExxonMobil is incorporated in New Jersey. ExxonMobil's earliest corporate ancestor was Vacuum Oil Company, though Standard Oil is its largest ancestor prior to its breakup. The entity today known as ExxonMobil grew out of the Standard Oil Company of New Jersey (or Jersey Standard for short), the corporate entity which effectively controlled all of Standard Oil prior to its breakup. Jersey Standard g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosneft
PJSC Rosneft Oil Company ( stylized as ROSNEFT) is a Russian Vertical integration, integrated energy company headquartered in Moscow. Rosneft specializes in the exploration, Extraction of petroleum, extraction, production, refining, Petroleum transport, transport, and sale of petroleum, natural gas, and petroleum products. The company is controlled by the Government of Russia, Russian government through the Rosneftegaz holding company. Its name is a portmanteau of the Russian words (russian: Российская нефть, lit=Russian oil). Rosneft was founded in 1993 as a State-owned enterprises of Russia, state enterprise and then incorporated in 1995, acquiring a number of state-controlled gas and oil assets. It became Russia's leading oil company after purchasing assets of the former oil company Yukos at state-run auctions. After acquiring Open joint-stock company, OJSC TNK-BP in 2013, then one of the largest oil companies of Russia, Rosneft became the world's largest Publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ONGC
The Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) is a central public sector undertaking under the ownership of Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India. It is headquartered in New Delhi. ONGC was founded on 14 August 1956 by the Government of India. It is the largest government-owned-oil and gas explorer and producer in the country, and produces around 70% of India's crude oil (equivalent to around 57% of the country's total demand) and around 84% of its natural gas. In November 2010, the Government of India conferred the '' Maharatna'' status to ONGC. In a survey by the Government of India for fiscal year 2019–20, it was ranked as the largest profit making Central Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) in India. It is ranked 25th among the Top 250 Global Energy Companies by Platts. ONGC is involved in exploring for and exploiting hydrocarbons in 26 sedimentary basins of India, and owns and operates over 11,000 kilometers of pipelines in the country. Its internation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exxon Mobil
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November 30, 1999, by the merger of Exxon and Mobil, both of which are used as retail brands, alongside Esso, for fueling stations and downstream products today. The company is vertically integrated across the entire oil and gas industry, and within it is also a chemicals division which produces plastic, synthetic rubber, and other chemical products. ExxonMobil is incorporated in New Jersey. ExxonMobil's earliest corporate ancestor was Vacuum Oil Company, though Standard Oil is its largest ancestor prior to its breakup. The entity today known as ExxonMobil grew out of the Standard Oil Company of New Jersey (or Jersey Standard for short), the corporate entity which effectively controlled all of Standard Oil prior to its breakup. Jersey Standard grew a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De-Kastri Terminal
De-Kastri Oil Terminal (russian: Нефтеотгрузочный терминал Де-Кастри) is an oil export terminal located away from the village of De-Kastri in Khabarovsk Krai, Russian Federation. It is one of the biggest oil terminals in the Far East that serves as a hub for crude oil deliveries to Asian markets. The terminal which started operations in 2006 belongs to the Sakhalin-I consortium led by Exxon Neftegas Ltd which also includes 20% stake held by Russian affiliates of Rosneft: Sakhalinmorneftegas-Shelf and RN-Astra. The overall capacity of the export terminal is approximately of oil. Tanker loading capacity is suitable for Aframax tankers up to . The five Aframax tankers servicing the terminal are purpose-designed double-hull ice class vessels. The area of the terminal covers nearly The construction of the terminal started in 2003 and was completed by August 2006. Construction subcontractors included Russian-Turkish joint venture, ''Enka-Technstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatar Strait
Strait of Tartary or Gulf of Tartary (russian: Татарский пролив; ; ja, 間宮海峡, Mamiya kaikyō, Mamiya Strait; ko, 타타르 해협) is a strait in the Pacific Ocean dividing the Russian island of Sakhalin from mainland Asia (South-East Russia), connecting the Sea of Okhotsk on the north with the Sea of Japan on the south. It is long, wide, and less than deep at its deepest point. History Yuan dynasty During the Yuan dynasty, the Yuan armies crossed the strait in the Mongol invasions of Sakhalin. Alleged remnants of a Chinese fort dating back to the Mongol Yuan era can be found in Sakhalin today. "Tartary" is an older name used by Europeans to refer to a vast region covering Inner Asia, Central Asia and North Asia. The toponym is derived from the Medieval ethnonym Tartars, which was applied to various Turkic peoples, Turkic and Mongol semi-nomadic empires, including the Yuan dynasty that ruled over China and the straits of Northeast Asia. Qing dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipeline Transport
Pipeline transport is the long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas through a system of pipes—a pipeline—typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries of the world. The United States had 65%, Russia had 8%, and Canada had 3%, thus 76% of all pipeline were in these three countries. ''Pipeline and Gas Journals worldwide survey figures indicate that of pipelines are planned and under construction. Of these, represent projects in the planning and design phase; reflect pipelines in various stages of construction. Liquids and gases are transported in pipelines, and any chemically stable substance can be sent through a pipeline. Pipelines exist for the transport of crude and refined petroleum, fuels – such as oil, natural gas and biofuels – and other fluids including sewage, slurry, water, beer, hot water or steam for shorter distances. Pipelines are useful for transporting water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and north. The northeast corner is the Shelikhov Gulf. The sea is named after the Okhota river, which in turn named after the Even word () meaning "river". Geography The Sea of Okhotsk covers an area of , with a mean depth of and a maximum depth of . It is connected to the Sea of Japan on either side of Sakhalin: on the west through the Sakhalin Gulf and the Gulf of Tartary; on the south through the La Pérouse Strait. In winter, navigation on the Sea of Okhotsk is impeded by ice floes. Ice floes form due to the large amount of freshwater from the Amur River, lowering the salinity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1000000000 (number)
1,000,000,000 (one billion, short scale; one thousand million or one milliard, one yard, long scale) is the natural number following 999,999,999 and preceding 1,000,000,001. With a number, "billion" can be abbreviated as b, bil or bn. In standard form, it is written as 1 × 109. The metric prefix giga indicates 1,000,000,000 times the base unit. Its symbol is G. One billion years may be called an ''eon'' in astronomy or geology. Previously in British English (but not in American English), the word "billion" referred exclusively to a million millions (1,000,000,000,000). However, this is no longer common, and the word has been used to mean one thousand million (1,000,000,000) for several decades. The term ''milliard'' can also be used to refer to 1,000,000,000; whereas "milliard" is rarely used in English, variations on this name often appear in other languages. In the South Asian numbering system, it is known as 100 crore or 1 arab. 1,000,000,000 is also the cube of 1000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force Majeure
In contract law, (from Law French: 'overwhelming force', ) is a common clause in contracts which essentially frees both parties from liability or obligation when an extraordinary event or circumstance beyond the control of the parties, such as a war, strike, riot, crime, epidemic or sudden legal changes prevents one or both parties from fulfilling their obligations under the contract. Explicitly excluded is any event described as an ''act of God,'' which covers a separate domain and legally differs, yet it is still related to contract law. In practice, most clauses do not excuse a party's non-performance entirely but only suspend it for the duration of the .Supreme Court of India">Supreme Court (of India) 1285 it was held that "An analysis of ruling on the subject shows that reference to the expression is made where the intention is to save the defaulting party from the consequences of anything over which he had no control." Even if a ''force majeure'' clause covers the rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




