|
Saint Tremeur
Tremorus of Brittany, also known as Trémeur, Treveur, and Tromeur, is a sixth-century child martyr venerated by the Roman Catholic Church. He was baptized by his mother against his stepfather's wishes. His baptismal name was Gildas, after Gildas the Wise, and given the title Trech-meur ("great victory" in Breton) to distinguish him from the older Gildas. He was murdered by his stepfather Count Conmore while being educated at a monastery in Carhaix, Brittany. Conmore killed the boy because he hated Christianity. He was the son of Triphina (Triphena), who retired to a convent after her son's murder, and was taught by Gildas the Wise. References 6th-century Christian saints 6th-century Breton people Christian child saints Medieval Breton saints Medieval murder victims {{saint-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armorica
Armorica or Aremorica (Gaulish: ; br, Arvorig, ) is the name given in ancient times to the part of Gaul between the Seine and the Loire that includes the Brittany Peninsula, extending inland to an indeterminate point and down the Atlantic Coast. Name The name ''Armorica'' is a Latinized form of the Gaulish toponym , which literally means 'place in front of the sea'. It is formed with the prefix ''are''- ('in front of') attached to -''mori''- ('sea') and the feminine suffix ''-(i)cā'', denoting the localization (or provenance). The inhabitants of the region were called ''Aremorici'' (sing. ''Aremoricos''), formed with the stem ''are-mori''- extended by the determinative suffix -''cos''. It is glossed by the Latin ''antemarini'' in Endlicher's Glossary. The Slavs use a similar formation, ''Po-mor-jane'' ('those in front of the sea'), to designate the inhabitants of Pomerania. The Latin adjective ''Armoricani'' was an administrative term designating in particular a sector of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gildas The Wise
Gildas (Breton: ''Gweltaz''; c. 450/500 – c. 570) — also known as Gildas the Wise or ''Gildas Sapiens'' — was a 6th-century British monk best known for his scathing religious polemic ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', which recounts the history of the Britons before and during the coming of the Saxons. He is one of the best-documented figures of the Christian church in the British Isles during the sub-Roman period, and was renowned for his Biblical knowledge and literary style. In his later life, he emigrated to Brittany where he founded a monastery known as St Gildas de Rhuys. Hagiography Differing versions of the ''Life of Saint Gildas'' exist, but both agree that he was born in what is now Scotland on the banks of the River Clyde, and that he was the son of a royal family. These works were written in the eleventh and twelfth centuries and are regarded by scholars as unhistorical. He is now thought to have his origins farther south. In his own work, he claims to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conomor
Conomor ( ), also known as Conomerus or Conomor the Cursed, was an early medieval ruler of Brittany. His name, which has the Welsh (language), Welsh cognate Cynfawr, means "Great Dog", but could also indicate "Sea Dog" in early Brythonic languages, Brythonic. Conomor was notorious for his cruelty, becoming a legendary villain in Breton culture. He is widely regarded as one of the probable sources for the myth of Bluebeard and possibly also of Tristan's uncle King Mark of Cornwall. The wife-beating giant Cormoran may also retain a garbled folk memory of the same character. Conomor was king of Domnonée, Dumnonia and Prince of Poher. Dumnonia was, at this time, expanding to claim control over all Brythonic territory in Armorica (Brittany). It is difficult to disentangle the Conomor of legend from the historical ruler. As with other early Breton rulers most written information about him comes from the lives of Breton saints. Historical record The name Conomor is mentioned in Cornish g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carhaix
Carhaix-Plouguer (; br, Karaez-Plougêr ), commonly known as just Carhaix (), is a Communes of France, commune in the Departments of France, French department of Finistère, region of Brittany (administrative region), Brittany, France.Commune de Carhaix-Plouguer (29024) INSEE The commune was created in 1957 by the merger of the former communes Carhaix and Plouguer. Geography 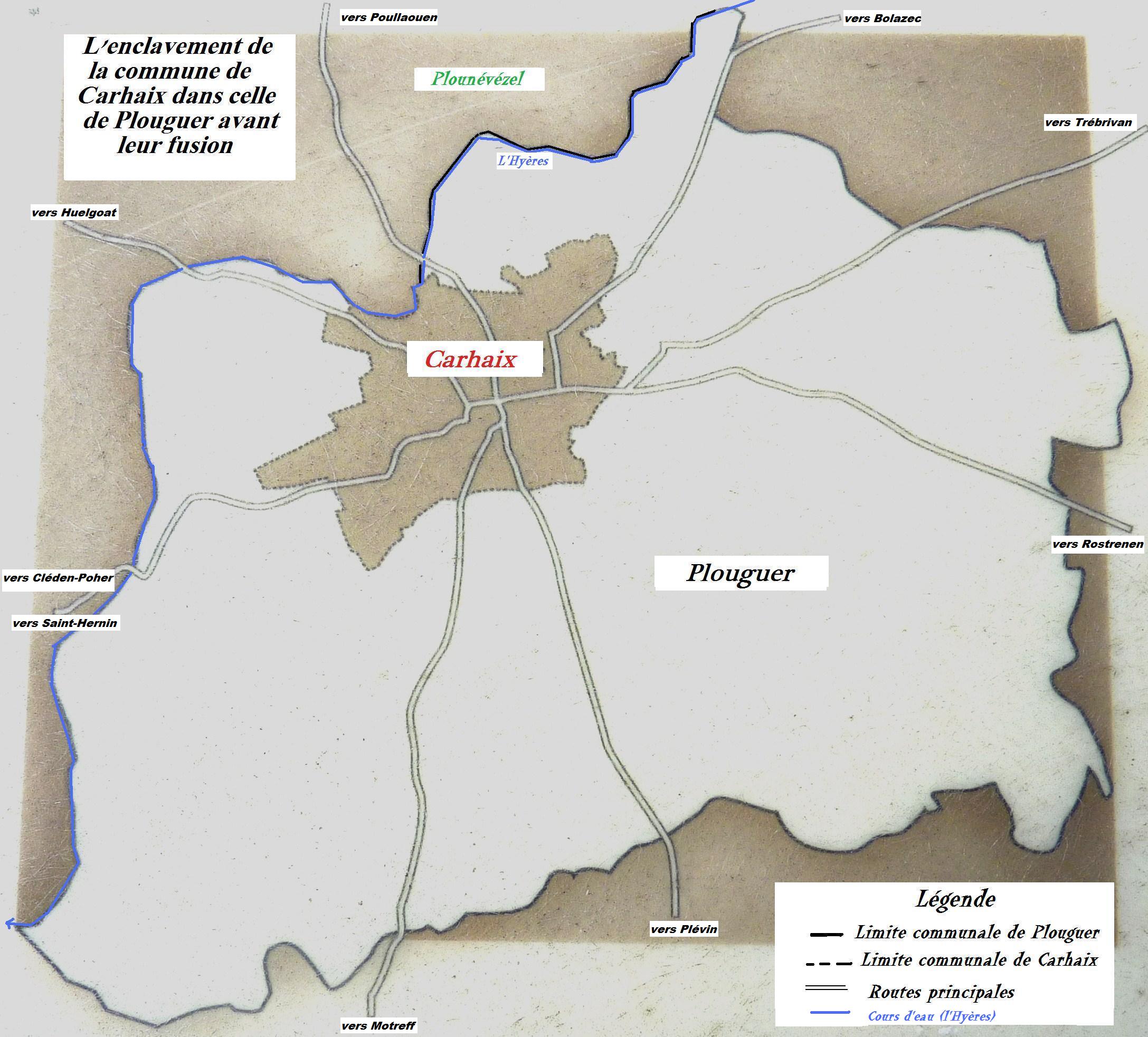 Carhaix is located in the Poher, an important territory of Brittany, sandwiched between the Arrée Mountains to the north and the Bla ...
Carhaix is located in the Poher, an important territory of Brittany, sandwiched between the Arrée Mountains to the north and the Bla ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period of Roman occupation. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duchy of Brittany, duchy before being Union of Brittany and France, united with the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a provinces of France, province governed as a separate nation under the crown. Brittany has also been referred to as Little Britain (as opposed to Great Britain, with which it shares an etymology). It is bordered by the English Channel to the north, Normandy to the northeast, eastern Pays de la Loire to the southeast, the Bay of Biscay to the south, and the Celtic Sea and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its land area is 34,023 km2 . Brittany is the site of some of the world's oldest standing architecture, ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryphine
Saint Tryphine (also spelled Trifine, Triphine and Tréphine) is a semi-legendary Breton saint whose life is often considered to be the basis of the story of Bluebeard. In Brittany she is widely revered as a patron saint of sick children and those whose birth is overdue. The legend of Saint Tryphine probably derives from a historical individual who was the wife of the early Breton ruler Conomor. Historical background Conomor is said to have married Tryphine, the daughter of his ally Waroch I, but seems later to have violently abused and then murdered her. Conomor was later killed in battle with a rival, and became a legendary villain in Breton history. Tryphine was elevated to the position of a martyred saint, along with her son Tremeur, and there are many churches dedicated to them. The village of Sainte-Tréphine is named for the former. Myth of Tryphine and Tremeur In later legend Conomor's villainy is extended to include the murders of three wives before Tryphine. Tryphine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Christian Saints
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Breton People
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Child Saints
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χριστός), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term ''mashiach'' (מָשִׁיחַ) (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." It does not have a meaning of 'of Christ' or 'related or pertaining to Christ'. According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Breton Saints
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



