|
Safavid Harem
The royal harem of the Safavid ruler played an important role in the history of Safavid Persia (1501-1736). Hierarchy and organisation The Safavid harem consisted of mothers, wives, slave concubines and female relatives, and was staffed with female slaves and with eunuchs who acted as their guards and channel to the rest of the world.Sussan Babaie, Kathryn Babayan, Ina Baghdiantz-MacCabe, Mussumeh Farhad: Slaves of the Shah: New Elites of Safavid Iran, Bloomsbury Academic, 2004 Shah Sultan Hossain's (r. 1694–1722) court has been estimated to include five thousand slaves; male and female, black and white, of whom one hundred were black eunuchs. Consorts The monarchs of the Safavid dynasty preferred to procreate through slave concubines, which would neutralize potential ambitions from relatives and other inlaws and protect patrimony. The slave concubines (and later mothers) of the Shah's mainly consisted of enslaved Circassian, Georgian and Armenian women, captured as war bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Soleiman Safavi
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of Persianate societies, such as the Ottoman Empire, the Kazakh Khanate, the Khanate of Bukhara, the Emirate of Bukhara, the Mughal Empire, the Bengal Sultanate, historical Afghan dynasties, and among Gurkhas. Rather than regarding himself as simply a king of the concurrent dynasty (i.e. European-style monarchies), each Iranian ruler regarded himself as the Shahanshah ( fa, شاهنشاه, translit=Šâhanšâh, label=none, ) or Padishah ( fa, پادشاه, translit=Pâdešâh, label=none, ) in the sense of a continuation of the original Persian Empire. Etymology The word descends from Old Persian ''xšāyaθiya'' "king", which used to be considered a borrowing from Median, as it was compared to Avestan ''xšaθra-'', "power" and "command" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghilman
Ghilman (singular ar, غُلاَم ',Other standardized transliterations: '' / ''. . plural ')Other standardized transliterations: '' / ''. . were slave-soldiers and/or mercenaries in the armies throughout the Islamic world, such as the Safavid, Afsharid and Qajar empires. Islamic states from the early 9th century to the early 19th century consistently deployed slaves as soldiers, a phenomenon that was very rare outside of the Islamic world. The Quran mentions ''ghilman'' () as serving boys who are one of the delights of ''Jannah'' or paradise/heaven of Islam, in vers 52:24 (Vers56:17is also thought to refer to ghilman.) Etymology The words ''ghilman'' () and its singular variant ''ghulam'' () are of Arabic origin, meaning ' or '. It derives from the Arabic root ''ḡ-l-m'' (). History The ''ghilman'' were slave-soldiers taken as prisoners of war from conquered regions or frontier zones, especially from among the Turkic people of Central Asia and the Caucasian peoples ( Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Imperial Harem
The Imperial Harem ( ota, حرم همايون, ) of the Ottoman Empire was the Ottoman sultan's harem – composed of the wives, servants (both female slaves and eunuchs), female relatives and the sultan's concubines – occupying a secluded portion (seraglio) of the Ottoman imperial household. This institution played an important social function within the Ottoman court, and wielded considerable political authority in Ottoman affairs, especially during the long period known as the Sultanate of Women (approximately 1533 to 1656). Multiple historians claim that the sultan was frequently lobbied by harem members of different ethnic or religious backgrounds to influence the geography of the Ottoman wars of conquest. The utmost authority in the Imperial Harem, the valide sultan, ruled over the other women in the household; the consorts of the sultan were normally of slave origin, and thus were also his mother, the valide sultan. The Kizlar Agha (, also known as the "Chief Black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qajar Harem
The harem of the monarchs of the Qajar dynasty (1785-1925) consisted of several thousand people. The harem had a precise internal administration, based on the women's rank. Hierarchy and organisation Mother of the Shah As was customary in Muslim harems, the highest rank of the harem hierarchy was that of the monarchs' mother, who in Qajar Iran had the title ''Mahd-e ʿOlyā'' (Sublime Cradle). She had many duties and prerogatives, such as safeguarding the harem valuables, particularly the jewels, which she administered with the help of female secretaries. Consorts In contrast to what was common in the Ottoman Empire, where the sultans normally only had slave consorts, the Qajar shah's also had a custom of diplomatic marriages with free Muslim women, daughters of Qajar dignitaries and princes. Another phenomena of the Qajar harem was that the Shah entered two different kinds of marriages with his harem women: '' ṣīḡa'' (temporary wife), which was often done with concubines, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Harem
The harem of the caliphs of the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258) in Baghdad was composed of his mother, wives, slave concubines, female relatives and slave servants (women and eunuchs), occupying a secluded portion of the Abbasid household. This institution played an important social function within the Abbasid court and was that part were the women were confined and secluded. The senior woman in rank in the harem was the mother of the Caliph. The Abbasid harem acted as a role model for the harems of other Islamic dynasties, as it was during the Abbasid Caliphate that the harem system was fully enforced in the Muslim world. Background and origin The harem system first became fully institutionalized in the Islamic world under the Abbasid caliphate. Although the term ''harem'' does not denote women's quarters in the Quran, a number of Quranic verses discussing modesty and seclusion were held up by Quranic commentators as religious rationale for the separation of women f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan Husayn
Soltan Hoseyn ( fa, شاه سلطان حسین, Soltān-Hoseyn; 1668 – 9 September 1727) was the Safavid shah of Iran from 1694 to 1722. He was the son and successor of Shah Solayman (). Born and raised in the royal harem, Soltan Hoseyn ascended the throne with limited life experience and more or less no expertise in the affairs of the country. He was installed on the throne through the efforts of powerful great-aunt, Maryam Begum, as well as the court eunuchs, who wanted to increase their authority by taking advantage of a weak and impressionable ruler. Throughout his reign, Soltan Hoseyn became known for his extreme devotion, which had blended in with his superstition, impressionable personality, excessive pursuit of pleasure, debauchery, and wastefulness, all of which have been considered by both contemporary and later writers as elements that played a part in the decline of the country. The last decade of Soltan Hoseyn's reign was marked by urban dissension, tribal uprisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Baqir Majlisi
Mohammad Baqer Majlesi (b. 1037/1628-29 – d. 1110/1699) ( fa, علامه مجلسی ''Allameh Majlesi''; also Romanized as: Majlessi, Majlisi, Madjlessi), known as Allamah Majlesi or Majlesi Al-Thani (Majlesi the Second), was a renowned and very powerful Iranian Twelver Shia Scholar and Thinker, during the Safavid era. He has been described as "one of the most powerful and influential Shi'a ulema of all time", whose "policies and actions reoriented Twelver Shia'ism in the direction that it was to develop from his day on." He was buried next to his father in a family mausoleum located next to the Jamé Mosque of Isfahan. Early life and education Born in Isfahan in 1617, his father, Mulla Mohammad Taqi Majlesi (''Majlesi-ye Awwal''—Majlesi the First, 1594 AD-1660 AD), was a cleric of Islamic jurisprudence. The genealogy of his family is traced back to Abu Noaym Ahámad b. Abdallah Esfahani (d. 1038 AD), the author, inter alia, of a History of Isfahan, entitled Zikr-i akhbar- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suleiman I Of Persia
Suleiman I (; born Sam Mirza, February or March 1648 – 29 July 1694) was the eighth and the penultimate Shah of Safavid Iran from 1666 to 1694. He was the eldest son of Abbas II and his concubine, Nakihat Khanum. Born as Sam Mirza, Suleiman spent his childhood in the harem among women and eunuchs and his existence was hidden from the public. When Abbas II died in 1666, his grand vizier, Mirza Mohammad Karaki, did not know that the shah had a son. The nineteen-years-old Sam Mirza was crowned king under the regnal name, Safi II, after his grandfather, Safi I. His reign as Safi II undergone troublesome events which led to a second coronation being held for him in 20 March 1668, simultaneously with Nowruz, in which he was crowned king as Suleiman I. After his second coronation, Suleiman retreated into his harem to enjoy sexual activities and excessive drinking. He was indifferent to the state affairs, and often would not appear in the public for months. As a result for his idlene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Abbas II
Abbas II (; born Soltan Mohammad Mirza; 30 August 1632 – 26 October 1666) was the seventh Shah of Safavid Iran, ruling from 1642 to 1666. As the eldest son of Safi and his Circassian wife, Anna Khanum, he inherited the throne when he was nine, and had to rely on a regency led by Saru Taqi, the erstwhile grand vizier of his father, to govern in his place. During the regency, Abbas received formal kingly education that until then, he had been denied. In 1645, at age fifteen, he was able to remove Saru Taqi from power, and after purging the bureaucracy ranks, asserted his authority over his court and began his absolute rule. Abbas II's reign was marked by peacefulness and progression. He intentionally avoided a war with the Ottoman Empire, and his relations with the Uzbeks in the east were friendly. He enhanced his reputation as a military commander by leading his army during the war with the Mughal Empire, and successfully recovering the city of Kandahar. On his behest, Ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
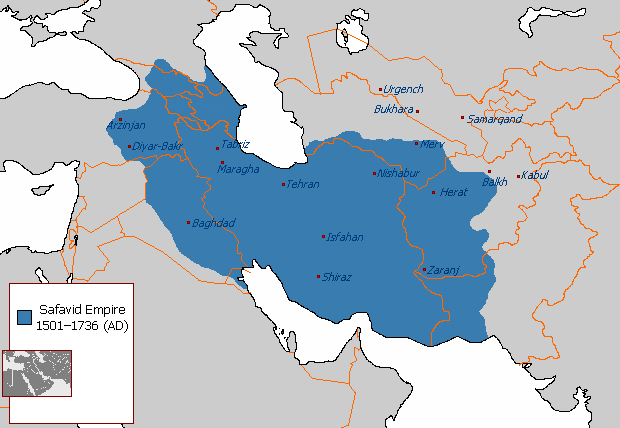
Safavid Dynasty
The Safavid dynasty (; fa, دودمان صفوی, Dudmâne Safavi, ) was one of Iran's most significant ruling dynasties reigning from 1501 to 1736. Their rule is often considered the beginning of modern Iranian history, as well as one of the gunpowder empires. The Safavid Shāh Ismā'īl I established the Twelver denomination of Shīʿa Islam as the official religion of the Persian Empire, marking one of the most important turning points in the history of Islam. The Safavid dynasty had its origin in the Safavid order of Sufism, which was established in the city of Ardabil in the Iranian Azerbaijan region. It was an Iranian dynasty of Kurdish origin, but during their rule they intermarried with Turkoman, Georgian, Circassian, and Pontic GreekAnthony Bryer. "Greeks and Türkmens: The Pontic Exception", ''Dumbarton Oaks Papers, Vol. 29'' (1975), Appendix II "Genealogy of the Muslim Marriages of the Princesses of Trebizond" dignitaries, nevertheless they were Turkish-spea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portrait Of Corasi, Sultan Agha Khanum, Second Wife Of Tahmasp I
A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expressions are predominant. The intent is to display the likeness, personality, and even the mood of the person. For this reason, in photography a portrait is generally not a snapshot, but a composed image of a person in a still position. A portrait often shows a person looking directly at the painter or photographer, in order to most successfully engage the subject with the viewer. History Prehistorical portraiture Plastered human skulls were reconstructed human skulls that were made in the ancient Levant between 9000 and 6000 BC in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B period. They represent some of the oldest forms of art in the Middle East and demonstrate that the prehistoric population took great care in burying their ancestors below their homes. The skulls denote some of the earliest sculptural examples of portraiture in the history of art. Historical portraitur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Abbas I
Abbas I ( fa, ; 27 January 157119 January 1629), commonly known as Abbas the Great (), was the 5th Safavid Shah (king) of Iran, and is generally considered one of the greatest rulers of Iranian history and the Safavid dynasty. He was the third son of Shah Mohammad Khodabanda. Although Abbas would preside over the apex of Safavid Iran's military, political and economic power, he came to the throne during a troubled time for the country. Under the ineffective rule of his father, the country was riven with discord between the different factions of the Qizilbash army, who killed Abbas' mother and elder brother. Meanwhile, Iran's enemies, the Ottoman Empire (its archrival) and the Uzbeks, exploited this political chaos to seize territory for themselves. In 1588, one of the Qizilbash leaders, Murshid Qoli Khan, overthrew Shah Mohammed in a coup and placed the 16-year-old Abbas on the throne. However, Abbas soon seized power for himself. Under his leadership, Iran developed the ghilma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)