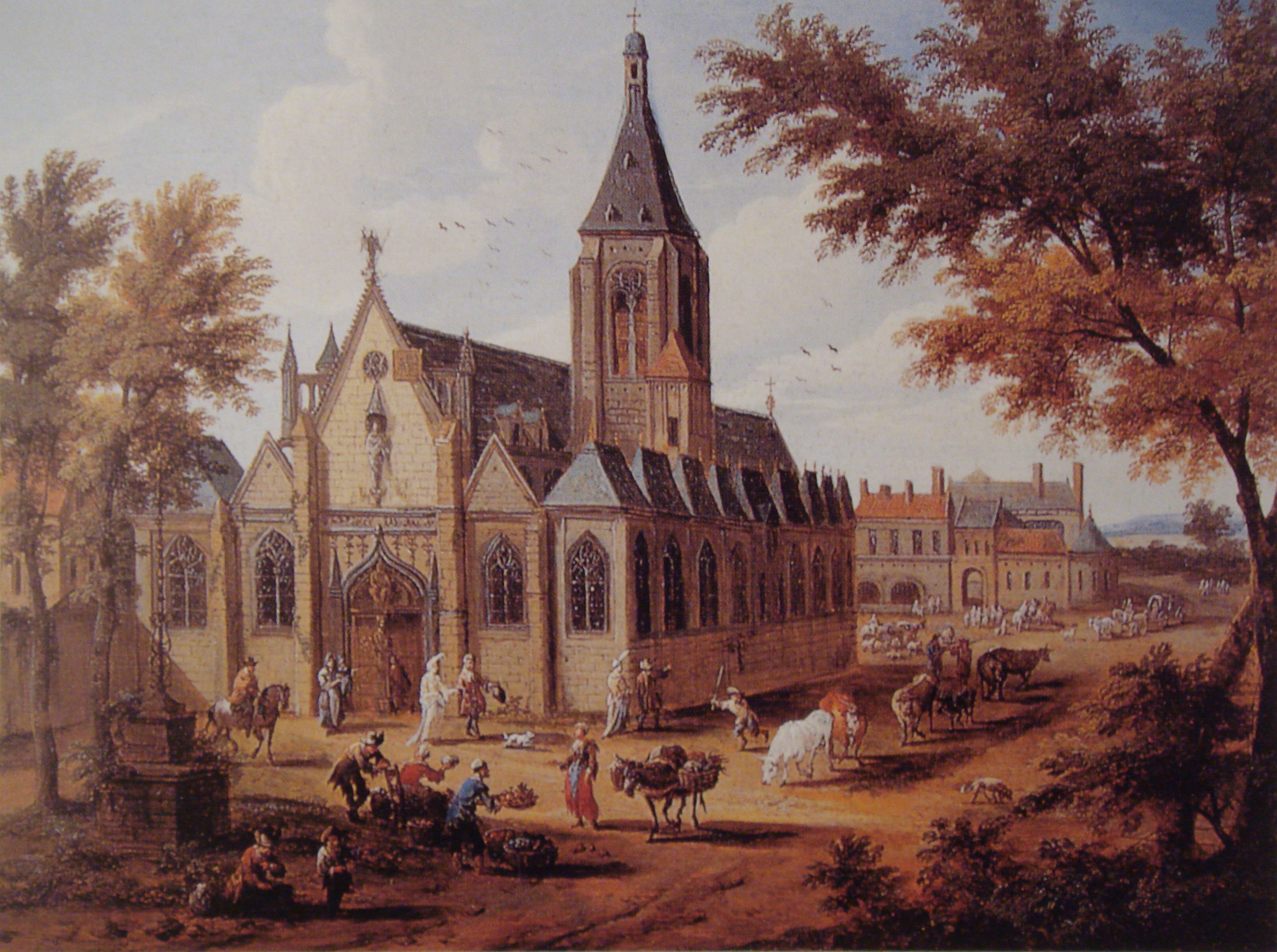|
Saint-Sulpice, Paris
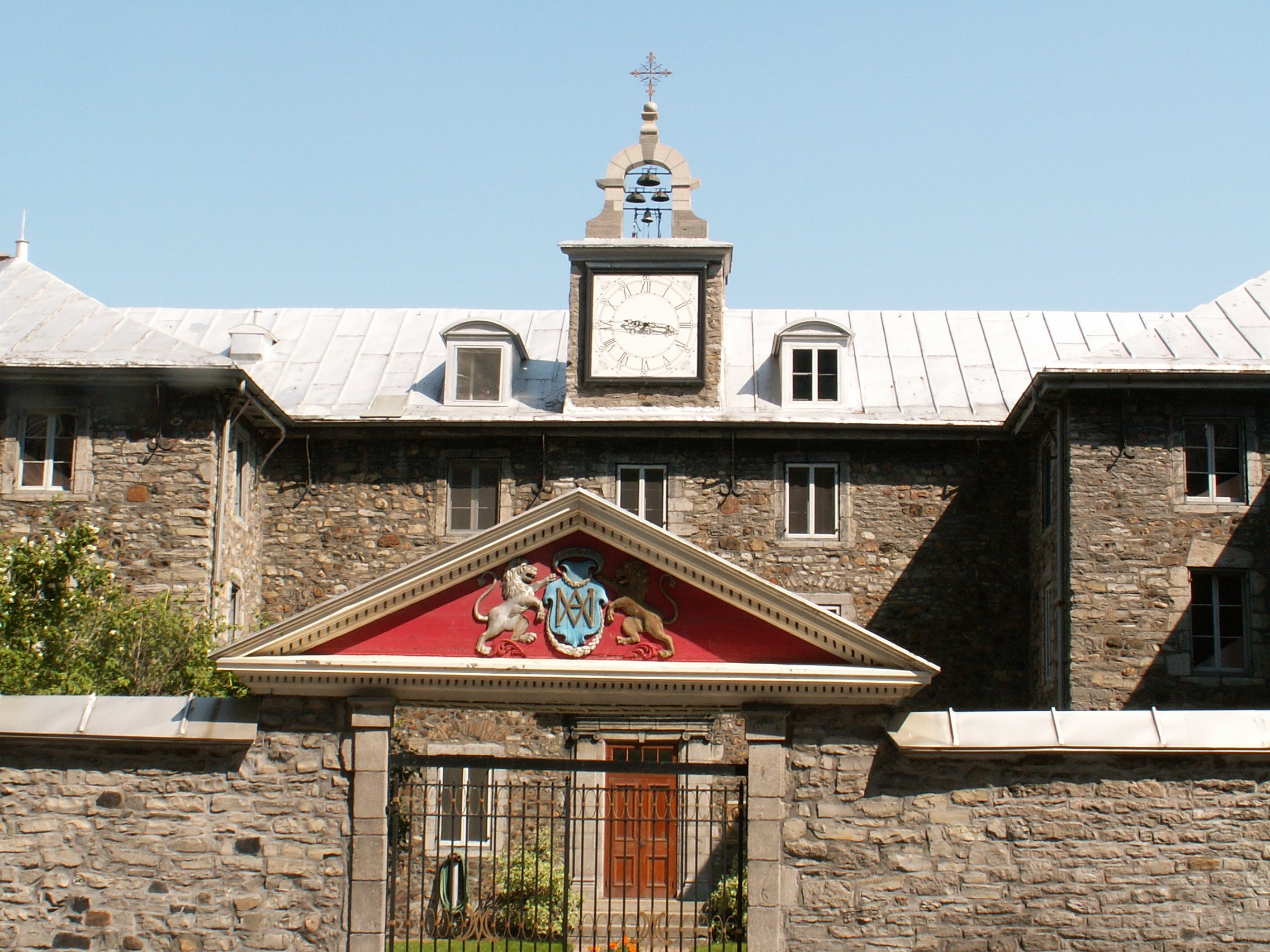
The Church of Saint-Sulpice () is a Catholic church in Paris, France, on the east side of Place Saint-Sulpice, in the 6th arrondissement. Only slightly smaller than Notre-Dame and Saint-Eustache, it is the third largest church in the city. It is dedicated to Sulpitius the Pious. Construction of the present building, the second on the site, began in 1646. During the 18th century, an elaborate gnomon, the Gnomon of Saint-Sulpice, was constructed in the church. Saint-Sulpice is also known for its Great Organ, one of the most significant organs in the world. History The present church is the second building on the site, erected over a Romanesque church originally constructed during the 13th century. Additions were made over the centuries, up to 1631. The new building was founded in 1646 by parish priest Jean-Jacques Olier (1608–1657) who had established the Society of Saint-Sulpice, a clerical congregation, and a seminary attached to the church. Anne of Austria laid t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Saint-Sulpice
The Place Saint-Sulpice is a large public square, dominated on its eastern side by the Saint-Sulpice (Paris), Church of Saint-Sulpice. It was built in 1754 as a tranquil garden in the Latin Quarter, Paris, Latin Quarter of the 6th arrondissement of Paris. History as a tourist destination By 1855, the Place was already a tourist destination, with several Horse-drawn omnibus, omnibuses traversing the square, and the Church highlighted. Ticket offices for the omnibuses and trains opened on the Place by 1857. By 1867, a “generally well kept public toilet, water-closet” opened for people who were waiting to change omnibuses, as well as railroad ticket offices. After the Franco-Prussian War, war and Paris Commune, insurrection, British and American tourists were directed to see the fountain and flowers sold at the Place. As of 1894, the square, laid out in 1811 by Napoleon’s decree, was already described as “Old and New Paris” and a flower market had been established. As of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Saint-Sulpice
The Society of Priests of Saint-Sulpice (; PSS), also known as the Sulpicians, is a society of apostolic life of Pontifical Right for men, named after the Church of Saint-Sulpice, Paris, where it was founded. The members of the Society add the nominal letters PSS after their names to indicate membership in the Congregation. Typically, priests become members of the Society of the Priests of St. Sulpice only after ordination and some years of pastoral work. The purpose of the society is mainly the education of priests and to some extent parish work. As their main role is the education of those preparing to become priests, Sulpicians place great emphasis on the academic and spiritual formation of their own members, who commit themselves to undergoing lifelong development in these areas. The Society is divided into three provinces, operating in various countries: the Province of France, Canada, and the United States. In France The Society of Priests of Saint Sulpice was founded in F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilles-Marie Oppenord
Gilles-Marie Oppenordt (27 July 1672 – 13 March 1742) was a celebrated French designer at the ''Bâtiments du Roi'', the French royal works, and one of the initiators of the Rocaille and Rococo styles, nicknamed "the French Borromini".Gietmann 1911. He specialized in interior architecture and decoration, though he has been connected with the furniture of Charles Cressent. His surname has also been spelled Oppenord and Oppenort. Biography Gilles-Marie Oppenordt was born in Paris. His father Alexandre-Jean Oppenord (1639–1713) was an ''ébéniste'', born Cander-Johan Oppen Oordt at Guelders, one of numerous cabinet-makers from the Low Countries who were drawn to Paris by the opportunity of patronage; the elder Oppenord was naturalized in 1679, when he was a ''menuisier en ebène'' ("furniture-maker in ebony") at the Manufacture Royale des Gobelins; in 1684 the elder Oppenord was appointed an ''ébéniste du Roi'', with official lodgings in the Galeries du Louvre that had be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal (architecture)
A portal is an opening in a wall of a building, gate or fortification, especially a grand entrance to an important structure. Doors, metal gates, or portcullis in the opening can be used to control entry or exit. The surface surrounding the opening may be made of simple building materials or decorated with ornamentation. The elements of a portal can include the voussoir, tympanum, an ornamented mullion or ''trumeau'' between doors, and columns with carvings of saints in the westwork of a church. Examples File:Baroque portal in Brescia.jpg, Baroque portal of a private palace in Brescia File:Quito Iglesia de El Carmen Bajo Southwestern carved door.jpg, Baroque portal of the Church of El Carmen Bajo Monastery in Quito File:Dülmen, St.-Viktor-Kirche, Eingangsportal -- 2021 -- 4504-10.jpg, Wooden portal of the Church of St. Victor in Dülmen File:Porto - Sant Martí de Cedofeita - Façana principal.JPG, Romanesque portal of the Church of São Martinho de Cedofeita, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
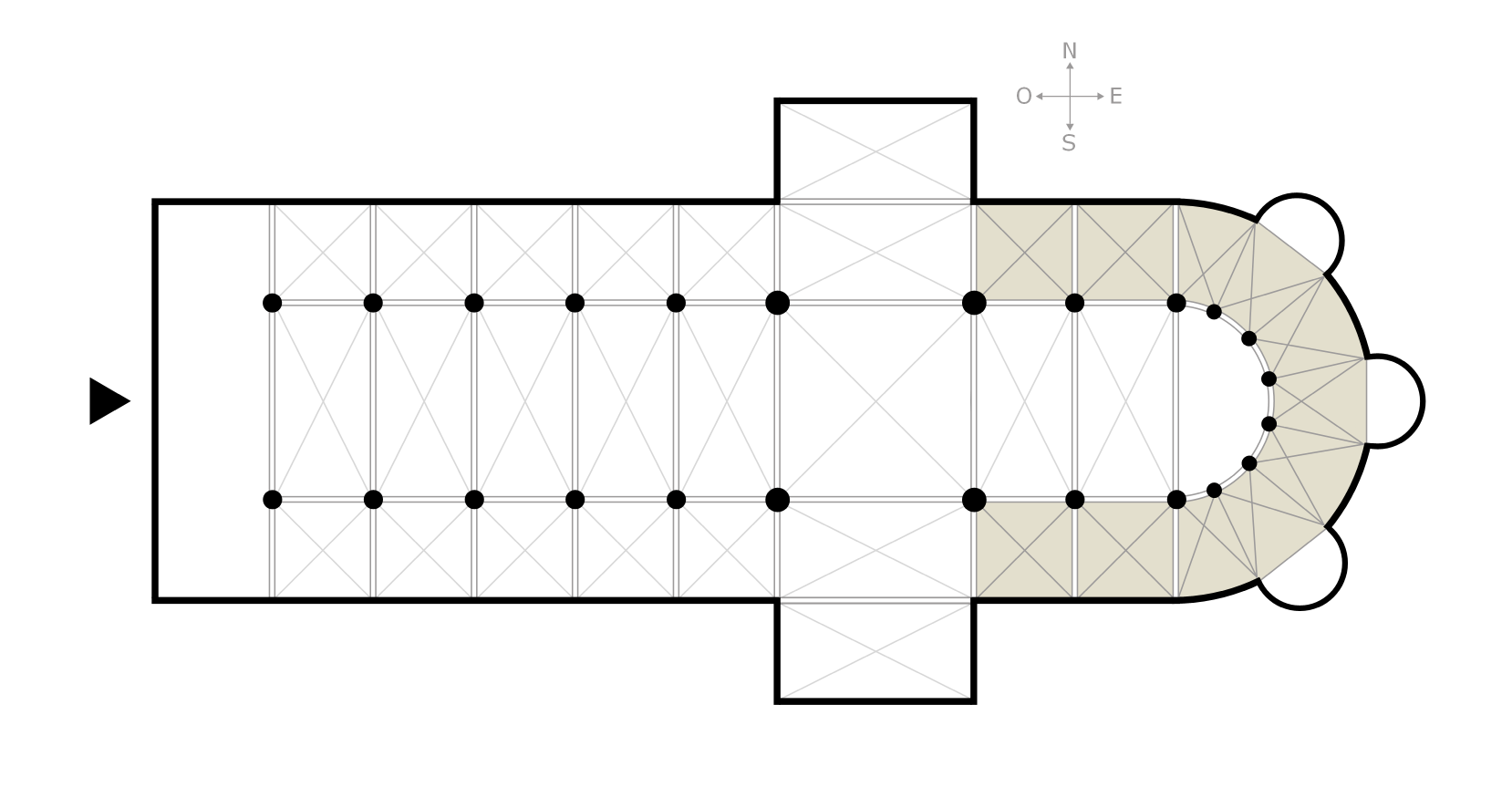
Transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform ("cross-shaped") cruciform plan, churches, in particular within the Romanesque architecture, Romanesque and Gothic architecture, Gothic Christianity, Christian church architecture, church architectural traditions, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave. Each half of a transept is known as a semitransept. Description The transept of a church separates the nave from the sanctuary, apse, Choir (architecture), choir, chevet, presbytery (architecture), presbytery, or chancel. The transepts cross the nave at the crossing (architecture), crossing, which belongs equally to the main nave axis and to the transept. Upon its four Pier (architecture), piers, the crossing may support a spire (e.g., Salisbury Cathedral), a central tower (e.g., Gloucester Cathedral) or a crossing dome (e.g., St Paul's Cathedral). Since the altar is usually located a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apse Chapel
An apse chapel, apsidal chapel, or chevet is a chapel in traditional Christian church architecture, which radiates tangentially from one of the bays or divisions of the apse. It is reached generally by a semicircular passageway, or ambulatory, exteriorly to the walls or piers of the apse. Features In plan, the normal type of the tangential chapel is semicircular; some, however, are pentagonal, and some composed of a small circle, serving as choir, and part of a large circle, as nave; some are oblong with eastern apses. In England, sometimes an ambulatory connects the north and south aisles of the choir and from the ambulatory projects an eastern chapel or chapels. The eastern chevet of Westminster Abbey, surrounded by five apsidal chapels, is the only complete example of this feature in England. The common source of the ambulatory and radiating chapels seems to have been the church of St. Martin of Tours, where originally there was a choir of two bays, and an apse of five bays, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( 'walking place') is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucestershire, England. File:A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred space, sacred place, such as a shrine, protected by ecclesiastical immunity. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This secondary use can be categorized into human sanctuary, a safe place for people, such as a political sanctuary; and non-human sanctuary, such as an animal or plant sanctuary. Religious sanctuary ''Sanctuary'' is a word derived from the Latin , which is, like most words ending in , a container for keeping something in—in this case holy things or perhaps cherished people (/). The meaning was extended to places of holiness or safety. Its origin is the principle of independence and immunity of religious orders from "temporal" powers. In many Place of worship, religious buildings ''sanctuary'' has a specific meaning, covering part of the interior. Sanctuary as area around the altar In many Western Christianity, Western Christian traditions in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Le Vau
Louis Le Vau (; c. 1612 – 11 October 1670) was a French Baroque architect, who worked for Louis XIV of France. He was an architect that helped develop the French Classical style in the 17th century.''Encyclopedia of World Biography''"Louis Le Vau", vol. 9, pp. 360-361 Early life and career Born Louis Le Veau, he was the son of Louis Le Veau (died February 1661), a stonemason, who was active in Paris.Feldmann 1996, p. 262. His younger brother François Le Vau (born in 1624) also became an architect. The father and his two sons worked together in the 1630s and 1640s. The two brothers later changed the spelling of their surname from "Le Veau" to "Le Vau" to avoid its association with the French word ''veau'' (calf). Le Vau started his career by designing the Hotel de Bautru in 1634. By 1639, he was developing town houses ('' hôtels particuliers'') for rich citizens such as Sainctot, Hesselin, Gillier, Gruyn des Bordes, and Jean Baptiste Lambert in the île Saint-Louis, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Gittard
Daniel Gittard (March 14, 1625, in Blandy-les-Tours – December 15, 1686, in Paris) was a French architect. In 1671, he became one of the first eight members of the Académie royale d'architecture created by Louis XIV LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign .... External links Structurae entry 17th-century French architects Members of the Académie royale d'architecture 1625 births 1686 deaths {{France-architect-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fronde
The Fronde () was a series of civil wars in the Kingdom of France between 1648 and 1653, occurring in the midst of the Franco-Spanish War, which had begun in 1635. The government of the young King Louis XIV confronted the combined opposition of the princes, the nobility, the noble regional court assemblies (''parlements''), as well as much of the French population, and managed to subdue them all. The dispute started when the government of France issued seven fiscal edicts, six of which were to increase taxation. The ''parlements'' resisted, questioned the constitutionality of the king's actions, and sought to check his powers. The Fronde was divided into two campaigns, the Parlementary Fronde and the Fronde of the Princes. The timing of the outbreak of the Parlementary Fronde, directly after the Peace of Westphalia (1648) that ended the Thirty Years' War, was significant. The nuclei of the armed bands that terrorized parts of France under aristocratic leaders during that peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christophe Gamard
Christophe Gamard, Gamar or Gamart, was a 17th-century French architect, who worked in Paris and died there in 1649. Biography He was a master mason in 1613, an architect of the old Saint-Sulpice in 1623 (and began its reconstruction after 1643), and a city juror (''juré de la Ville'') in 1626. He was an assistant of Claude Vellefaux, the supervising architect (''architecte voyer'') of the Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Prés, and succeeded him in that position in 1627. He became an architect of the king (''architecte du roi'') in 1639. Jean-Pierre Babelon, ''Demeures parisiennes sous Henri IV et Louis XIII'', Paris, Éditions Hazan, 1991, , . Family He married Claude Vellefaux's daughter, Étiennette Vellefaux. They had two sons, Christophe and Hubert. Widowed, he married Marie Gillier in 1648, despite the opposition of his sons. His brother, Philippot Gamard, worked on the Hotel de Nemours, , in 1620, and at houses, current rues de Sévigné and between 1616 and 1619. Works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |