|
Saint Marcellus's Flood
Saint Marcellus's flood or (Low Saxon: ; , 'Great Drowning of Men') was an intense extratropical cyclone, coinciding with a new moon, which swept across the British Isles, the Netherlands, northern Germany, and Denmark (including Schleswig/Southern Jutland) around 16 January 1362, causing at least 25,000 deaths. The storm tide is also called the "Second St. Marcellus flood" because it peaked on 16 January, the feast day of St. Marcellus. A previous "First St. Marcellus flood" had drowned 36,000 people along the coasts of West Friesland and Groningen on 16 January 1219. An immense storm tide from the North Sea swept far inland from England and the Netherlands to Denmark and the German coast, breaking up islands, making parts of the mainland into islands, and wiping out entire towns and districts. These included Rungholt, said to have been located on the island of Strand in North Frisia, Ravenser Odd in East Yorkshire, and the harbour of Dunwich in Suffolk. This storm tide, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
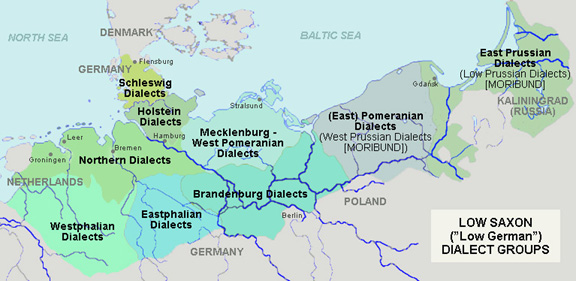
Low German
Low German is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language variety, language spoken mainly in Northern Germany and the northeastern Netherlands. The dialect of Plautdietsch is also spoken in the Russian Mennonite diaspora worldwide. "Low" refers to the altitude of the areas where it is typically spoken. Low German is most closely related to Frisian languages, Frisian and English language, English, with which it forms the North Sea Germanic group of the West Germanic languages. Like Dutch language, Dutch, it has historically been spoken north of the Benrath line, Benrath and Uerdingen line, Uerdingen isoglosses, while forms of High German languages, High German (of which Standard German is a standardized example) have historically been spoken south of those lines. Like Frisian, English, Dutch and the North Germanic languages, Low German has not undergone the High German consonant shift, as opposed to Standard German, Standard High German, which is based on High German langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffolk
Suffolk ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Norfolk to the north, the North Sea to the east, Essex to the south, and Cambridgeshire to the west. Ipswich is the largest settlement and the county town. The county has an area of and a population of 758,556. After Ipswich (144,957) in the south, the largest towns are Lowestoft (73,800) in the north-east and Bury St Edmunds (40,664) in the west. Suffolk contains five Non-metropolitan district, local government districts, which are part of a two-tier non-metropolitan county administered by Suffolk County Council. The Suffolk coastline, which includes parts of the Suffolk & Essex Coast & Heaths National Landscape, is a complex habitat, formed by London Clay and Crag Group, crag underlain by chalk and therefore susceptible to erosion. It contains several deep Estuary, estuaries, including those of the rivers River Blyth, Suffolk, Blyth, River Deben, Deben, River Orwell, Orwell, River S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1362 In Europe
136 may refer to: *136 (number) *AD 136 *136 BC *136 (MBTA bus), a Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority bus route *136 Austria 136 Austria is a main-belt asteroid that was found by the prolific asteroid discoverer Johann Palisa on 18 March 1874, from the Austrian Naval Observatory in Pola, Istria. It was his first asteroid discovery and was given the Latin name of h ..., a main-belt asteroid * Škoda 136, a small family car {{numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Floods
The 14th century lasted from 1 January 1301 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCCI) to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of King Charles IV of France led to a claim to the French throne by King Edward III of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and the Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever established by a single conqueror. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th Century In The Netherlands
14 (fourteen) is the natural number following 13 and preceding 15. Mathematics Fourteen is the seventh composite number. Properties 14 is the third distinct semiprime, being the third of the form 2 \times q (where q is a higher prime). More specifically, it is the first member of the second cluster of two discrete semiprimes (14, 15); the next such cluster is ( 21, 22), members whose sum is the fourteenth prime number, 43. 14 has an aliquot sum of 10, within an aliquot sequence of two composite numbers (14, 10, 8, 7, 1, 0) in the prime 7-aliquot tree. 14 is the third companion Pell number and the fourth Catalan number. It is the lowest even n for which the Euler totient \varphi(x) = n has no solution, making it the first even nontotient. According to the Shapiro inequality, 14 is the least number n such that there exist x_, x_, x_, where: :\sum_^ \frac < \frac, with and A |
1362 In England
136 may refer to: *136 (number) *AD 136 *136 BC *136 (MBTA bus), a Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority bus route *136 Austria 136 Austria is a main-belt asteroid that was found by the prolific asteroid discoverer Johann Palisa on 18 March 1874, from the Austrian Naval Observatory in Pola, Istria. It was his first asteroid discovery and was given the Latin name of h ..., a main-belt asteroid * Škoda 136, a small family car {{numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Windstorms
European windstorms are powerful extratropical cyclones which form as cyclone, cyclonic windstorms associated with areas of low atmospheric pressure. They can occur throughout the year, but are most frequent between October and March, with peak intensity in the winter months. Deep areas of low pressure are common over the North Atlantic, and occasionally start as nor'easters off the New England coast. They frequently track across the North Atlantic Ocean towards the north of Scotland and into the Norwegian Sea, which generally minimizes the impact to inland areas; however, if the track is further south, it may cause adverse weather conditions across Central Europe, Northern Europe and especially Western Europe. The countries most commonly affected include the United Kingdom, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, the Netherlands, Norway, Germany, the Faroe Islands and Iceland. The strong wind phenomena intrinsic to European windstorms, that give rise to "damage footprints" at the surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Disasters In Denmark
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part of nature, human activity or humans as a whole are often described as at times at odds, or outright Anthropocentrism, separate and even superior to nature. During the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries, nature became the passive reality, organized and moved by divine laws. With the Industrial Revolution, nature increasingly became seen as the part of reality deprived from intentional intervention: it was hence considered as sacred by some traditions (Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Rousseau, American transcendentalism) or a mere decorum for divine providence or human history (Hegel, Marx). However, a vitalist vision of nature, closer to the pre-Socratic one, got reborn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floods In England
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant concern in agriculture, civil engineering and public health. Human changes to the environment often increase the intensity and frequency of flooding. Examples for human changes are land use changes such as deforestation and removal of wetlands, changes in waterway course or flood controls such as with levees. Global environmental issues also influence causes of floods, namely climate change which causes an intensification of the water cycle and sea level rise. For example, climate change makes extreme weather events more frequent and stronger. This leads to more intense floods and increased flood risk. Natural types of floods include river flooding, groundwater flooding coastal flooding and urban flooding sometimes known as flash flooding. Tidal flooding may inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floods In Germany
Floods in Germany are a common phenomenon that causes significant economic damage and loss of life. Heavy rainfall, exceeding 100 mm within 24 hours, can lead to rapid rises in water levels, causing floods. The Rhine, Elbe, Danube, and Moselle rivers are prone to flooding due to their proximity to the Alps and dense tributary network. According to the German Federal Ministry of the Interior, Building, and Community (BMI), floods have caused an average of €1.3 billion in damages annually between 1990 and 2019. ''List of floods'' 1962 Floods The North Sea flood of 1962, also known as the Great Flood of Hamburg, occurred between February 16 and 17, 1962. A powerful storm surge caused flooding in the Elbe River The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Germany and flo ..., with water l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storm Tides Of The North Sea
Storm tides of the North Sea are coastal floods associated with extratropical cyclones crossing over the North Sea, the severity of which is affected by the shallowness of the sea and the orientation of the shoreline relative to the storm's path, as well as the timing of tides. The water level can rise to more than 5 metres (17 ft) above the normal tide as a result of storm tides. Northern Germany and Denmark are particularly susceptible to storm tides. The coastline of the German Bight forms an L-shape facing northwest. Also vulnerable are the United Kingdom and the Netherlands, where the sea shallows and is funnelled toward the English Channel. Storm tides are a regular occurrence in the North Sea basin; several form each year. Although most do not cause significant damage, the impact of some has been devastating. During one, the February flood of 1825, the Danish coastline changed, as the North Jutlandic Island became separated from the Jutland Peninsula. Major s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |