|
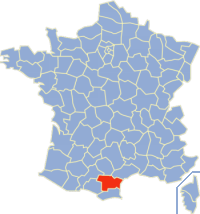
Saint-Papoul
Saint-Papoul (; Languedocien: ''Sant Pàpol'') is a commune in the Aude department in southern France. History The town of Saint-Papoul was founded during the 8th century when an abbey was established here, dedicated to Saint Papulus. The diocese of Saint-Papoul, of which Saint-Papoul Cathedral was the center, was created an episcopal see by John XXII in 1317. Population Literature Saint-Papoul is a location mentioned briefly in the M.R. James short ghost story Canon Alberic's Scrap-Book published in Ghost Stories of an Antiquary ''Ghost Stories of an Antiquary'' is a horror short story collection by British writer M. R. James, published in 1904 (some had previously appeared in magazines). Some later editions under this title contain both the original collection and its su ... in 1904 See also * Communes of the Aude department References Communes of Aude Aude communes articles needing translation from French Wikipedia {{Aude-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Saint-Papoul
The former French Roman Catholic Diocese of Saint-Papoul, now a Latin titular see, was created by Pope John XXII in 1317 and existed until the Napoleonic Concordat of 1811. The seat of the diocese was at Saint-Papoul, in south-west France, in the modern department of Aude; it was some distance northeast of the main highway between Carcassonne and Toulouse, where there was already a Benedictine monastery, founded in the eighth century and dedicated to Saint Papoul. The bishop of Saint-Papoul was suffragan of the Archbishop of Toulouse. The diocese existed until the French Revolution. It was one of the diocese scheduled to be suppressed under the Civil Constitution of the Clergy (1790). Under the Concordat of 1801 its territory was taken over by the Diocese of Carcassonne. History In his bull of erection, issued on 22 February 1317, Pope John XXII stated that the population in the diocese of Toulouse was growing at such a pace that the Bishop was no longer able to govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Papoul Cathedral
Saint-Papoul Cathedral (french: Cathédrale Saint-Papoul de Saint-Papoul) was a Roman Catholic church located in the village of Saint-Papoul in Languedoc. The cathedral is dedicated to Saint Papulus (french: Papoul), an early Christian bishop and martyr, from whom the settlement also took its name. It was the seat of the Bishop of Saint-Papoul. This diocese, along with a number of others in the region, was created in 1317 in the aftermath of the suppression of the Albigensians. The Abbey of Saint-Papoul had been founded here in the 8th century, and in 1317 the abbot was elevated to the status of bishop, and the abbey church to that of cathedral. The diocese and the abbey were suppressed during the French Revolution and the diocese was abolished under the Concordat of 1801, its territory being transferred almost entirely to the Diocese of Carcassonne The Diocese of Carcassonne and Narbonne (Latin: ''Dioecesis Carcassonensis et Narbonensis''; French: ''Diocèse de Carcassonne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Papulus
Saint Papulus (french: Papoul) was, according to Christian tradition, a priest who worked with Saturninus of Toulouse to evangelize southern Gaul. Papulus is considered an evangelist of the Lauragais.abbaye de Saint-Papoul Legends associated with Saturninus state that after consecrated him a bishop, "he was given for his companion Papulus, later to become Saint Papulus the Martyr." He was martyred, like Saturninus, during the persecutions of . Papulus' unreliable legend states that upon reaching |
Communes Of The Aude Department
The following is a list of the 433 communes of the Aude department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):BANATIC Périmètre des EPCI à fiscalité propre. Accessed 3 July 2020. * *Communauté d'agglomération Le * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
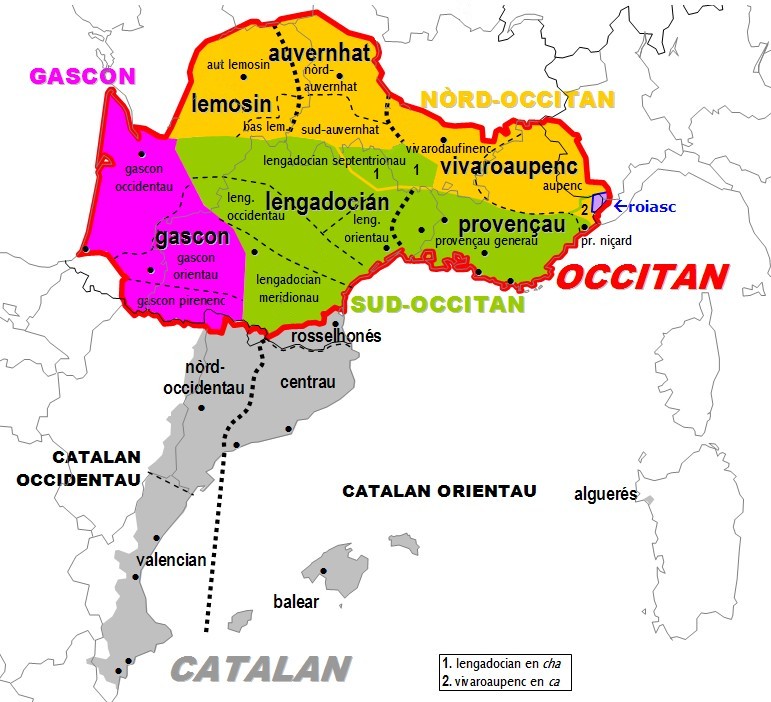
Languedocien Dialect
Languedocien (French name, ), Languedocian or Lengadocian (), is an Occitan dialect spoken in rural parts of southern France such as Languedoc, Rouergue, Quercy, Agenais and Southern Périgord. It is sometimes also called Languedocien-Guyennais. Due to its central position among the dialects of Occitan, it is often used as a basis for a Standard Occitan. About 10% of the population of Languedoc are fluent in the language (about 300,000), and another 20% (600,000) "have some understanding" of the language. All speak French as their first or second language. Geographic distribution Languedocien is spoken in certain parts of three French regions. * Occitanie: Aveyron, Lot, Tarn, Tarn-et-Garonne except Lomagne, Ariège (except a western part), Haute-Garonne (except the districts of Saint-Gaudens and Muret), Aude, Hérault, Lozère, western and northern parts of Gard and Fenouillèdes. * Nouvelle-Aquitaine: south of the Dordogne, east of the Gironde, north-eastern two-thirds of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aude
Aude (; ) is a Departments of France, department in Southern France, located in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region and named after the river Aude (river), Aude. The departmental council also calls it "Catharism, Cathar Country" (French language, French: ''Pays cathare'') after a group of religious dissidents active in the 12th to 14th centuries. Its Prefectures in France, prefecture is Carcassonne and its Subprefectures in France, subprefectures are Limoux and Narbonne. As of 2019, it had a population of 374,070.Populations légales 2019: 11 Aude INSEE Aude is a frequent feminine French given name in Francophone countries, deriving initially from Aude or Oda, a wife of Bertrand, Duke of Aquitaine, and mother of Eudo, brother of Saint Hubertus. Aude was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (french: département, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. Ninety-six departments are in metropolitan France, and five are overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 332 arrondissements, and these are divided into cantons. The last two levels of government have no autonomy; they are the basis of local organisation of police, fire departments and, sometimes, administration of elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council ( ing. lur.. From 1800 to April 2015, these were called general councils ( ing. lur.. Each council has a president. Their main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior high school () buildings and technical staff, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope John XXII
Pope John XXII ( la, Ioannes PP. XXII; 1244 – 4 December 1334), born Jacques Duèze (or d'Euse), was head of the Catholic Church from 7 August 1316 to his death in December 1334. He was the second and longest-reigning Avignon Pope, elected by the Conclave of Cardinals, which was assembled in Lyon through the work of King Louis X's brother Philip, the Count of Poitiers. Like his predecessor, Clement V, Pope John centralized power and income in the Papacy and lived a princely life in Avignon. John excommunicated the enemies of Edward II of England, while warning Edward of a possible reassessment of the papal grant of Ireland. He opposed the political policies of Louis IV of Bavaria as Holy Roman Emperor, which prompted Louis to invade Italy and set up an antipope, Nicholas V. John opposed the Franciscan understanding of the poverty of Christ and his apostles passing multiple papal bulls to enforce his views. This led William of Ockham to write against unlimited papal power. Fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Alberic's Scrap-Book
"Canon Alberic's Scrap-Book" is a horror story by British writer M. R. James, which was written in 1894 and published the following year in the '' National Review''. It was included in his first short story collection, ''Ghost Stories of an Antiquary'' of 1904. Plot summary The story has a detailed and realistic setting in the tiny decaying cathedral city of Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges, at the foot of the Pyrenees in southern France. An English tourist spends a day photographing the interior of the eponymous cathedral and is encouraged by the sacristan to buy an unusual manuscript. This, he concludes, had been created long ago by Canon Albéric de Mauléon (an invented character, said to be a collateral descendant of the real 16th-century bishop Jean de Mauléon), who had cut up volumes in the old cathedral library. A disturbing illustration of King Solomon and a demon in the back of the book is a key to the story's suspenseful arc. Adaptations The story has inspired a musical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghost Stories Of An Antiquary
''Ghost Stories of an Antiquary'' is a horror short story collection by British writer M. R. James, published in 1904 (some had previously appeared in magazines). Some later editions under this title contain both the original collection and its successor, ''More Ghost Stories'' (1911), combined in one volume. It was his first short story collection. Contents of the original edition * "Canon Alberic's Scrap-Book" * "Lost Hearts" * "The Mezzotint" * "The Ash-tree" * " Number 13" * "Count Magnus" * 'Oh, Whistle, and I'll Come to You, My Lad' * "The Treasure of Abbot Thomas" Reception A. M. Burrage praised ''Ghost Stories of an Antiquary'' and its successor, ''More Ghost Stories of an Antiquary'' as "two really admirable books of ghost stories". Burrage also described 'Oh, Whistle, and I'll Come to You, My Lad' as "a real gem".Burrage, A. M. "The Supernatural in Fiction", ''The Home Magazine'', October 1921. Reprinted in Burrage, ''Someone in the Room: Strange Tales Old and New'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |