|
Sailing Ship Effect
The sailing ship effect is a phenomenon by which the introduction of a new technology to a market accelerates the innovation of an incumbent technology. Despite the fact that the term was coined by W.H. Ward in 1967 the concept was made clear much earlier in a book by S.C. Gilfillan entitled “''Inventing the ship''” published in 1935. The name of the “effect” is due to the reference to advances made in sailing ships in the second half of the 1800s in response to the introduction of steamships. According to Ward, in the 50 years after the introduction of the steam ship, sailing ships made more improvements than they had in the previous 300 years. The term “Sailing Ship Effect” applies to situations in which an old technology is revitalized, experiencing a “last gasp” when faced with the risk of being replaced by a newer technology. Here is how Gilfillan put it: ”It is paradoxical, but on examination logical, that this noble flowering of the sailing ship, this apothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations.Based on definition from: Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
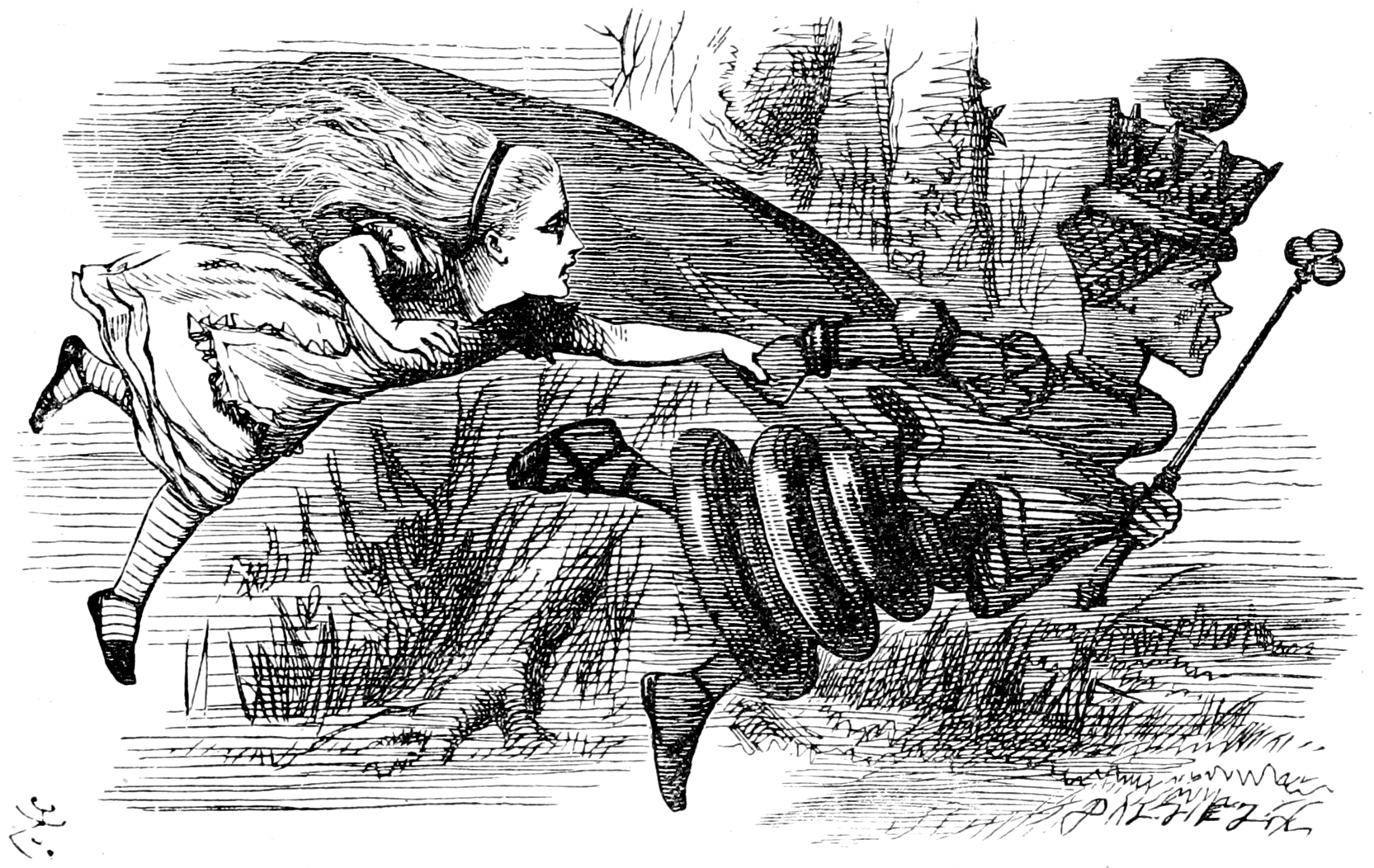
Red Queen Hypothesis
The Red Queen hypothesis is a hypothesis in evolutionary biology proposed in 1973, that species must constantly adapt, evolve, and proliferate in order to survive while pitted against ever-evolving opposing species. The hypothesis was intended to explain the constant (age-independent) extinction probability as observed in the paleontological record caused by co-evolution between competing species; however, it has also been suggested that the Red Queen hypothesis explains the advantage of sexual reproduction (as opposed to asexual reproduction) at the level of individuals,Bell, G. (1982). The Masterpiece Of Nature: The Evolution and Genetics of Sexuality. University of California Press, Berkeley, 378 pp. and the positive correlation between speciation and extinction rates in most higher taxa. Origin In 1973, Leigh Van Valen proposed the hypothesis as an "explanatory tangent" to explain the "law of extinction" known as "Van Valen's law", which states that the probability of exti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Effect
In economics, a network effect (also called network externality or demand-side economies of scale) is the phenomenon by which the value or utility a user derives from a good or service depends on the number of users of compatible products. Network effects are typically positive, resulting in a given user deriving more value from a product as more users join the same network. The adoption of a product by an additional user can be broken into two effects: an increase in the value to all other users ( "total effect") and also the enhancement of other non-users' motivation for using the product ("marginal effect"). Network effects can be direct or indirect. Direct network effects arise when a given user's utility increases with the number of other users of the same product or technology, meaning that adoption of a product by different users is complementary. This effect is separate from effects related to price, such as a benefit to existing users resulting from price decreases as m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penn Effect
The Penn effect is the economic finding that real income ratios between high and low income countries are systematically exaggerated by gross domestic product (GDP) conversion at market exchange rates. It is associated with what became the Penn World Table, and it has been a consistent econometric result since at least the 1950s. The "Balassa–Samuelson effect" is a model cited as the principal cause of the Penn effect by neo-classical economics, as well as being a synonym of "Penn effect". History Classical economics made simple predictions about exchange rates; it was said that a basket of goods would cost roughly the same amount everywhere in the world, when paid for in some common currency (like gold) 1. This is called the purchasing power parity (PPP) hypothesis, also expressed as saying that the real exchange rate (RER) between goods in various countries should be close to one. Fluctuations over time were expected by this theory but were predicted to be small and non-system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigou Effect
In economics, the Pigou effect is the stimulation of output and employment caused by increasing consumption due to a rise in real balances of wealth, particularly during deflation. The term was named after Arthur Cecil Pigou by Don Patinkin in 1948. Real wealth was defined by Arthur Cecil Pigou as the summation of the money supply and government bonds divided by the price level. He argued that Keynes' '' General Theory'' was deficient in not specifying a link from "real balances" to current consumption and that the inclusion of such a "wealth effect" would make the economy more "self correcting" to drops in aggregate demand than Keynes predicted. Because the effect derives from changes to the "Real Balance", this critique of Keynesianism is also called the Real Balance effect. History The Pigou effect was first popularised by Arthur Cecil Pigou in 1943, in ''The Classical Stationary State'' an article in the ''Economic Journal''. He had proposed the link from balances to consu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Analysis
Business analysis is a professional discipline of identifying business needs and determining solutions to business problems. Solutions often include a software-systems development component, but may also consist of process improvements, organizational change or strategic planning and policy development. The person who carries out this task is called a business analyst or BA. Business analysts do not work solely on developing software systems. But work across the organisation, solving business problems in consultation with business stakeholders. Whilst most of the work that business analysts do today relate to software development/solutions, this derives from the ongoing massive changes businesses all over the world are experiencing in their attempts to digitise. Although there are different role definitions, depending upon the organization, there does seem to be an area of common ground where most business analysts work. The responsibilities appear to be: * To investigate busine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Models
A business model describes how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value,''Business Model Generation'', Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur, Alan Smith, and 470 practitioners from 45 countries, self-published, 2010 in economic, social, cultural or other contexts. The process of business model construction and modification is also called ''business model innovation'' and forms a part of business strategy. In theory and practice, the term ''business model'' is used for a broad range of informal and formal descriptions to represent core aspects of an organization or business, including purpose, business process, target customers, offerings, strategies, infrastructure, organizational structures, sourcing, trading practices, and operational processes and policies including culture. Context The literature has provided very diverse interpretations and definitions of a business model. A systematic review and analysis of manager responses to a survey defines business models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics Effects
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational and beh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |