|
Saint-Valéry-sur-Somme
Saint-Valery-sur-Somme (, literally ''Saint-Valery on Somme''; ), commune in the Somme department, is a seaport and resort on the south bank of the River Somme estuary. The town's medieval character and ramparts, its Gothic church and long waterside boardwalk, make it a popular tourist destination. Geography The commune lies on the Hauts-de-France coast by the Baie de la Somme and at the mouth of the canalised river Somme. It is north west of Abbeville and to the west of the battlefields of the Somme. Most of the commune lies adjacent to the sea and the Somme river on the Quai du Romerel, Quai Courbet, Quai Jeanne d'Arc, Quai Blavet and the Quai Perree. The oldest part of the commune lies on the northern coast to the north west of the main settlement. To the south is the main road, the CD940 between Abbeville and Cayeux-sur-Mer. River Somme The River Somme is canalised, with sea locks at the eastern end of the town. From Saint-Valery-sur-Somme to Abbeville, the Canal de la S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal De La Somme
The Canal de la Somme () is a canal in northern France. Its total length is 156.4 km with 25 locks, from the English Channel at Saint-Valery-sur-Somme, Saint-Valéry-sur-Somme to the Canal de Saint-Quentin at Saint-Simon, Aisne, Saint-Simon. History The Somme (river), Somme River was river engineering, canalized beginning in 1770. The 54 km section from Saint-Simon, Aisne, St. Simon to Bray-sur-Somme, Bray was completed by 1772, but the rest was not finished until 1843. Overview The canal as originally built has seen substantial modifications since construction of the Canal du Nord in 1904–1965, and is now made up of four distinct sections: * and 1 lock from Saint-Valery-sur-Somme to Abbeville (the ''Canal maritime'') * and 18 locks from Abbeville to Péronne, Somme, Péronne * with 2 locks the section upgraded as part of the Canal du Nord * and 4 locks from Voyennes to Saint-Simon, Aisne, Saint-Simon, closed upstream from Offoy, Somme, Offoy since 2004. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Canals In France
This is a list of the navigable canals and rivers in France. For reference purposes, all waterways are listed, including many that have been abandoned for navigation, mostly in the period 1925-1955, but some in later years. Although several sources are used and listed in the references below, an important source of up-to-date information on French waterways is Inland Waterways of France, by David Edwards-May (published by Imray Ltd in 2010), and its online versionnavigation details for 80 French rivers and canals(French waterways website section). Other sources using the same public information are the historic publishing house Berger-Levrault, Hugh McKnight, David Jefferson, Editions de l'Ecluse (Fluvial magazine) and the series of waterway guides published by Les Editions du Breil, all listed below the table. A comprehensive historic list with 513 entries for French canals is published online by Charles Berg. List The list includes two major rivers, the Rhine and the Rhône, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
A () is a level of administrative divisions of France, administrative division in the France, French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipality, municipalities in Canada and the United States; ' in Germany; ' in Italy; ' in Spain; or civil parishes in the United Kingdom. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlet (place), hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the Municipal arrondissem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
130-T-15 Haine-St-Pierre Saint-Valery 2016
Thirteen or 13 may refer to: * 13 (number) * Any of the years 13 BC, AD 13, 1913, or 2013 Music Albums * ''13'' (Black Sabbath album), 2013 * ''13'' (Blur album), 1999 * ''13'' (Borgeous album), 2016 * ''13'' (Brian Setzer album), 2006 * ''13'' (Die Ärzte album), 1998 * ''13'' (The Doors album), 1970 * ''13'' (Havoc album), 2013 * ''13'' (HLAH album), 1993 * ''13'' (Indochine album), 2017 * ''13'' (Marta Savić album), 2011 * ''13'' (Norman Westberg album), 2015 * ''13'' (Ozark Mountain Daredevils album), 1997 * ''13'' (Six Feet Under album), 2005 * ''13'' (Suicidal Tendencies album), 2013 * ''13'' (Solace album), 2003 * ''13'' (Second Coming album), 2003 * 13 (Timati album), 2013 * ''13'' (Ces Cru EP), 2012 * ''13'' (Denzel Curry EP), 2017 * ''Thirteen'' (CJ & The Satellites album), 2007 * ''Thirteen'' (Emmylou Harris album), 1986 * ''Thirteen'' (Harem Scarem album), 2014 * ''Thirteen'' (James Reyne album), 2012 * ''Thirteen'' (Megadeth album), 2011 * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
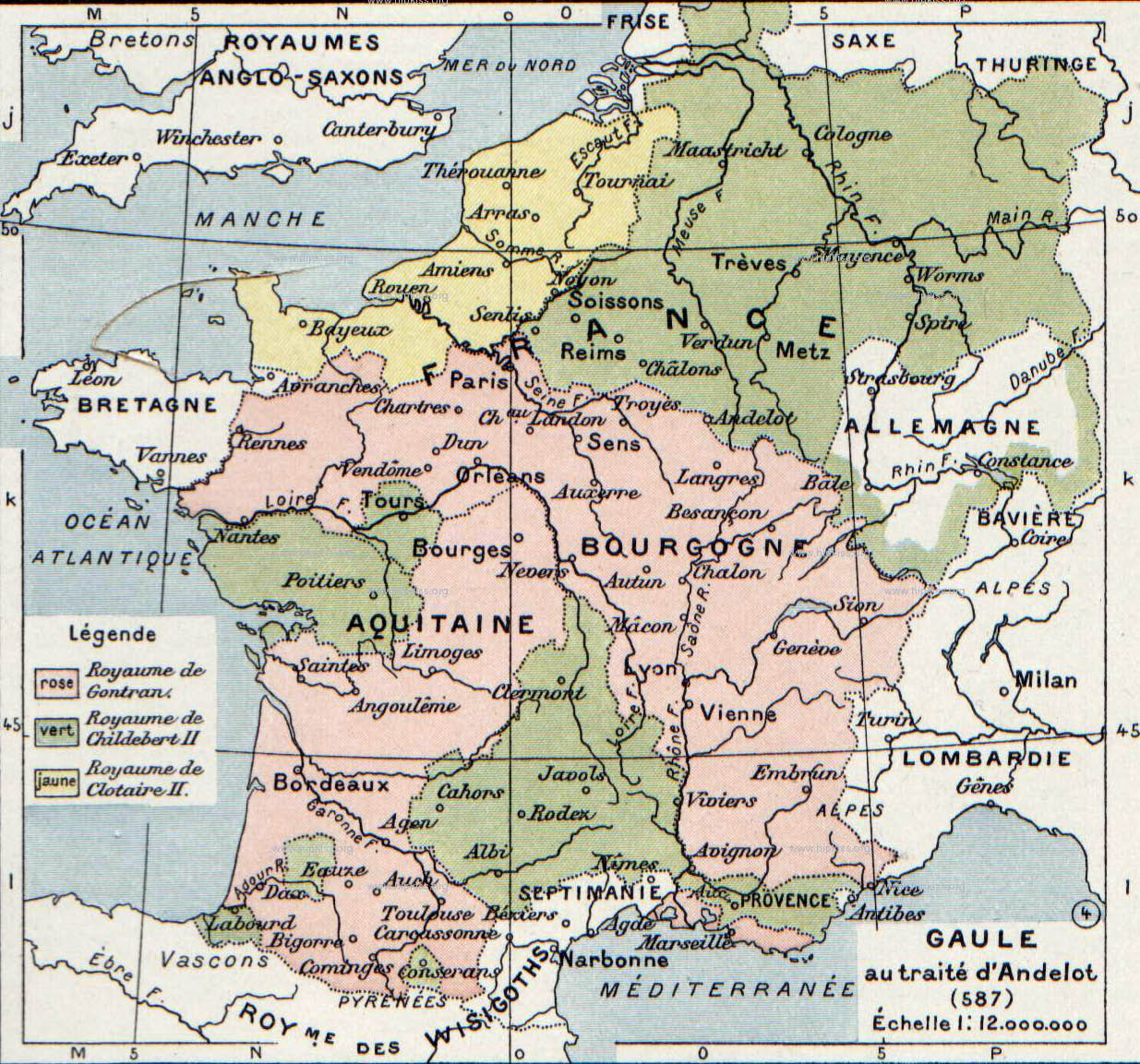
Clotaire II
Chlothar II, sometimes called "the Young" (French language, French: le Jeune), (May/June 584 – 18 October 629) was king of the Franks, ruling Neustria (584–629), Kingdom of Burgundy, Burgundy (613–629) and Austrasia (613–623). The son of Chilperic I and his third wife, Fredegund, he started his reign as an infant under the regency of his mother, who was in an uneasy alliance with Chlothar's uncle King Guntram of Burgundy, who died in 592. Chlothar took power upon the death of his mother in 597; though rich, his realm was one of the smallest portions of Francia. He continued his mother's feud with Queen Brunhilda of Austrasia, Brunhilda with equal viciousness and bloodshed, finally achieving her execution by dismemberment in 613, after winning the battle that enabled Chlothar to unite Francia under his rule. Like his father, he built up his territories by seizing lands after the deaths of other kings. His reign was long by contemporary standards, but saw the continuing ero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walaric
Saint Walaric, modern French Valery (died 620), was a Frankish monk turned hermit who founded the . His cult was recognized in Normandy and England. Life Walaric was born in the Auvergne to a peasant family. Taught to read at a young age, he abandoned the occupation of tending sheep to join the abbey of Autumo. He later moved on to the abbey of Saint-Germain d'Auxerre and finally the abbey of Luxeuil under the famous abbot Columbanus. At Luxeuil he was renowned for his horticultural skills. His ability to protect his vegetables from insects was regarded as miraculous.David Hugh Farmer, "Walaric (Waleric, Valery) (d. 620)", ''The Oxford Dictionary of Saints'', 5th rev. ed. (Oxford University Press, 2011), p. 441. When Theuderic II, king of Burgundy (), expelled Columbanus from his domains, Walaric and a fellow monk named Waldolanus left the kingdom to preach the gospel in Neustria and, according to tradition, the Pas-de-Calais. He eventually settled down as a hermit at a place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which was the most northerly province of the Roman Empire in continental Europe. These Frankish tribes lived for centuries under varying degrees of Roman hegemony and influence, but after the collapse of Roman institutions in western Europe they took control of a large empire including areas which had been ruled by Rome, and what it meant to be a Frank began to evolve. Once they were deeply established in Gaul, the Franks became a multilingual, Catholic Christian people, who subsequently came to rule over several other post-Roman kingdoms both inside and outside the old empire. In a broader sense much of the population of western Europe could eventually described as Franks in some contexts. The term "Frank" itself first appeared in the third cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy (Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and Gallic invasion of the Balkans, into the Balkans, leading to Battle of Thermopylae (279 BC), war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatole France
(; born ; 16 April 1844 – 12 October 1924) was a French poet, journalist, and novelist with several best-sellers. Ironic and skeptical, he was considered in his day the ideal French man of letters.Anatole France, Great Author, Dies , ''The New York Times'', October 13, 1924, p.1 He was a member of the Académie Française, and won the 1921 Nobel Prize in Literature "in recognition of his brilliant literary achievements, characterized as they are by a nobility of style, a profound human sympathy, grace, and a true French people, Gallic temperament". France is also widely believed to be the model for narrator Marcel's literary idol Bergotte in Marcel Proust's ''In Search of Lost Time''. Early years The son of a bookseller, ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeanne D'Arc
Joan of Arc ( ; ; – 30 May 1431) is a patron saint of France, honored as a defender of the French nation for her role in the siege of Orléans and her insistence on the Coronation of the French monarch, coronation of Charles VII of France during the Hundred Years' War. Claiming to be acting under divine guidance, she became a military leader who transcended gender roles and gained recognition as a savior of France. Joan was born to a propertied peasant family at Domrémy-la-Pucelle, Domrémy in northeast France. In 1428, she requested to be taken to Charles VII, later testifying that she was guided by visions from the archangel Michael, Margaret the Virgin, Saint Margaret, and Catherine of Alexandria, Saint Catherine to help him save France from English domination. Convinced of her devotion and purity, Charles sent Joan, who was about seventeen years old, to the siege of Orléans as part of a relief army. She arrived at the city in April 1429, wielding her banner a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lock (water Transport)
A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a chamber in a permanently fixed position in which the water level can be varied. (In a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself (usually then called a caisson (engineering), caisson) that rises and falls.) Locks are used to make a river more easily navigable, or to allow a canal to cross land that is not level. Over time, more and larger locks have been used in canals to allow a more direct route to be taken. History Ancient Egypt In Ancient Egypt, the river-locks was probably part of the Canal of the Pharaohs: Ptolemy II is credited by some for being the first to solve the problem of keeping the Nile free of salt water when his engineers invented the lock around 274/273 BC. Ancient China During 960–1279 CE, the natural extension o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |